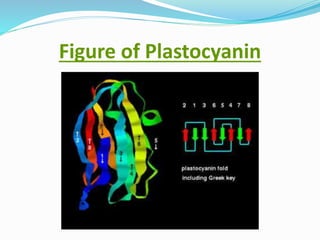
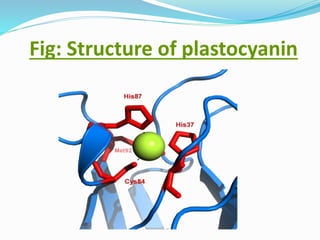
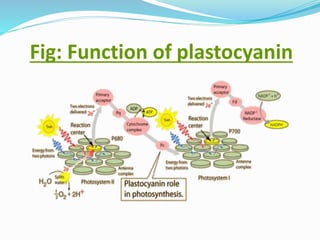
Plastocyanin is a copper-containing protein involved in electron transfer during photosynthesis. It carries electrons from cytochrome f to photosystem I. The structure of plastocyanin has been characterized through X-ray crystallography, revealing a beta-barrel structure and trigonal copper binding site. Plastocyanin cycles between its reduced and oxidized states as it transfers electrons between cytochrome f and photosystem I via specific reaction pathways. As an essential component of photosynthesis, plastocyanin plays an important role in environmental processes.