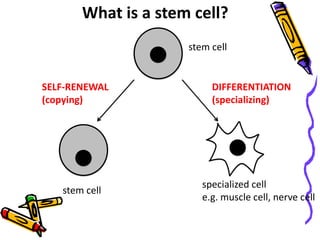
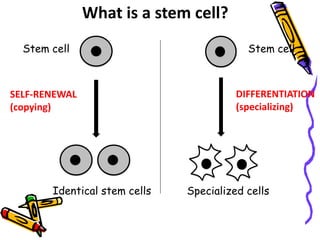
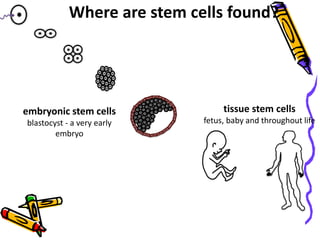
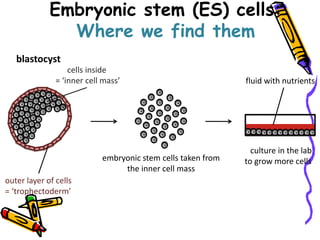
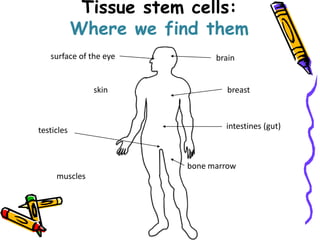
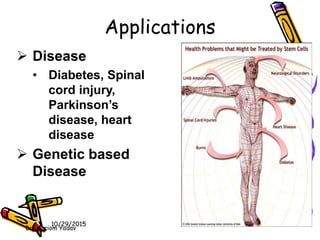
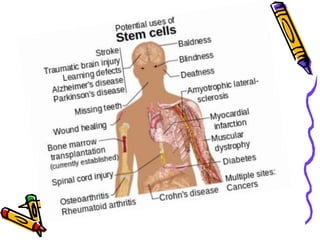
This document discusses stem cells, which are unspecialized cells that can divide and differentiate into specialized cell types. It defines stem cells as cells that can continuously divide and differentiate into various tissues. The key characteristics of stem cells are that they are unspecialized, can proliferate and renew themselves for long periods, and have the potential to become specialized cells. There are two main types of stem cells: embryonic stem cells, which are pluripotent and can become any cell type, and tissue stem cells, which are multipotent and can only become certain specialized cell types. The document provides examples of where different stem cells are found and their potential applications in treating diseases.