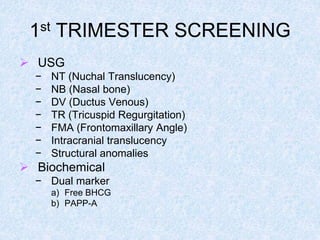
The document discusses antenatal screening tests in the first and second trimesters. In the first trimester, screening includes ultrasound markers like nuchal translucency, nasal bone, ductus venosus Doppler, and biochemical markers like PAPP-A and beta-hCG. Combined first trimester screening using these markers can detect around 85-90% of Down syndrome cases at a 5% false positive rate. In the second trimester, screening includes a genetic sonogram and biochemical markers, with a detection rate of around 82% for Down syndrome. The document provides details on measuring and interpreting various first trimester ultrasound markers and their association with chromosomal abnormalities.