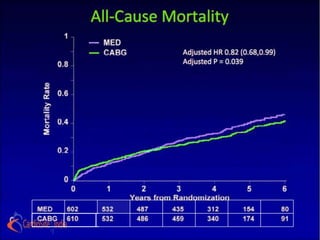
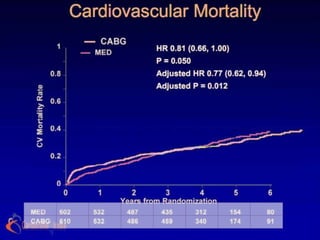
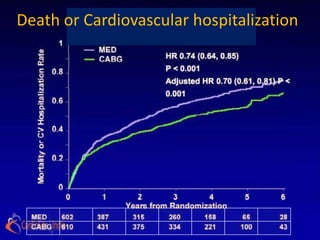
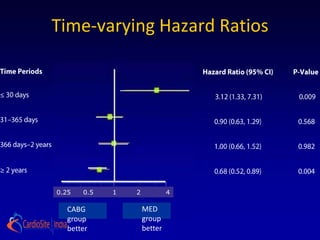
The STICH trial tested two hypotheses regarding the treatment of ischemic heart failure:
1) Adding CABG to medical therapy improves long-term survival more than medical therapy alone.
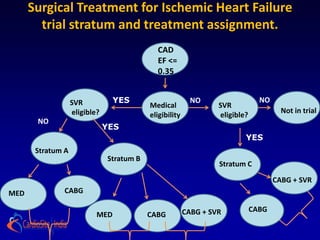
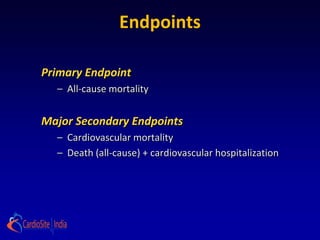
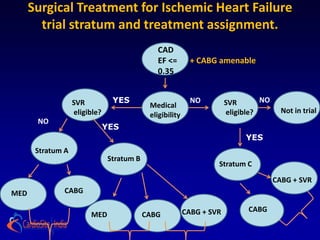
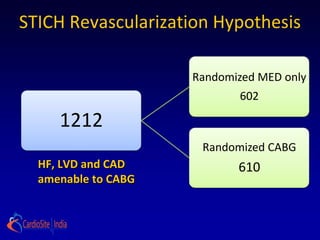
2) For patients with anterior left ventricular dysfunction, surgical ventricular reconstruction plus CABG and medical therapy improves survival free of cardiac hospitalization more than CABG and medical therapy without ventricular reconstruction. The trial randomized over 1200 patients to test these hypotheses but did not find conclusive evidence to support either the primary or secondary hypotheses.


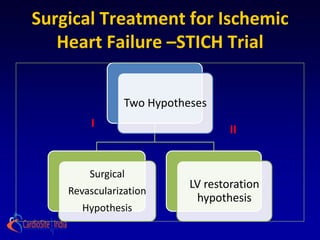
![I] Surgical Revascularization
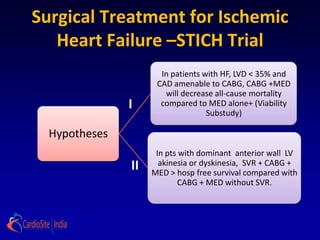
Hypothesis
Primary Hypothesis:
In patients with HF, LVD and CAD amenable to surgical
revascularization, CABG added to intensive medical therapy
(MED) will decrease all-cause mortality compared to MED
alone.
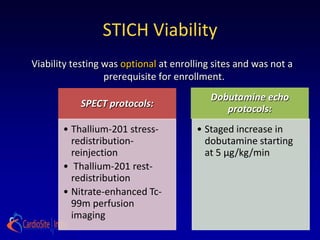
Secondary hypothesis:
Presence and extent of dysfunctional but viable myocardium,
as defined by radionuclide imaging, dobutamine stress
echocardiography, or both, will identify patients with greatest
survival advantage of MED + CABG compared with MED
alone.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reworked-stichtrial-120813041706-phpapp02/85/Critical-appraisal-of-Stitch-Trial-by-Dr-Akshay-Mehta-5-320.jpg)
![II] LV restoration hypothesis
In patients with dominant anterior wall LV akinesia or
dyskinesia, LV shape and size optimization by SVR
combined with CABG and MED improves long-term
survival free of cardiac hospitalization compared
with CABG and MED without SVR.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reworked-stichtrial-120813041706-phpapp02/85/Critical-appraisal-of-Stitch-Trial-by-Dr-Akshay-Mehta-6-320.jpg)




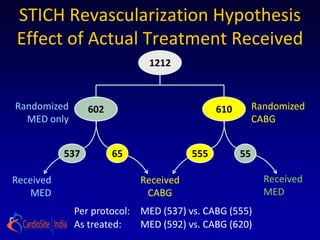
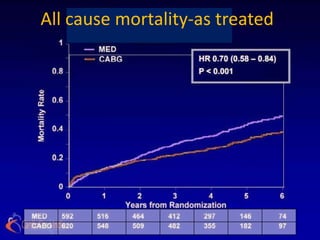
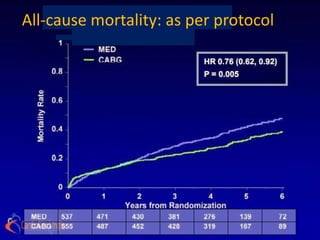





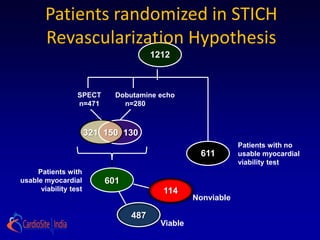
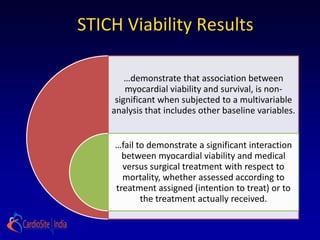

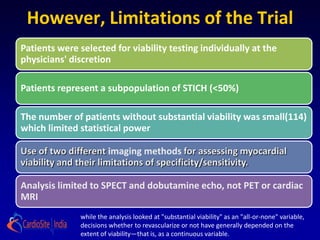

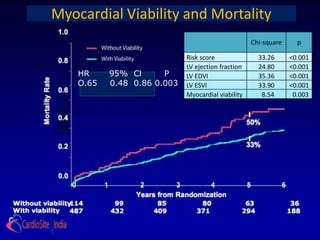
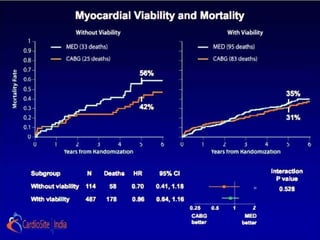
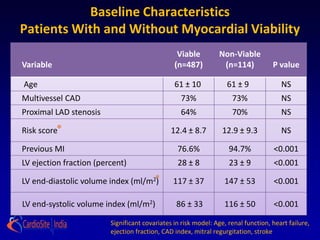
![ the patients without substantial viability, "who had perhaps
less likelihood of functional recovery [than those with
substantial viability], did as well from CABG as patients who
did. . . . I think that's what we have to take away from this: we
shouldn't be using [viability] studies to exclude patients from
cardiac surgery
-Dr Eric Velazquez](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reworked-stichtrial-120813041706-phpapp02/85/Critical-appraisal-of-Stitch-Trial-by-Dr-Akshay-Mehta-36-320.jpg)