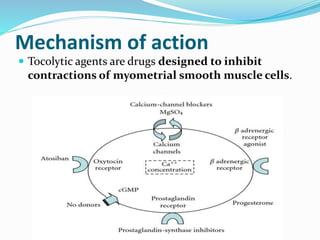
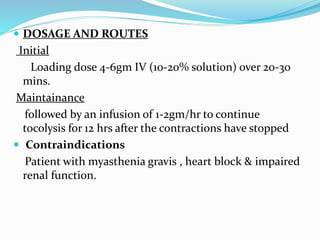
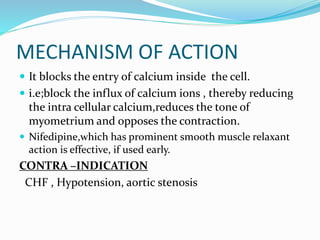
The document discusses tocolytic agents, which are medications used to suppress premature labor. It defines tocolytics as medications that can inhibit, slow down, or halt contractions of the uterus. The document then covers various classes of tocolytics including beta-adrenergic agonists, magnesium sulfate, calcium channel blockers, oxytocin receptor antagonists, prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors, and nitric oxide donors. For each class, it discusses examples of medications, mechanisms of action, dosages, side effects, and contraindications. The purpose is to explain how tocolytics work to suppress premature labor and allow time for fetal lung maturity.