1) Stroke is a leading cause of death and disability worldwide, with the majority caused by ischemia and hemorrhage. Intracerebral hemorrhage accounts for 20% of strokes and has a high mortality rate of 62% at 1 year.
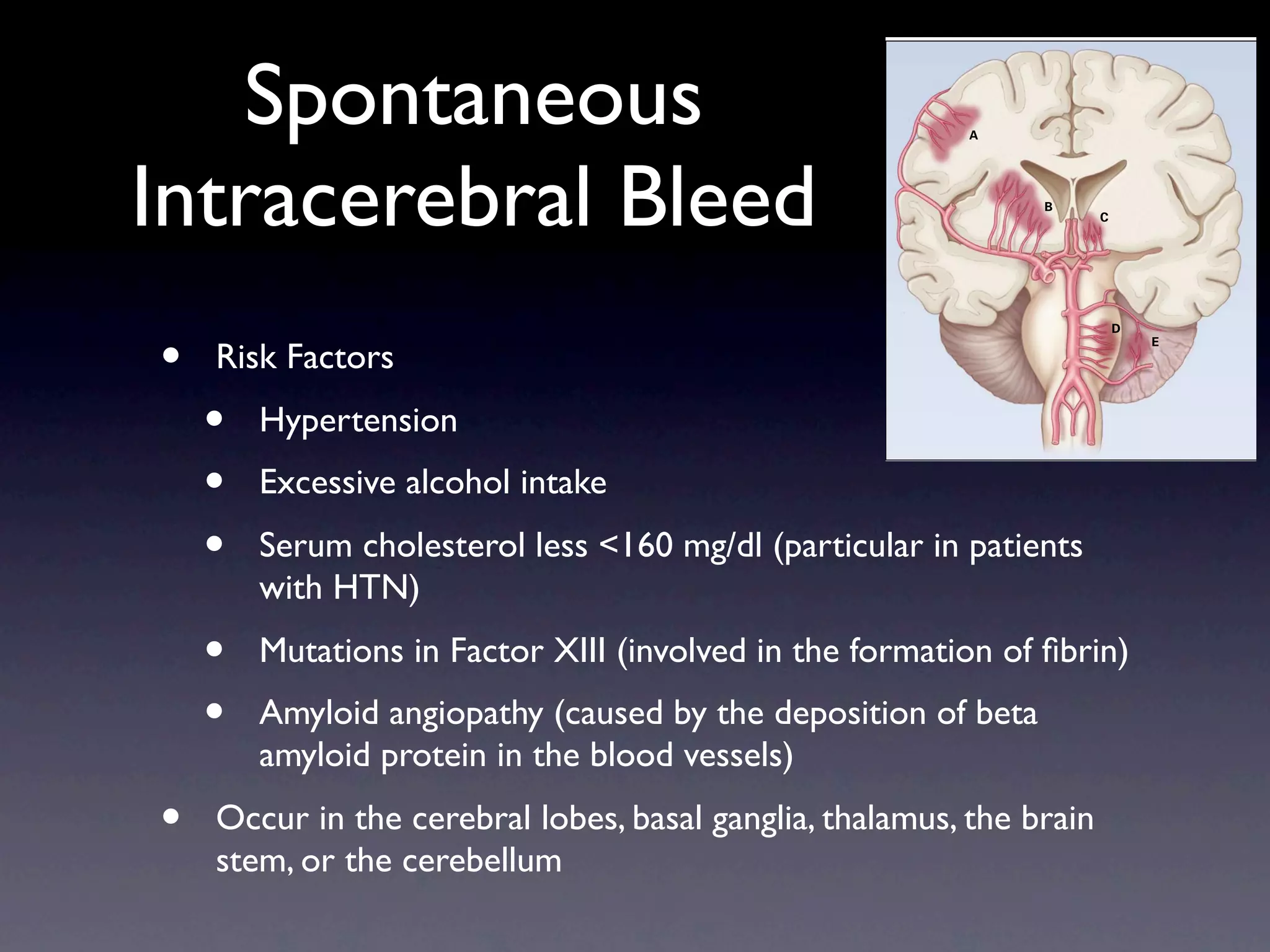
2) Intracerebral hemorrhages most commonly occur in the cerebral lobes, basal ganglia, thalamus, brain stem, or cerebellum from the rupture of small blood vessels damaged by hypertension or amyloid angiopathy.
3) Patients receiving oral anticoagulation have a 7-10 fold increased risk of intracerebral hemorrhage compared to spontaneous hemorrhage. Hematoma expansion occurs for a longer period of time




![Intracerebral Hemorrhage associated
with oral anticoaguation
• Mortality at one year is much higher in this population close to 67 %
• Patients receiving anticoagulation have a 7 to 10 fold increased in developing ICH
• Underlying cause of spontaneous versus anticoagulation associated ICH are likely the same
• Anticoagulation, however, may act as an exacerbating factor
• Hematoma expansion in patients on anticoagulation occurs for a longer period of time
• Treatment Strategies
• Vitamin K
• Takes at least 2 to 6 hrs to take effect
• Allows for a more sustained reversal of anticoagulation
• IV Vitamin K has a low risk of allergic or anaphylactic reaction in one study 3 per
10,000 doses [4]
• FFP
• Contains all factors in a non concentrated form requiring large volume to have
effective hemostasis
• Ideally, 1mL of FFP/kg body weight is required to bring INR down 1 to 2 IU/dL
• ? Novoseven
1 Steiner, T Stroke 2006](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stroke3033/75/stroke-6-2048.jpg)
![original article
Efficacy and Safety of Recombinant Activated
Factor VII for Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Stephan A. Mayer, M.D., Nikolai C. Brun, M.D., Ph.D., Kamilla Begtrup, M.Sc.,
Joseph Broderick, M.D., Stephen Davis, M.D., Michael N. Diringer,h M.D., e ng l a n d
T e ne w j o u r na l of m e dic i n e
Brett E. Skolnick, Ph.D., and Thorsten Steiner, M.D., for the FAST Trial Investigators*
Table 2. Hemorrhage Volumes at Baseline and Follow-up.*
A BS T R AC T rFVIIa, rFVIIa,
•
20 µg/kg 80 µg/kg Placebo
Background Variable (N = 276) (N = 297) (N = 268)
Volume of intracerebral hemorrhage
Background
•
At baseline — ml 24±26 23±26 22±24
Intracerebral hemorrhage is the least treatable form of stroke. We performed this From the Departments of Neurology and
Activated Factor VIIa directly activates
phase 3 trial to confirm a previous study in whichAtrecombinant activated factor VII Neurosurgery, Columbia University Col-
24 hr — ml 28±30 25±28 28±31
Factor Xa on the surface reduced growth of the hematoma and improved survival and functional (S.A.M.); Novo Nordisk, Bagsvaerd, to 17)
(rFVIIa) of activated
P value vs. placebo
lege of Physicians(13 toSurgeons, New York
Estimated percent increase from baseline — mean (95% CI) 18 and 24)
0.09
11 (6
Den-
<0.001
26 (20 to 32)
—
outcomes.
platelets resulting in a burst of thrombin mark (N.C.B., K.B.); the University of Cin-
Estimated milliliters of increase from baseline — mean (95% CI) 4.9Center, 7.0) 3.7 (1.7 to 5.7)
cinnati Medical (2.9 to Cincinnati ( J.B.); 7.5 (5.4 to 9.6)
and acceleration of Methods
coagulation P value vs. placebo the Royal Melbourne Hospital, University
0.08 0.009
of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia (S.D.);
—
We randomly assigned 841 patients with intracerebral of intraventricular hemorrhage pla- Washington University School of Medi-
Volume
hemorrhage to receive
cebo (268 patients), 20 µg of rFVIIa per kilogram of body weight (276 patients), or cine, St. Louis (M.N.D.); Novo 5.3±11.7
At baseline — ml 3.6±8.0 Nordisk, 2.7±7.5
• Methods 80 µg of rFVIIa per kilogram (297 patients) withinAt 24 hr — ml
Princeton, NJ (B.E.S.); and the University
5.8±17.2
4 hours after the onset of stroke. of Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany (T.S.).
Estimated milliliters of increase from baseline — mean (95% CI) 2.0 (0.6 to 3.3)
The primary end point was poor outcome, defined as severe disability or death ac- Address reprint requests to Dr. Mayer at
5.4±10.8
1.0 (−0.2 to 2.3)
4.6±10.3
1.6 (0.3 to 3.0)
cording to the modified Rankin scale 90 days aftervalue vs. placebo
P the Neurological 0.74
Institute, 710 W.0.51 —
•
the stroke. 168th
Multicenter, randomized double-blind, St., Box 39, New York, NY 10032, or at
Volume of intracerebral hemorrhage plus intraventricular
hemorrhage plus edema sam14@columbia.edu.
placebo controlled trial
Results
At baseline — ml 46±45 46±49 42±47
Treatment with 80 µg of rFVIIa per kilogram resultedhrin a significant reduction in *The institutions71±69 T h e in 65±66 e ng l68±67 d j o u r n
At 72 — ml
participating the Fac-
ne w an
tor Seven for Acute Hemorrhagic Stroke
growth in volume of the hemorrhage. The mean estimated increase in volume of themean (95% CI) are (21 to 31) the Appendix.27)
•
Estimated milliliters of increase from baseline — (FAST) trial 26 listed in 22 (17 to 29 (23 to 34)
Inclusion - Patients over 18
intracerebralyears oldat 24 hours was 26% inP the placebo group, as compared
hemorrhage value vs. placebo 0.53 0.06 —
with 18% in the group receiving 20 µg of rFVIIa per kilogram (P= 0.09) and 11% in N Engl J Med 2008;358:2127-37.
who had a spontaneous intracerebral(P<0.001). The growth*in volumevaluesintracerebral For estimatedCopyrightincreases, 95% confidence intervals (CIs) are derived from a
the group receiving 80 µg Plus–minus of are means ±SD. hemor- mean
© 2008 Massachusetts Medical Society.
1.00
linear mixed model with the patient and the reader as random effects and baseline volume of the hemorrhage, time
hemorrhage documented on a CT2.6 ml (95% confidence interval [CI], symptoms 5.5;patientsCT scan, and time fromreceiving 20 µg of rFVIIa (recombined activated CT scans at
rhage was reduced by scan from onset of −0.3 to to baseline P = 0.08) in Placebo
baseline CT scan to treatment as fixed effects.
factor VII) In th
the group receiving 20 µg of rFVIIa per kilogram 24 hours were missing for 12 0.9 to 6.7; placebo, 17
and by 3.8 ml (95% CI, receiving
within 3 hours afterPonsetin thesymptoms 80 µg, as compared with0.95 placebo group. Despite
= 0.009) of group receiving
per kilogram, and 12 receiving 80 µg of rFVIIa per kilogram.
the
20 µg/kg of rFVIIa
80 µg/kg of rFVIIa the o
this reduction in bleeding, there was no significant difference among the three
rhag
•
CLINICAL OUTCOMES
groups in the proportion of patients with poor treated within 3 hours after the onset of symp-
clinical outcome (24% in the pla-
Exclusion - Glasgowcebo group, 26% in the group receiving 20 µg of rFVIIa0.90 kilogram,−8.0 to −1.0) and was Mortality at 3 months was approximately 20% in toma
Score<5, toms (−4.5 ml; 95% CI,
per and 29% in
greater still among those treated within 2 hours the three groups (Table 3 and Fig. 2). The primary
hemorrhage secondary to receiving 80 µg). The overall frequencyafter onset (−5.6 ml; 95% CI, −13.1 to −2.0). How- outcome measure (the proportion of patients outco
the group trauma, AV of thromboembolic serious adverse
malformation, known the was similar in the80 µg groups; however,ever, thereeventsand themorefrom onset of symp- who died or were severelythree groups (Table 3). the c
events
in
anticoagulant use, of rFVIIa than inarterial0.85 nogrouptime interaction between significantly among the disabled) did not differ
group receiving
three
the placebo
was were
treatment effect
significant frequent
(9% vs. 4%,
myocardial infarction= 0.04).
P toms to treatment.
0.80
Similarly, the distribution of outcomes on the trial,
Although the intraventricular-hemorrhage vol- modified Rankin scale (Fig. 3) and the median
ume at 24 hours doubled in the placebo group scores on the Barthel index were similar among
tive r
•
Conclusions
Three treatment arms - Low dose 20 and was essentially unchanged in the group re- the three groups. The NIHSS scores were sig-
Hemostatic therapy with rFVIIa reduced growthceiving 80 µg of rFVIIa per kilogram, the differ- nificantly lower in the group receiving 80 µg of
of the 0.75
hematoma but did not im-
plana
micrograms/kg, High dose 80 prove survival or functional outcome after intracerebral hemorrhage. (ClinicalTrials.
ence between the groups was not statistically rFVIIa per kilogram than in the placebo group,
rand
0.00
gov number, NCT00127283.) significant. Growth in volume 20 the total lesion but the magnitude of 70 difference was small
of this rial t
micrograms/kg, placebo 0 10 30 40 50
(intracerebral hemorrhage, intraventricular hem- (Table 3).
60 80 90
the i
orrhage, and edema) was 7 ml less in the group In a series of exploratory post hoc analyses,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stroke3033/75/stroke-7-2048.jpg)
![PERSPECTIVE small vessels, big problems
Big versus Small
A B
Cerebral
amyloid Arteriolosclerosis
angiopathy
Vessels Thromboembolism
Saccular aneurysm
C
• Diseases of the big vessels (>0.1 mm)
• Account for two-thirds of symptomatic strokes
Atherosclerosis
•
Large-Vessel and Small-Vessel Brain Disease.
Atherosclerotic narrowing and occlusion of large neck vessels
The sites of the most common forms of cerebrovascular disease are shown in Panel A. Arteriolosclerosis typically affects small vessels that
penetrate the white matter and the deep gray nuclei, whereas cerebral amyloid angiopathy preferentially involves the small arteries and arterioles
of the cerebral cortex and gray–white-matter junction. Axial MRI with the use of gradient-echo technique (Panel B) and fluid-attenuated inversion
recovery (Panel C) highlight two prominent radiographic features of small-vessel brain disease: hemorrhages (Panel B, dark lesions [examples
•
shown by arrowheads]) and changes in white matter (Panel C, bright lesions). The images are of a 71-year-old man with probable cerebral amy-
Aneurysmal rupture and subarachnoid bleeds
loid angiopathy.
vessel brain disease: type IV col- host of microvascular abnormali- type IV collagen also appear to
lagen. Type IV collagen α1 and α2 ties. Among the prominent find- be responsible for some familial
•
chains, assembled as a heterotri- ings in the mice were increased forms of intracerebral hemorrhage,
Thromboembolic occlusion of major vessel branches mer, are a major component of
the vascular basement membrane
in the brain and elsewhere. Us-
fragility of brain microvessels in
response to stressors such as birth
trauma and hypertension, tortu-
white-matter lesions, and retinal-
vessel tortuosity.
These studies do not provide
ing random mutagenesis in mice, osity of the retinal vessels, and evidence that nonfamilial small-
•
Gould and colleagues found that albuminuria. Completing the con- vessel disease is caused by ab-
Diseases of the small vessels the deletion of an exon in the
gene encoding type IV collagen
α1 (Col4a1) prevented the normal
nections from molecule to mouse
to clinical disease, the authors
made the striking observation that
normalities of type IV collagen or
the vascular basement mem-
brane, but this intriguing hypoth-
assembly and secretion of vascu- mutations in the human COL4A1 esis seems worthy of testing. The
•
lar type IV collagen, resulting in a gene that affect the assembly of basement membrane is not only
Small arteries and arterioles that penetrate the brain cortex and reach the white and
deep gray matter 1452 n engl j med 354;14 www.nejm.org april 6, 2006
• Arteriosclerosis
Downloaded from www.nejm.org by RAJ M. KHANDWALLA MD on June 8, 2010 .
Copyright © 2006 Massachusetts Medical Society. All rights reserved.
• Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy
• These diseases can lead to occlusion causing lacunar brain infarctions or intracerebral
hemorrhage
• Cause silent strokes that can eventually lead to dementia
• Rotterdam Scan Study found that the rate of dementia was more than doubled in
the 20 percent of healthy adults who had evidence of lacunar infarcts [1]
Vermeer, NEJM 2003](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stroke3033/75/stroke-8-2048.jpg)

![Transient Ischemic Attack - the unstable angina of
the brain
• Defined as a neurologic deficit lasting less than 24 hrs that is attributed to focal cerebral
or retinal occlusion
• There is much controversy over how to define TIAs
• Rapid recovery may be the most important characteristic in defining a distinct clinic
entity
• But this may portend a more unstable pathophysiology
• Diagnosis is difficult because it is usually based on clinical history alone relying on the
memories of patients who were neurlogically impaired.
• Broad differential include migraine, seizure, vasovagal, syncope, arrhythmia,
compressive neuropathy, anxiety, and conversion disorder
• Risk of stroke after a TIA
• Study of 1707 patients given diagnosis of TIA were studied for a 90-day period [5]
• Roughly 1 in 9 patients had a stroke after diagnosis
• Half of all strokes happened within two days of diagnosis
• 2.6 percent of patients had a cardiac event
• 2.6 percent died
• Patients with atrial fibrillation had an 11 percent chance of stroke at 90 days
Johnston, SC NEJM 2002](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stroke3033/75/stroke-10-2048.jpg)
















