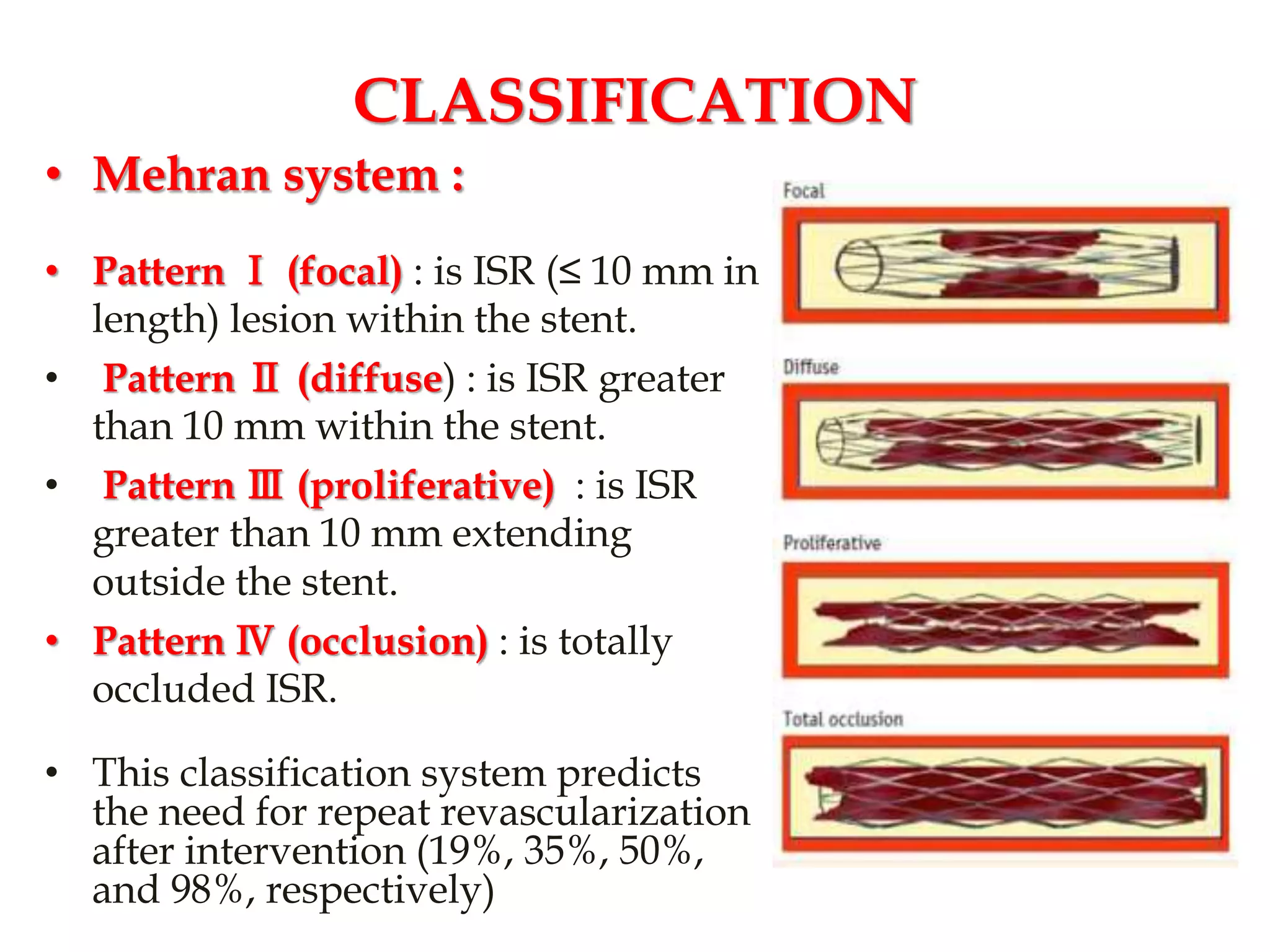
The document discusses in-stent restenosis (ISR), defined as the re-narrowing of a stented coronary artery due to neointimal tissue proliferation. ISR rates range from 3-20% with drug-eluting stents and 16-44% with bare-metal stents, usually occurring 3-20 months after stent placement. Predictors of ISR include patient characteristics like diabetes, lesion characteristics like length, and procedural characteristics like stent undersizing. The main mechanism is neointimal tissue proliferation due to arterial wall damage during stenting. ISR treatment involves revascularization like balloon angioplasty or additional stenting.