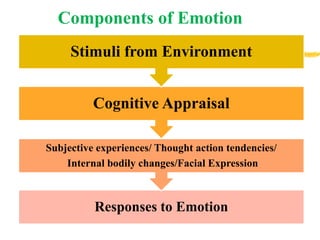
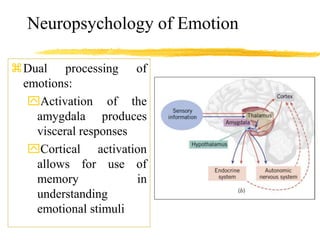
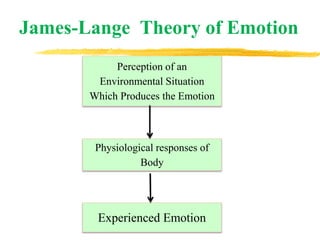
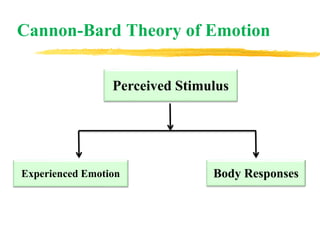
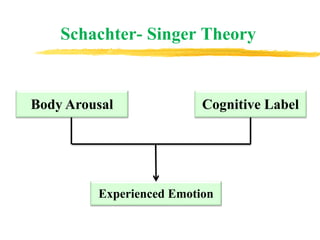
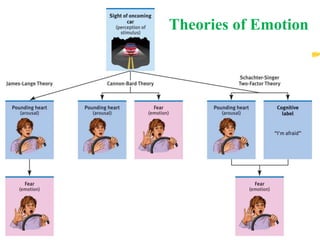
The document discusses the nature and characteristics of emotions, defining them as subjective responses accompanied by physiological changes and behavioral shifts. It categorizes emotions into positive and negative, primary and secondary, and explains the physiological and psychological changes that occur during emotional experiences. Additionally, it reviews various theories of emotion, including the James-Lange, Cannon-Bard, and Schachter-Singer theories, each illustrating different perspectives on the connection between physiological responses and emotional experiences.