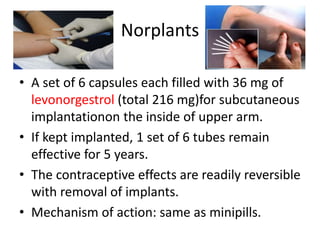
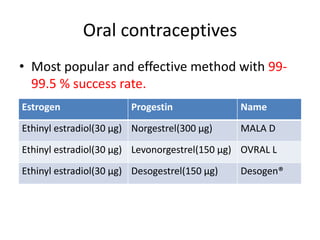
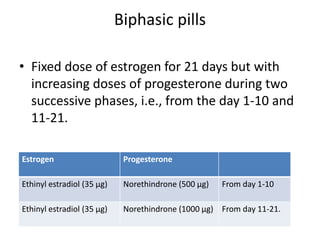
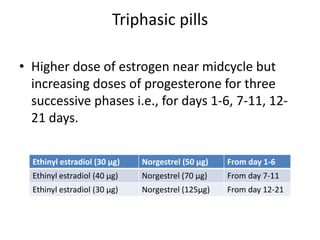
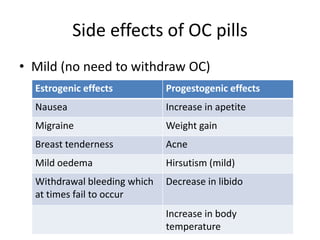
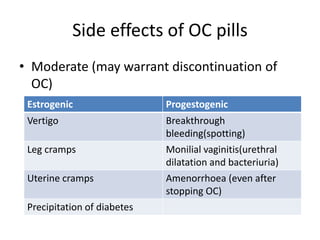
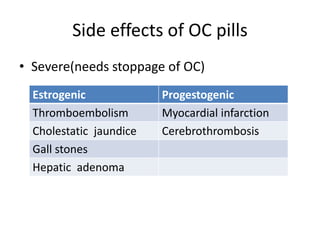
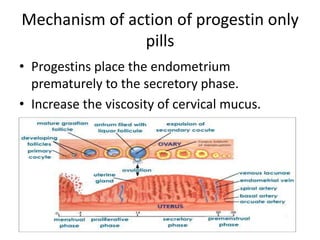
This document summarizes various hormonal contraceptive methods. It discusses oral contraceptive pills including combination and progestin-only pills. It describes injectable and implantable contraceptives such as DMPA and Norplant. Emergency contraception methods like Plan B are mentioned. The mechanisms of action, effectiveness, side effects, and contraindications are summarized for each method. Non-contraceptive health benefits are also noted such as reduced cancer risk. Research into male hormonal contraception is described though challenges in reversibly inhibiting spermatogenesis without affecting libido or hormones are acknowledged.














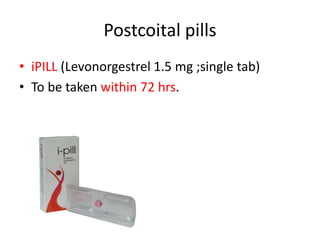
![Post coital contraception
• High dose estrogen and/or high dose
progestin.
• Two tablets of progestin levonorgestrel (750
µg each)[NORLEVO]. The first tablet must be
taken as soon as possible (within 48 hrs of the
coitus) and the second tablet taken after 12
hrs.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hormonalcontraception-150922084027-lva1-app6891/85/Hormonal-contraception-24-320.jpg)
![Post coital contraception
• Ethinyl estradiol (50 µg each tablet) +
Levonorgestrel (250 µg each tablet)[OVRAL].
Two such tablets are to be taken within 72 hrs
of unprotected coitus and next 2 tablets after
12 hrs.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hormonalcontraception-150922084027-lva1-app6891/85/Hormonal-contraception-25-320.jpg)