This document provides information on Methergine and Clomiphene Citrate.
Methergine is an ergot alkaloid administered postpartum to help deliver the placenta and control bleeding by improving uterine muscle tone and contractions. It has potential side effects like nausea and leg cramps. Nurses must monitor vital signs and uterine response after administration and educate patients on signs of problems.
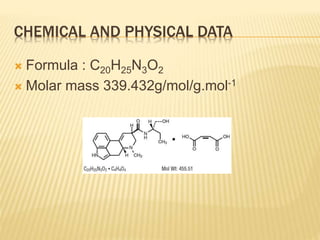
Clomiphene Citrate is used to induce ovulation in women with infertility. It works by inhibiting estrogen receptors in the brain to stimulate ovulation. It has potential visual and ovarian side effects and drug interactions. Nurses must monitor patients for abnormal bleeding or vision changes and educate them on proper administration and signs of problems.