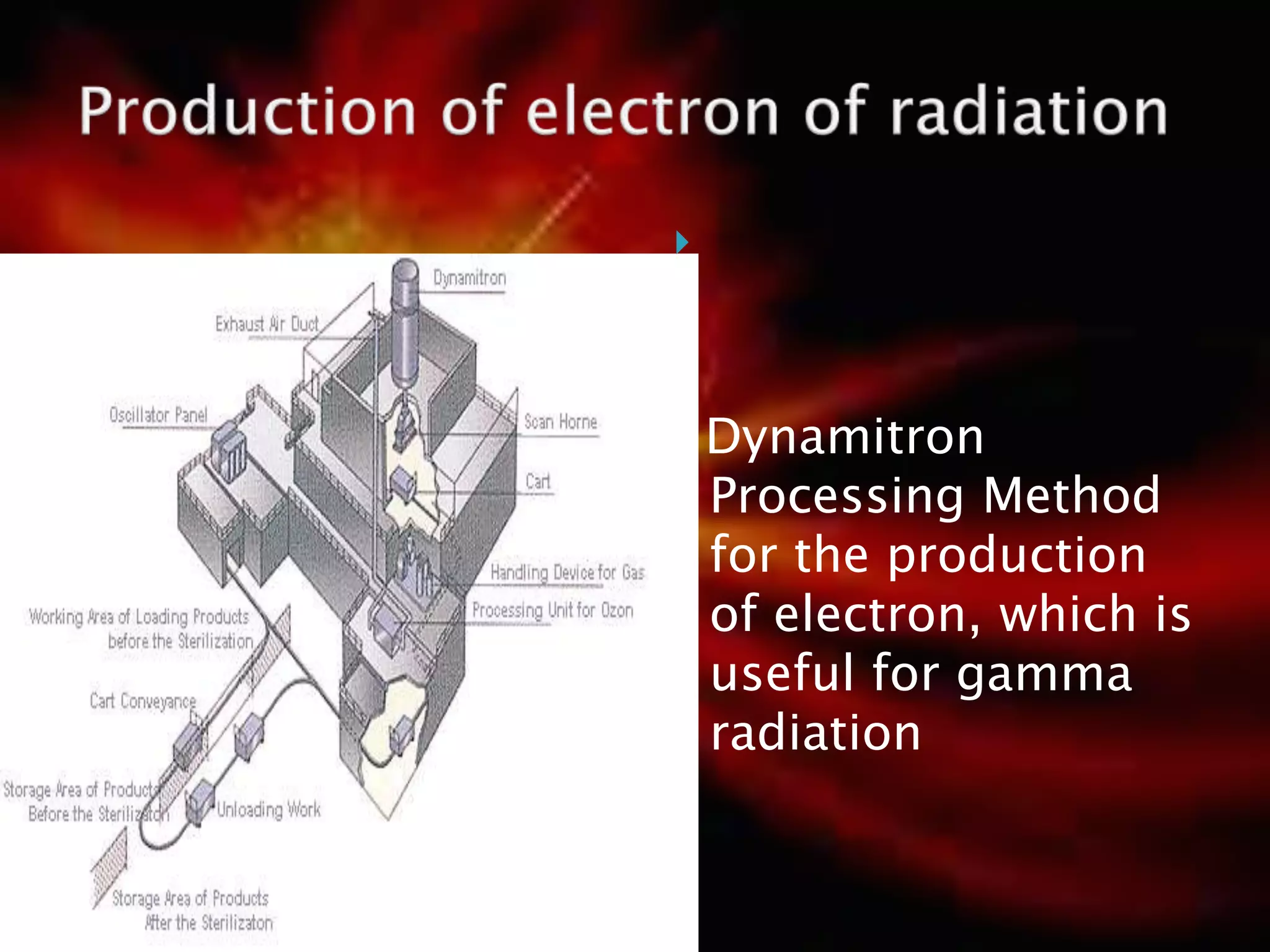
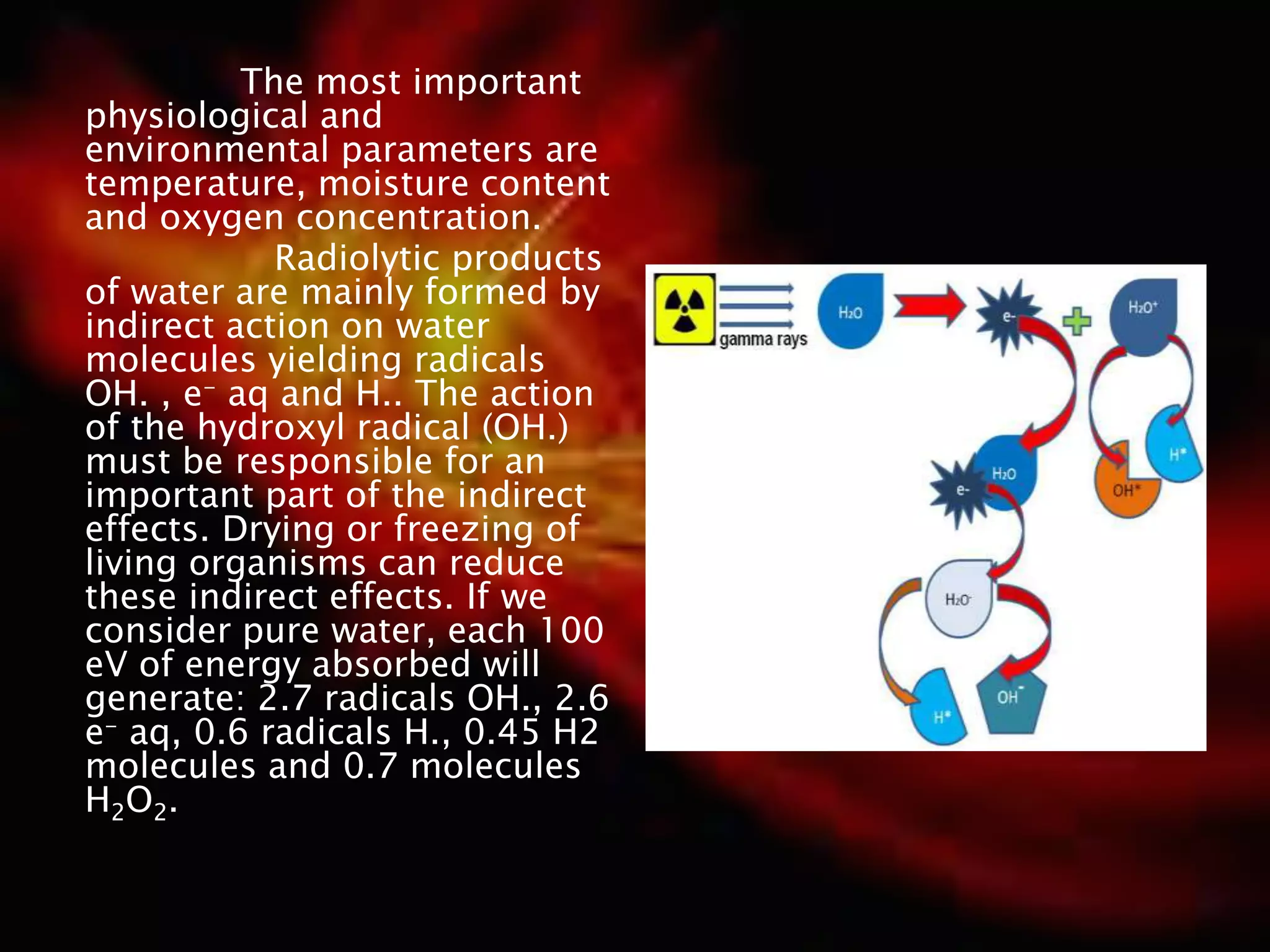
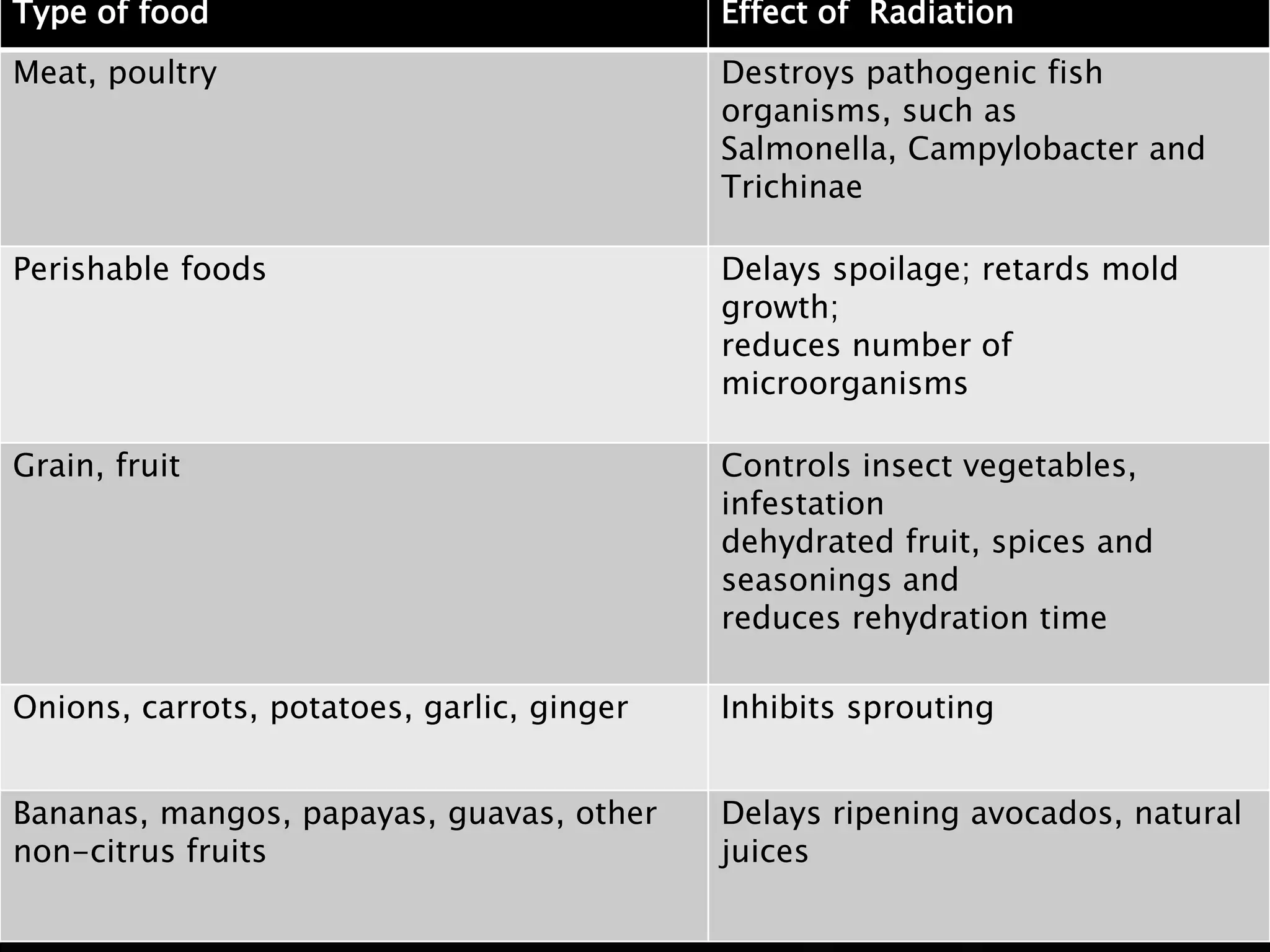
Gamma radiation sterilization uses Cobalt-60 or Cesium-137 sources to emit gamma rays that penetrate materials to destroy microorganisms. It is commonly used to sterilize medical devices, pharmaceuticals, tissues, and foods. The effectiveness depends on factors like dose level and microbial load. A dose of 25 kGy is typically used for sterilization of medical devices to achieve a sterility assurance level of 10-6. Gamma radiation sterilization provides advantages like deep penetration and reliability but can cause undesirable changes to heat-sensitive products. It is widely applied to sterilize items like syringes, sutures, and thermolabile medications.