Stroke - Cerebrovascular Accident - (CVA)
- 1. StrokeStroke
- 2. What is it?What is it? Stroke is a clinical diagnosis based on the history and the physicalStroke is a clinical diagnosis based on the history and the physical examinationexamination A sudden loss of brain function caused by a blockage or rupture of aA sudden loss of brain function caused by a blockage or rupture of a blood vessel to the brain, characterized by loss of muscular control,blood vessel to the brain, characterized by loss of muscular control, decrease or loss of sensation or consciousness, dizziness, slurreddecrease or loss of sensation or consciousness, dizziness, slurred speech, or other symptoms that vary with the extent and severity of thespeech, or other symptoms that vary with the extent and severity of the damage to the brain.damage to the brain. DefinitionDefinition Medical Emergency, classified as a ‘Brain Attack’Medical Emergency, classified as a ‘Brain Attack’ – Rapidly developing.Rapidly developing. – Focal / globalFocal / global loss of cerebral function.loss of cerebral function. – Symptoms lasting more than 24 hours, or resulting in death.Symptoms lasting more than 24 hours, or resulting in death. – No other cause identified other than vascularNo other cause identified other than vascular.. – TumourTumour – Infection (abscess)Infection (abscess)
- 3. Types of StrokeTypes of Stroke Haemorrhage-25%.Haemorrhage-25%. Rupture of the blood vessel, due to hypertension, aneurysm, congenital deformity.Rupture of the blood vessel, due to hypertension, aneurysm, congenital deformity. Infarction – 75%.Infarction – 75%. Blockage of cerebral circulation by thrombus or embolus.Blockage of cerebral circulation by thrombus or embolus. Thrombus is the formation of blood clots due to atheroma or arteritis.Thrombus is the formation of blood clots due to atheroma or arteritis. Embolism – clotted blood ,air or fat.Embolism – clotted blood ,air or fat.
- 4. A quick word about TIAA quick word about TIA Similar presentation to stroke but usually resolves within 24hrsSimilar presentation to stroke but usually resolves within 24hrs High risk of CVAHigh risk of CVA Modify risk factorsModify risk factors Anti-platelet drugsAnti-platelet drugs CT head normalCT head normal MRI may be abnormalMRI may be abnormal ABCD2 scores Done by GP and refers unless attends A&EABCD2 scores Done by GP and refers unless attends A&E –– Low risk ≤3 Neurology R/w –TIA Clinic in 7days, Not admittedLow risk ≤3 Neurology R/w –TIA Clinic in 7days, Not admitted - High Risk ≥4 TIA Clinic in 24hrs, Bloods, ECG, Carotid Doppler, ?- High Risk ≥4 TIA Clinic in 24hrs, Bloods, ECG, Carotid Doppler, ? Carotid MRA Discharge Home (unless worsening),Carotid MRA Discharge Home (unless worsening), Angiogram and stent within 6 months if indicated (otherwise riskAngiogram and stent within 6 months if indicated (otherwise risk outweighs benefits)outweighs benefits)
- 5. Blood SupplyBlood Supply Blood supply to the brain derived from 4Blood supply to the brain derived from 4 vesselsvessels Posterior circulation.Posterior circulation. Supported by vertebral arteries, which joinSupported by vertebral arteries, which join together to form the basilar artery. Thistogether to form the basilar artery. This supplies the posterior third of thesupplies the posterior third of the hemispheres, also supplying thehemispheres, also supplying the cerebellum and the mid brain.cerebellum and the mid brain. Anterior circulation.Anterior circulation. Supported by the carotid arteries, theySupported by the carotid arteries, they supply anterior two thirds of the cerebralsupply anterior two thirds of the cerebral hemispheres. As they travel upwardshemispheres. As they travel upwards they divide into two branches, anteriorthey divide into two branches, anterior and middle cerebral arteries.and middle cerebral arteries. Blood supplied from these vesselsBlood supplied from these vessels combines at base of brain in the circle ofcombines at base of brain in the circle of WillisWillis
- 6. Types of presentationTypes of presentation Left Hemisphere (i.e., dominant)Left Hemisphere (i.e., dominant) Right hemiparesisRight hemiparesis - variable involvement of face and upper and lower- variable involvement of face and upper and lower extremityextremity Right-sided sensory lossRight-sided sensory loss - in a similar pattern to the motor deficit;- in a similar pattern to the motor deficit; usually involves all modalities, decreased stereogenosis,usually involves all modalities, decreased stereogenosis, graphesthesiagraphesthesia Right homonymous hemianopiaRight homonymous hemianopia - visual field loss on the same side of- visual field loss on the same side of both eyesboth eyes DysarthriaDysarthria – affects the muscles that help produce speech– affects the muscles that help produce speech AphasiaAphasia - fluent( the input or reception of language ) and nonfluent- fluent( the input or reception of language ) and nonfluent (difficulties in articulating)(difficulties in articulating) AlexiaAlexia - unable to understand written words- unable to understand written words AgraphiaAgraphia – inability to communicate through writing– inability to communicate through writing AcalculiaAcalculia - difficulty performing simple mathematical tasks- difficulty performing simple mathematical tasks ApraxiaApraxia of the left limbs - inability to execute learned purposefulof the left limbs - inability to execute learned purposeful movementsmovements
- 7. Types of presentationTypes of presentation Right Hemisphere (i.e., nondominant)Right Hemisphere (i.e., nondominant) Left hemiparesisLeft hemiparesis (same pattern as on right)(same pattern as on right) Left-sided sensory lossLeft-sided sensory loss (similar pattern as the motor deficit)(similar pattern as the motor deficit) Left homonymous hemianopiaLeft homonymous hemianopia (same pattern as on right)(same pattern as on right) DysarthriaDysarthria affects the muscles that help produce speechaffects the muscles that help produce speech NeglectNeglect of left side of environmentof left side of environment AnosognosiaAnosognosia - seems unaware of the existence of his or her disability- seems unaware of the existence of his or her disability AsomatognosiaAsomatognosia - forgetting, ignoring, denying, disowning, or- forgetting, ignoring, denying, disowning, or misperceiving the bodymisperceiving the body Loss of prosody of speechLoss of prosody of speech -, tone, rhythm of voice-, tone, rhythm of voice Flat affectFlat affect - facial expression, lack of emotion- facial expression, lack of emotion
- 8. Types of presentationTypes of presentation Lacunar syndromes (Small vessels)Lacunar syndromes (Small vessels) Pure motor hemiparesisPure motor hemiparesis Pure sensory strokePure sensory stroke Dysarthria-clumsy hand syndromeDysarthria-clumsy hand syndrome Isolated motor/sensory strokeIsolated motor/sensory stroke Paralysis and sensory loss of the contralateral leg,Paralysis and sensory loss of the contralateral leg, arm, and facearm, and face
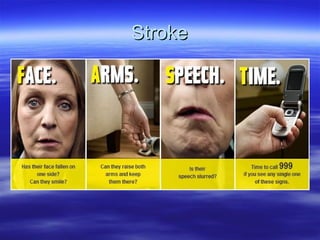
- 9. Acute ManagementAcute Management Ambulance – FAST, BM, Contact SNPAmbulance – FAST, BM, Contact SNP SNP – triage, decide if stroke or not,SNP – triage, decide if stroke or not, Yes – RHH, No A&E @ NGH,Yes – RHH, No A&E @ NGH, if other conditions such as ACS, send to A&E as limited medical cover at RHHif other conditions such as ACS, send to A&E as limited medical cover at RHH Met by SNP, Bloods, ECG, Obs, Strict Neuro obs, NIHSSMet by SNP, Bloods, ECG, Obs, Strict Neuro obs, NIHSS Onset time, Swallow assessment, Aspirin 300mgOnset time, Swallow assessment, Aspirin 300mg CT – Urgent or within 24 HrsCT – Urgent or within 24 Hrs Urgent CT within 1 hr of arrival or 4.5hrs since onset to assessUrgent CT within 1 hr of arrival or 4.5hrs since onset to assess whetherwhether for thrombolysis, also if on anticoagulant,for thrombolysis, also if on anticoagulant, GCS, severe headache,GCS, severe headache, papilloedema.papilloedema. If bleed treat conservativelyIf bleed treat conservatively If change in 1 of GCS, perform Urgent or repeat urgent CTIf change in 1 of GCS, perform Urgent or repeat urgent CT Admit to HASU, after 24hrs (unless unstable) to acute stoke ward, thenAdmit to HASU, after 24hrs (unless unstable) to acute stoke ward, then when ready stroke rehab bedwhen ready stroke rehab bed
- 10. CT / MRICT / MRI Only through imaging canOnly through imaging can an ischaemic stroke bean ischaemic stroke be distinguished from adistinguished from a hemorrhagic stroke, anhemorrhagic stroke, an important distinction asimportant distinction as treatments for ischaemictreatments for ischaemic stroke can lead to bleedingstroke can lead to bleeding which could be devastatingwhich could be devastating if given to a patient with aif given to a patient with a hemorrhagic strokehemorrhagic stroke
- 11. TreatmentTreatment Aspirin given initially as benefits outweigh risks ifAspirin given initially as benefits outweigh risks if bleeds (if no contraindications), continue tillbleeds (if no contraindications), continue till discharge or 14 days whichever soonerdischarge or 14 days whichever sooner If hypertensive (already on anti hypertensives –If hypertensive (already on anti hypertensives – give) if new onset do not try to lower Bp as this isgive) if new onset do not try to lower Bp as this is perfusing the brain, lowering Bp will be detrimentalperfusing the brain, lowering Bp will be detrimental Give clopidogrel 300mg after 14 days, unlessGive clopidogrel 300mg after 14 days, unless planned for Carotid Endarterectomyplanned for Carotid Endarterectomy
- 12. Why Classify?Why Classify? Classification is of prognostic significance as aClassification is of prognostic significance as a model for predicting outcome.model for predicting outcome. Prognosis following a stroke can be described inPrognosis following a stroke can be described in terms of survival, recurrence, or extent of longterms of survival, recurrence, or extent of long term disability.term disability. This can be useful when speaking to families, butThis can be useful when speaking to families, but be aware everyone can be different.be aware everyone can be different. Helpful to consider future management,Helpful to consider future management, rehabilitation, and discharge planning.rehabilitation, and discharge planning.
- 13. Bamford ClassificationBamford Classification The Bamford classification gives one of fourThe Bamford classification gives one of four stroke syndromes to be identified dependingstroke syndromes to be identified depending on the deficit or clinical signs observed inon the deficit or clinical signs observed in the first 24 hours. Now referred to as :-the first 24 hours. Now referred to as :- TACSTACS – Total Anterior Circulation Stroke– Total Anterior Circulation Stroke PACSPACS – Partial Anterior Circulation Stroke– Partial Anterior Circulation Stroke POCSPOCS – Posterior Circulation Stroke– Posterior Circulation Stroke LACSLACS – Lacunar Stroke– Lacunar Stroke
- 14. Clinical SignsClinical Signs The presence or absence of the following clinical signs identify the strokeThe presence or absence of the following clinical signs identify the stroke syndrome using the Bamford classification.syndrome using the Bamford classification. 1.1. Unilateral weakness (and/or sensory deficit) of face?Unilateral weakness (and/or sensory deficit) of face? Yes/no.Yes/no. 2.2. Unilateral weakness (and/or sensory deficit) of arm /leg?Unilateral weakness (and/or sensory deficit) of arm /leg? Yes/no.Yes/no. 3.3. Unilateral weakness (and/or sensory deficit) of leg/foot?Unilateral weakness (and/or sensory deficit) of leg/foot? Yes/no.Yes/no. 4.4. Dysphasia?Dysphasia? Yes/no.Yes/no. 5.5. Homonymous Hemianopia?Homonymous Hemianopia? Yes/no.Yes/no. 6.6. Visuospatial disorder?Visuospatial disorder? Yes/no.Yes/no. 7.7. Brainstem/Cerebellar signs?Brainstem/Cerebellar signs? Yes/no.Yes/no. 8.8. Other deficits?Other deficits? YY Yes/no.Yes/no.
- 15. Stroke Syndrome and Clinical SignsStroke Syndrome and Clinical Signs By looking at the presenting symptoms using the previousBy looking at the presenting symptoms using the previous table the stroke can be classified, as follows;-table the stroke can be classified, as follows;- TACSTACS. 1-3 and homonymous hemianopia and cerebral. 1-3 and homonymous hemianopia and cerebral dysfunction .dysfunction . 20%20% PACSPACS. Either 1 or 2 or 3 plus evidence of cerebral. Either 1 or 2 or 3 plus evidence of cerebral dysfunction.dysfunction. 35%35% LACSLACS. Either 1 and 2 or 2 and 3 or 1,2 and 3. Either 1 and 2 or 2 and 3 or 1,2 and 3 with no higher cerebral dysfunction.with no higher cerebral dysfunction. 20%20% POCSPOCS. Brainstem or Cerebellar signs and Isolated. Brainstem or Cerebellar signs and Isolated hemianopia.hemianopia. 25%25%
- 16. PrognosisPrognosis Points of note.Points of note. TACS-more than twice as many deaths areTACS-more than twice as many deaths are due to complications of immobility ratherdue to complications of immobility rather than direct effects of the stroke.than direct effects of the stroke. Recurrence at 1 yr - 6%Recurrence at 1 yr - 6% PACS-much more likely to have an earlyPACS-much more likely to have an early recurrent CVA.recurrent CVA. Recurrence at 1 yr – 17% (first 4/12)Recurrence at 1 yr – 17% (first 4/12) POCS-greater risk of recurrence later inPOCS-greater risk of recurrence later in year but have a better chance ofyear but have a better chance of recovery.recovery. Recurrence at 1 yr (early peak)Recurrence at 1 yr (early peak) LACS-despite small size of infarcts manyLACS-despite small size of infarcts many remain substantially handicapped.remain substantially handicapped. Recurrence at 1 yr 9%Recurrence at 1 yr 9% POCSLACSPACSTACS 6060555Indep 20303035Depe ndent 20101560Dead1 Year 6565555Indep 30304055Depe ndent 55540Dead30 days POCSLACSPACSTACS 6060555Indep 20303035Depe ndent 20101560Dead1 Year 6565555Indep 30304055Depe ndent 55540Dead30 days