Embed presentation
Downloaded 19 times


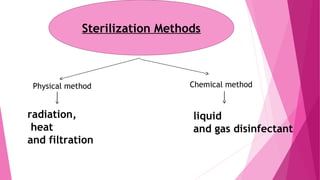
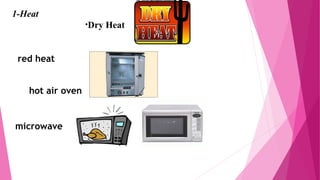





Sterilization refers to any process that eliminates all forms of life. There are physical and chemical sterilization methods. Physical methods include heat (dry heat, moist heat like autoclaving), radiation (electron beams, x-rays, gamma rays), and filtration. Chemical methods use liquid or gas disinfectants like ethylene oxide gas, alcohol, phenol, formaldehyde, and surfactants. Sterilization is important in medicine and surgery to sterilize instruments, medications, and devices entering the body to prevent infection.









