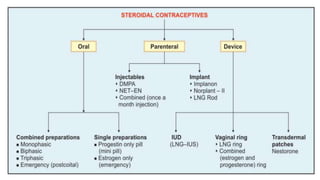
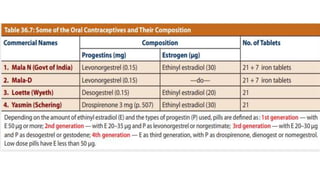
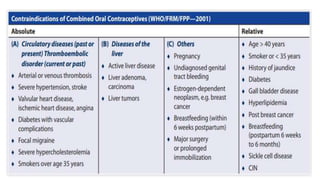
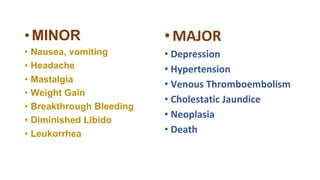
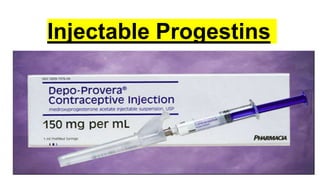
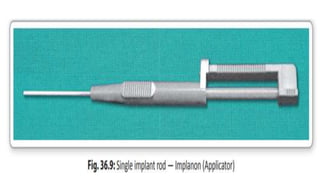
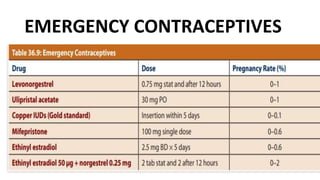
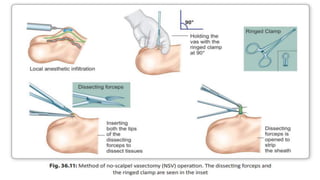
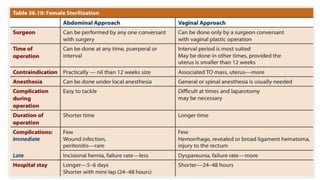
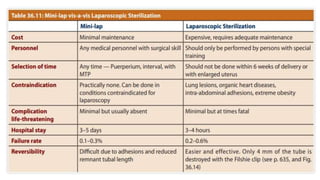
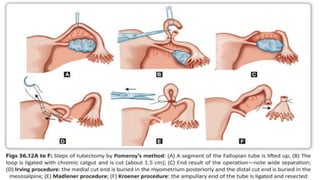
This document summarizes various contraceptive methods including combined oral contraceptives, progestin-only pills, injectable progestins, implants, emergency contraceptives, and permanent surgical methods. It describes the common hormones used, mechanisms of action, directions for use, advantages and disadvantages. Combined oral contraceptives are the most effective reversible method and work primarily by suppressing ovulation and thickening cervical mucus. Progestin-only options eliminate estrogen side effects. Surgical sterilization methods include vasectomy for males and tubectomy for females.