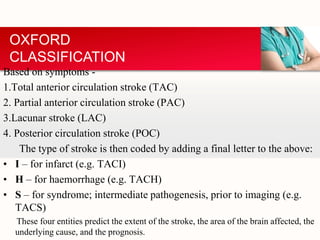
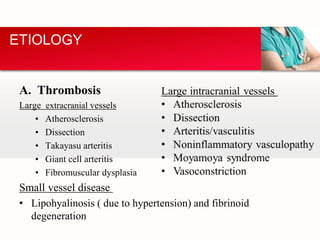
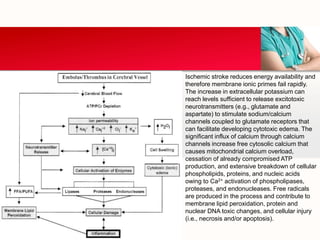
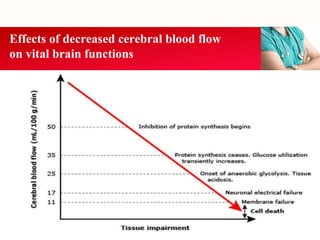
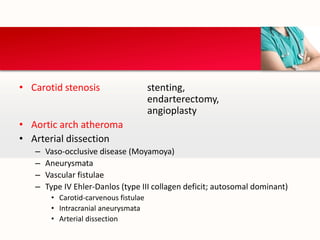
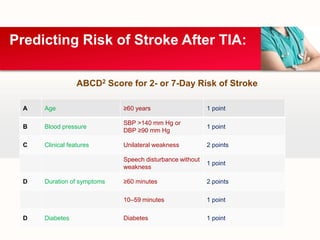
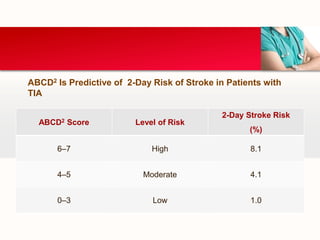
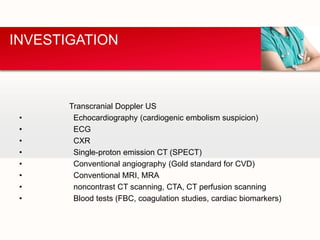
This document provides an outline on thromboembolic stroke. It begins with definitions and classifications of stroke, including the WHO and TOAST classifications. It then discusses the epidemiology, risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical presentation and diagnosis of stroke. It also covers management and prevention, noting that stroke is a major cause of death and disability worldwide, especially in sub-Saharan Africa. Modifiable risk factors include hypertension, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, hyperlipidemia and smoking.






![TOAST Classification [9]
1. Large-artery atherosclerosis (embolus/thrombosis)*
2. Cardioembolism (high-risk/medium-risk)*
3. Small-vessel occlusion (lacune)*
4. Stroke of other determined etiology*
5. Stroke of undetermined etiology
a. Two or more causes identified
b. Negative evaluation
c. Incomplete evaluation
*Possible or probable depending on results of ancillary studies.
STROKE SUBTYPES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stroke-150624155721-lva1-app6891/85/Stroke-8-320.jpg)
![Stroke Data Bank Subtype (NINDS) Classification [10]
Derived from the Harvard Stroke Registry classification,
the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
(NINDS) Stroke Data Bank recognised -
1. Atherothrombosis
2. Tandem arterial pathology
3. Cardiac Embolism
4. Lacune
5. Unusual Cause
6. Infarction of undetermined cause
7. Parenchymatous haemorrhage
SUBTYPES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stroke-150624155721-lva1-app6891/85/Stroke-9-320.jpg)