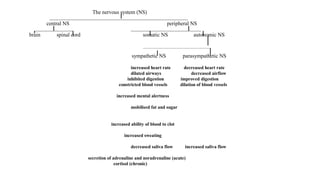
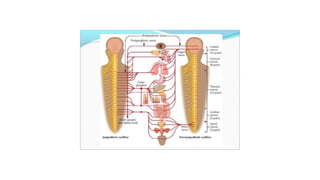
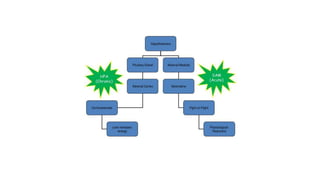
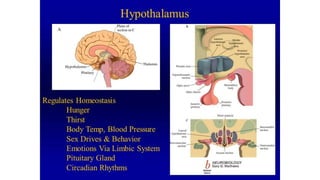
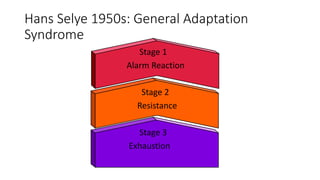
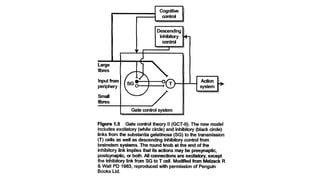
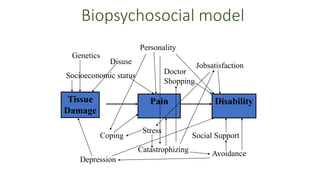
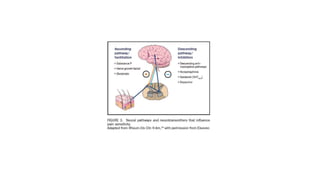
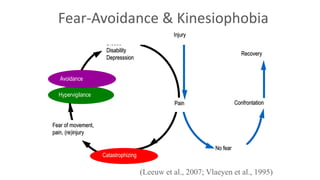
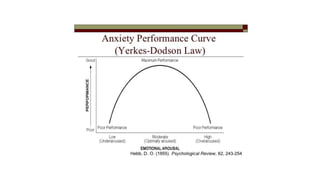
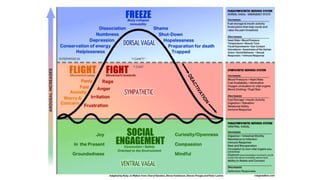
The document discusses various aspects of stress management and relaxation techniques, highlighting the differences between positive stress (eustress) and negative stress (distress), as well as the physiological and psychological responses to stress. It explores concepts such as the biopsychosocial model of pain, chronic pain's relationship to stress, and various coping strategies, including autogenic training and cognitive-behavioral therapies. The importance of physical activity and specific relaxation techniques for managing stress and pain is emphasized, with references to key theories and models in the field.