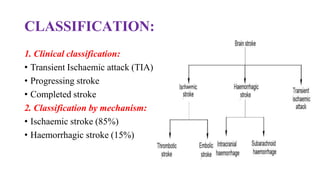
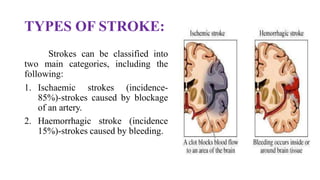
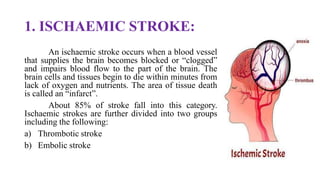
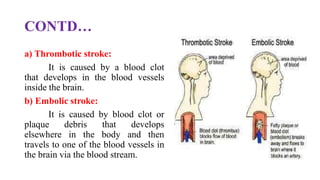
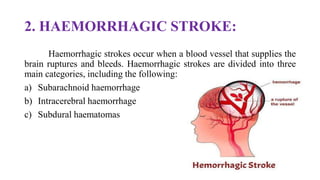
Stroke is defined as a neurological deficit persisting beyond 24 hours caused by occlusion or hemorrhage of brain arteries. The main types are ischemic (85%) caused by clot or embolism, and hemorrhagic (15%) caused by ruptured blood vessels. Risk factors include age, gender, race, family history, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, smoking, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. Diagnosis involves tests like CT, MRI, Doppler, and echocardiogram. Treatment goals are to reduce injury, prevent complications, and recurrence with approaches like thrombolytics, antiplatelets, anticoagulants, statins, and blood pressure control.