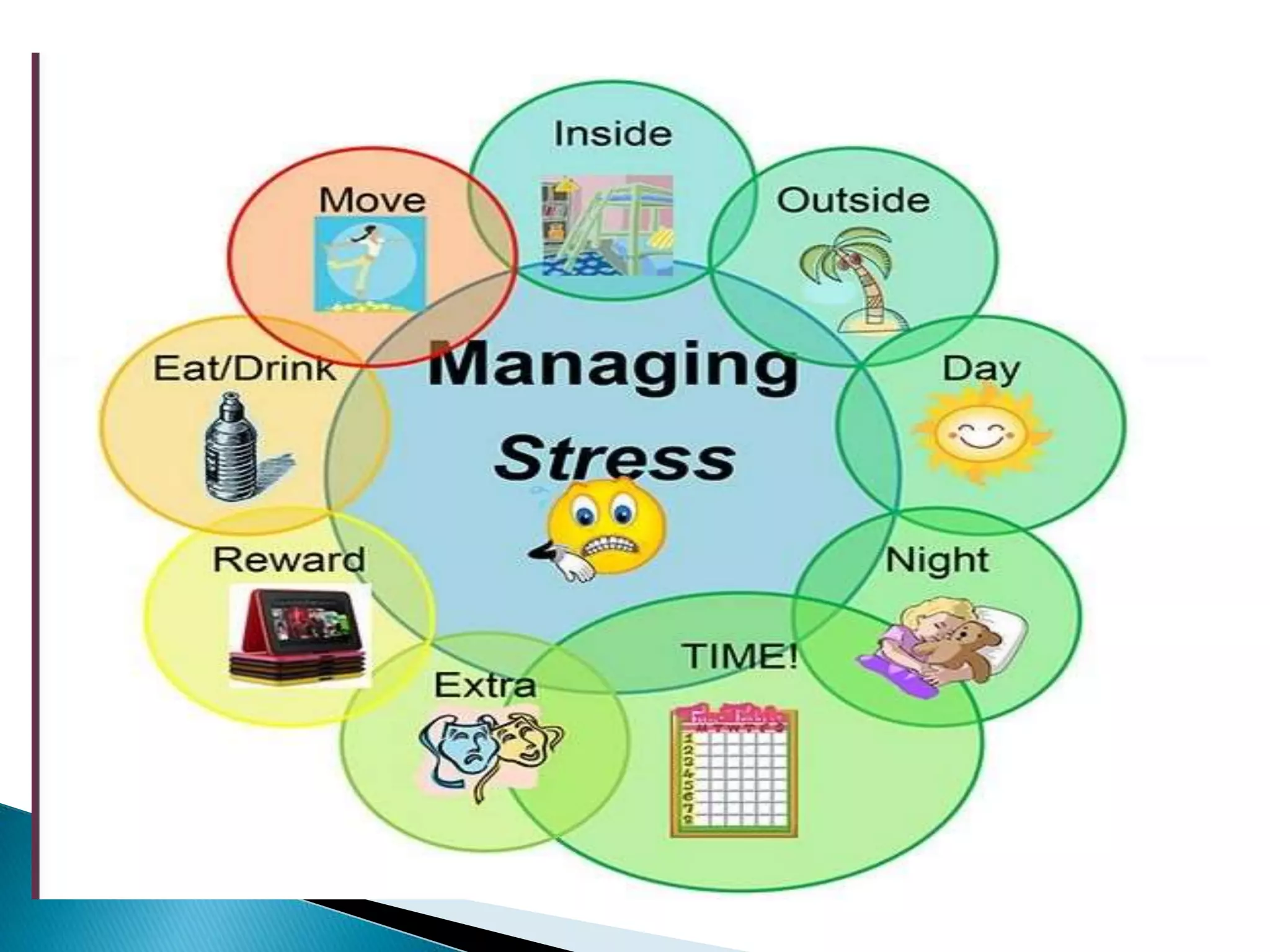
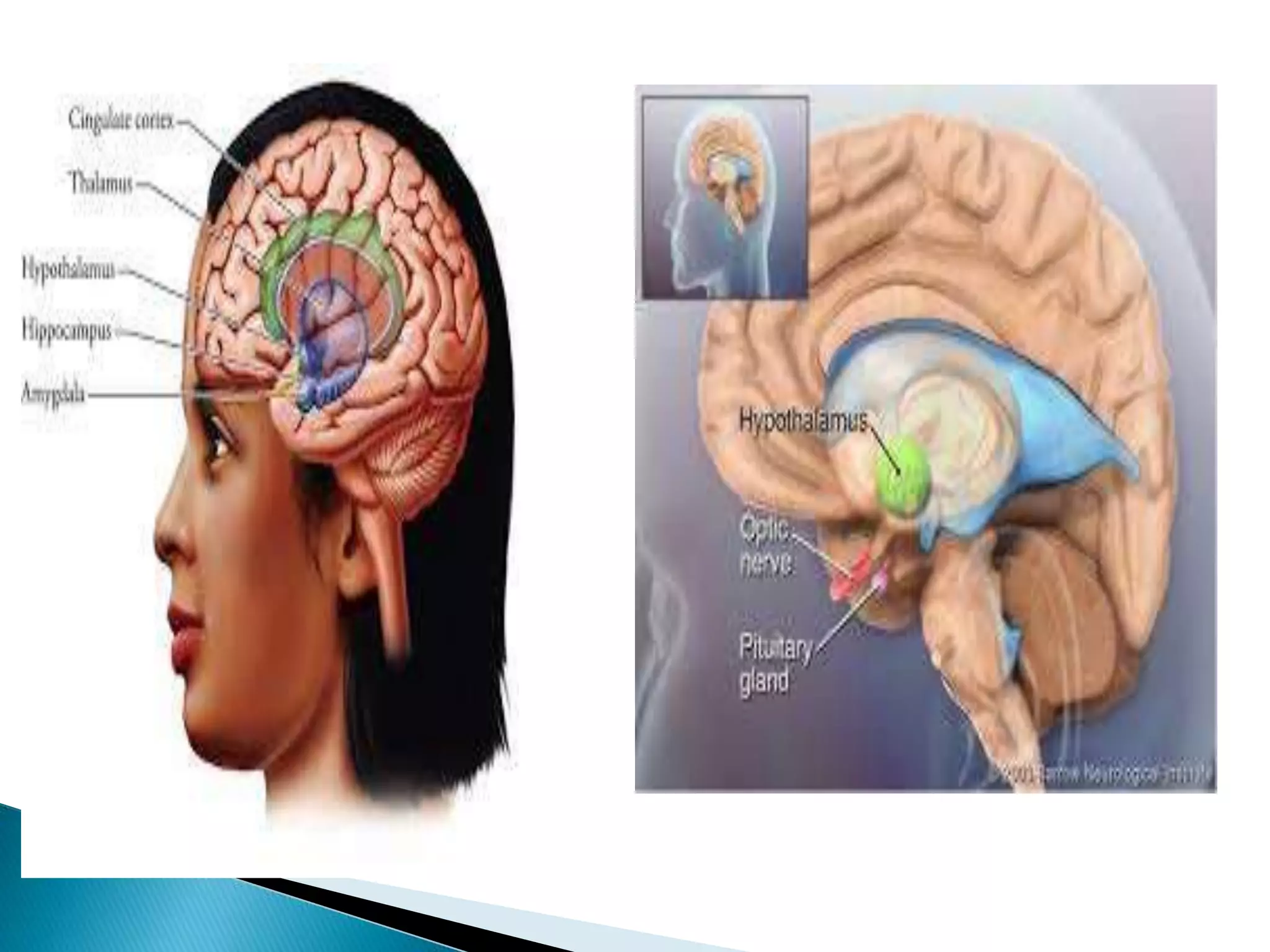
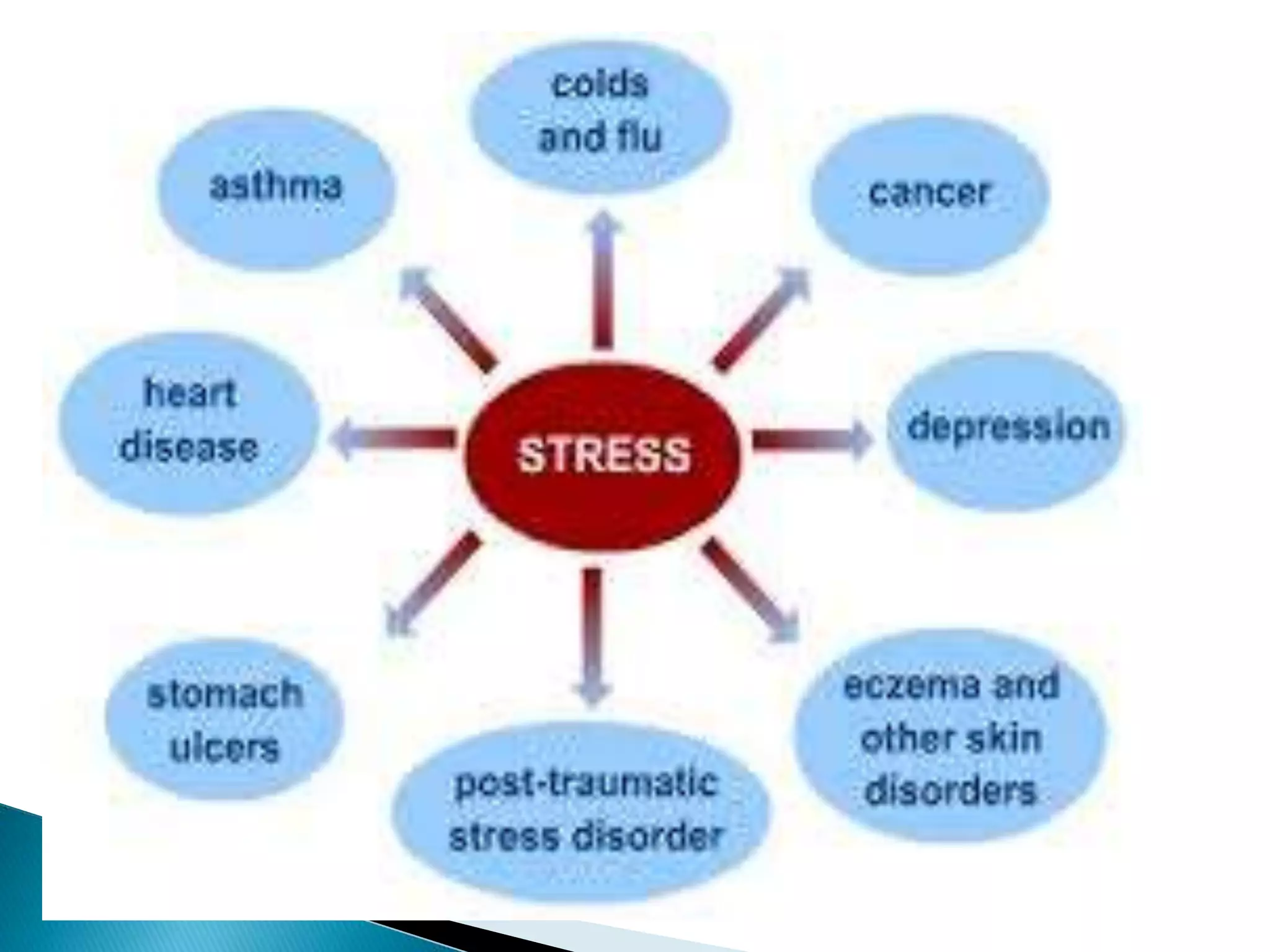
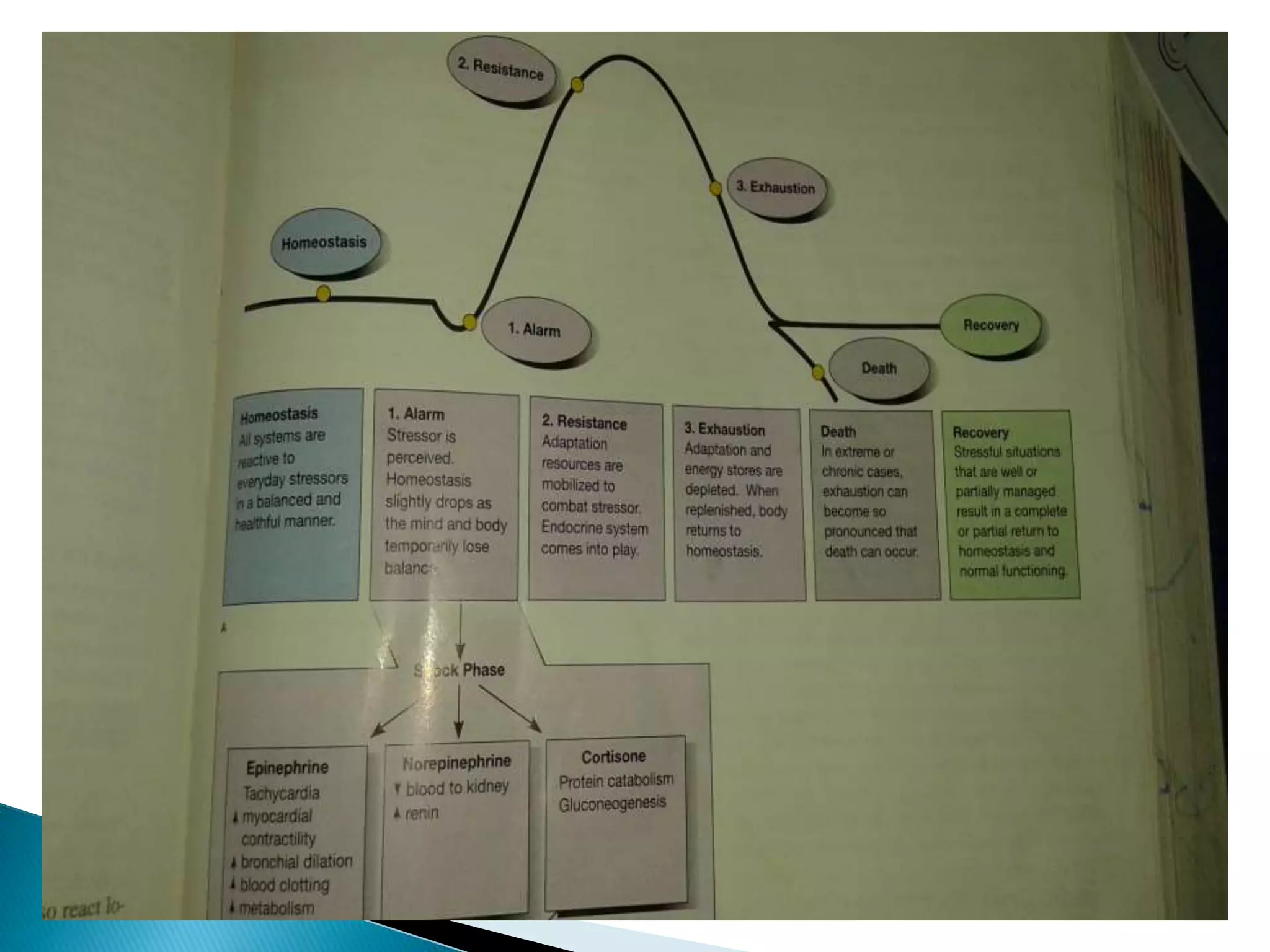
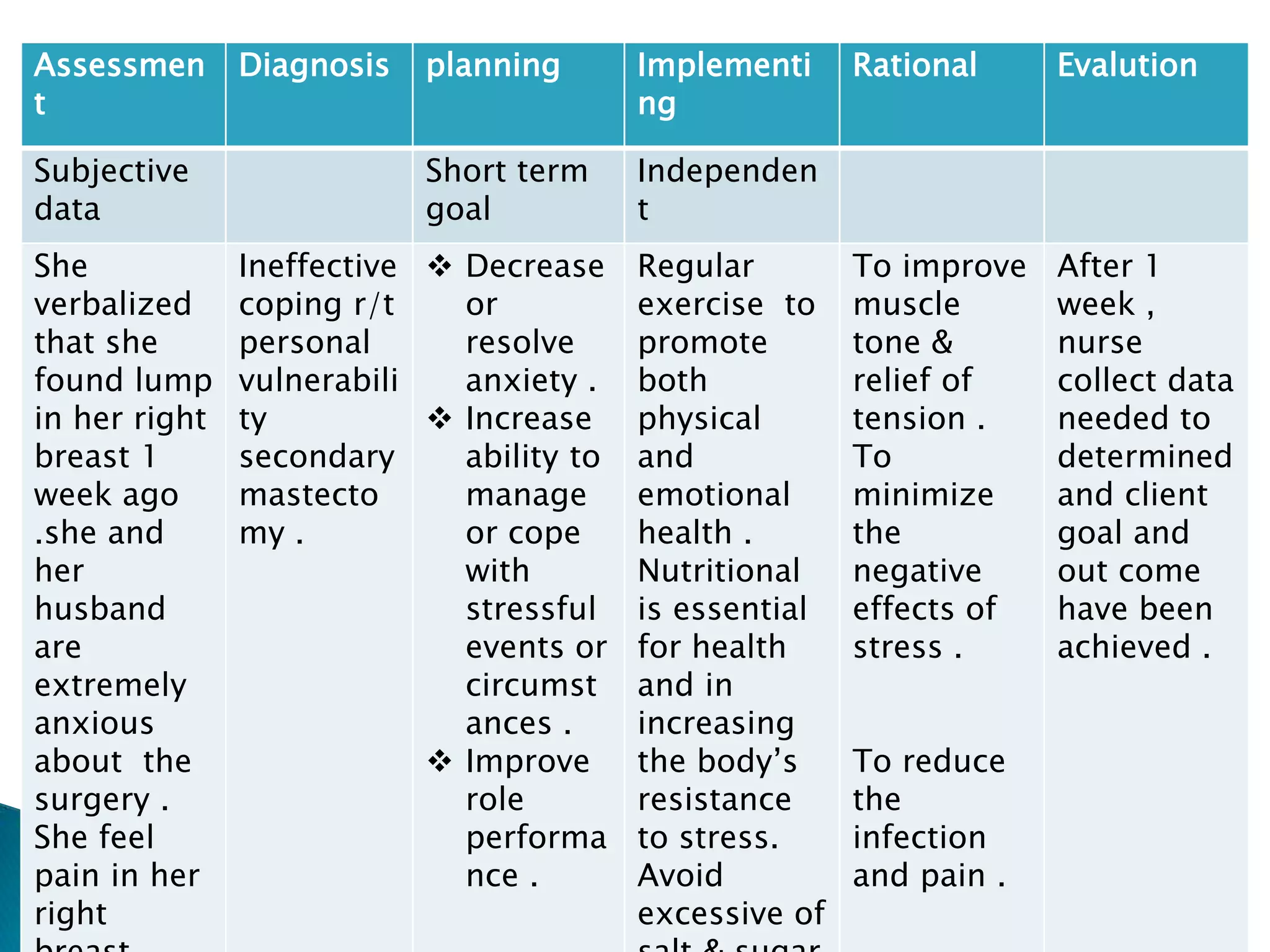
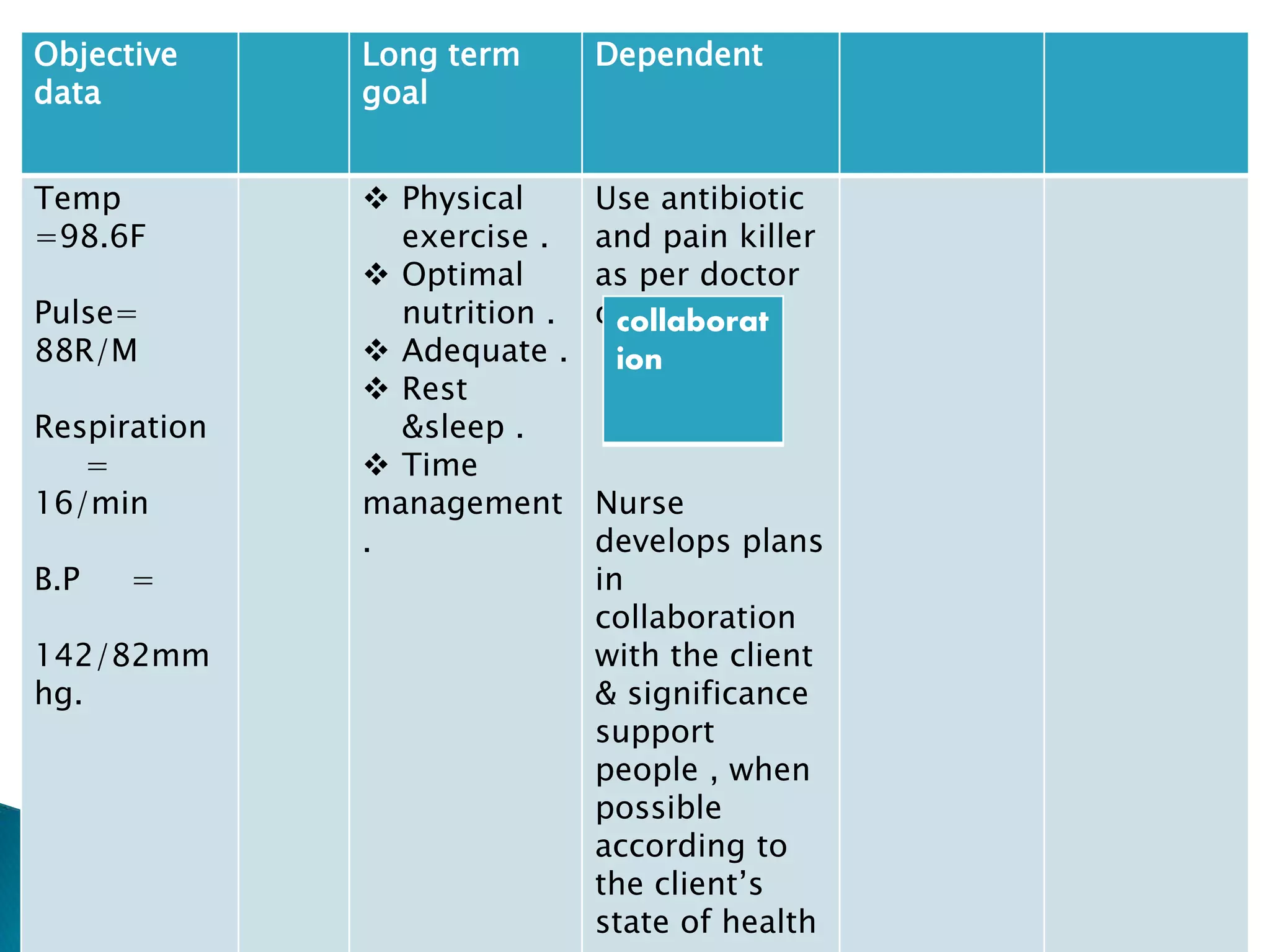
This document provides an outline and summary of a student assignment on stress and coping. It discusses various topics related to stress including the concept of stress, sources of stress, effects of stress, models of stress response, indicators of stress, anxiety vs fear, anger vs depression, ego defense mechanisms, and coping strategies. The assignment was submitted by two students, Nadia Khan and Abubakar, for their Fundamentals of Nursing course taught by Mahwish Younas at Multan Medical Dental & Nursing College in Multan, Pakistan.