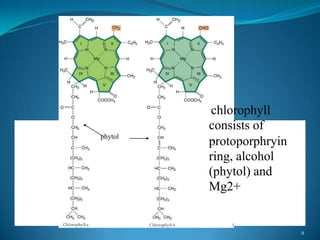
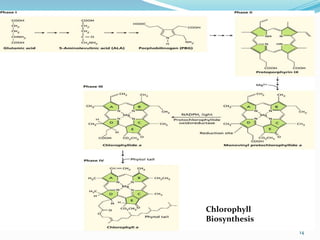
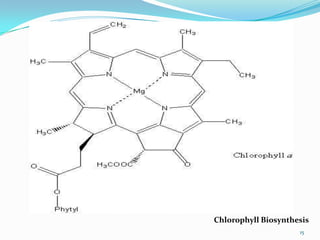
Chlorophyll is the green pigment found in plants that is essential for photosynthesis. It contains a porphyrin ring structure and a magnesium ion at its center. During photosynthesis, chlorophyll absorbs light energy and uses it to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and glucose. The light energy causes electrons in chlorophyll to become excited and get transferred through an electron transport chain, ultimately being used to produce ATP and NADPH for the Calvin cycle to fix carbon. Chlorophyll biosynthesis is a complex process that involves the transformation of glutamate into chlorophyll through a series of enzymatic steps.