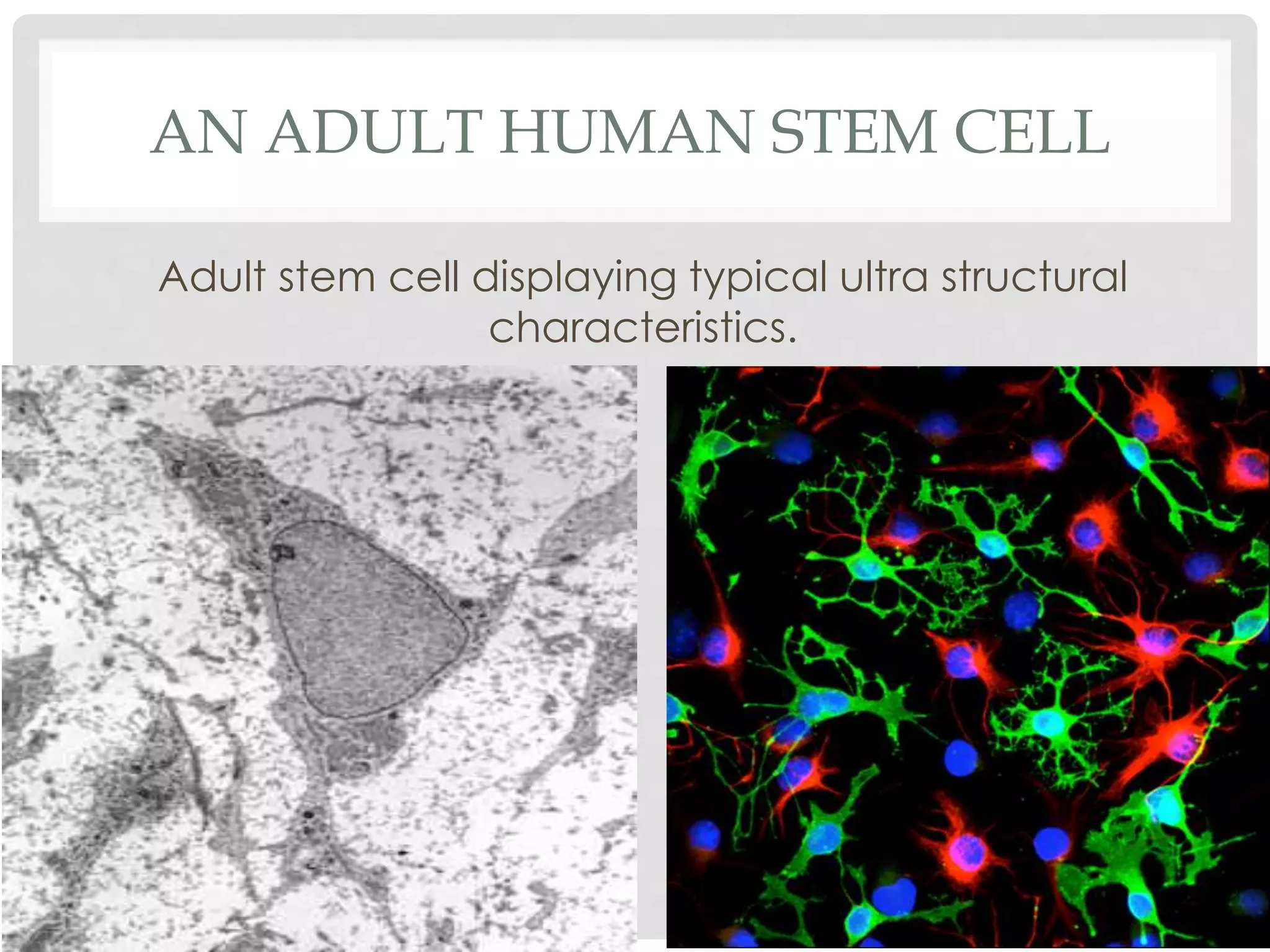
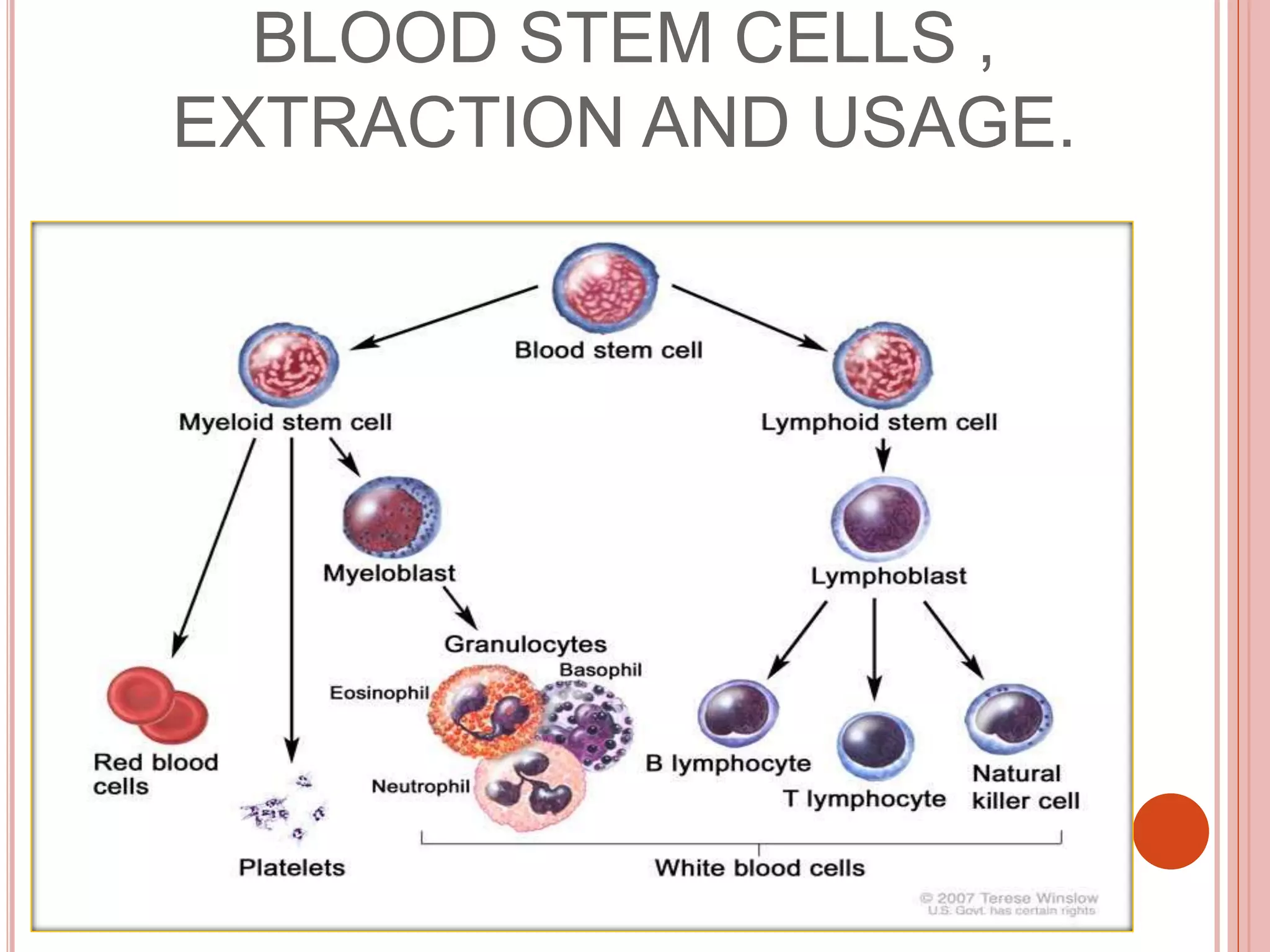
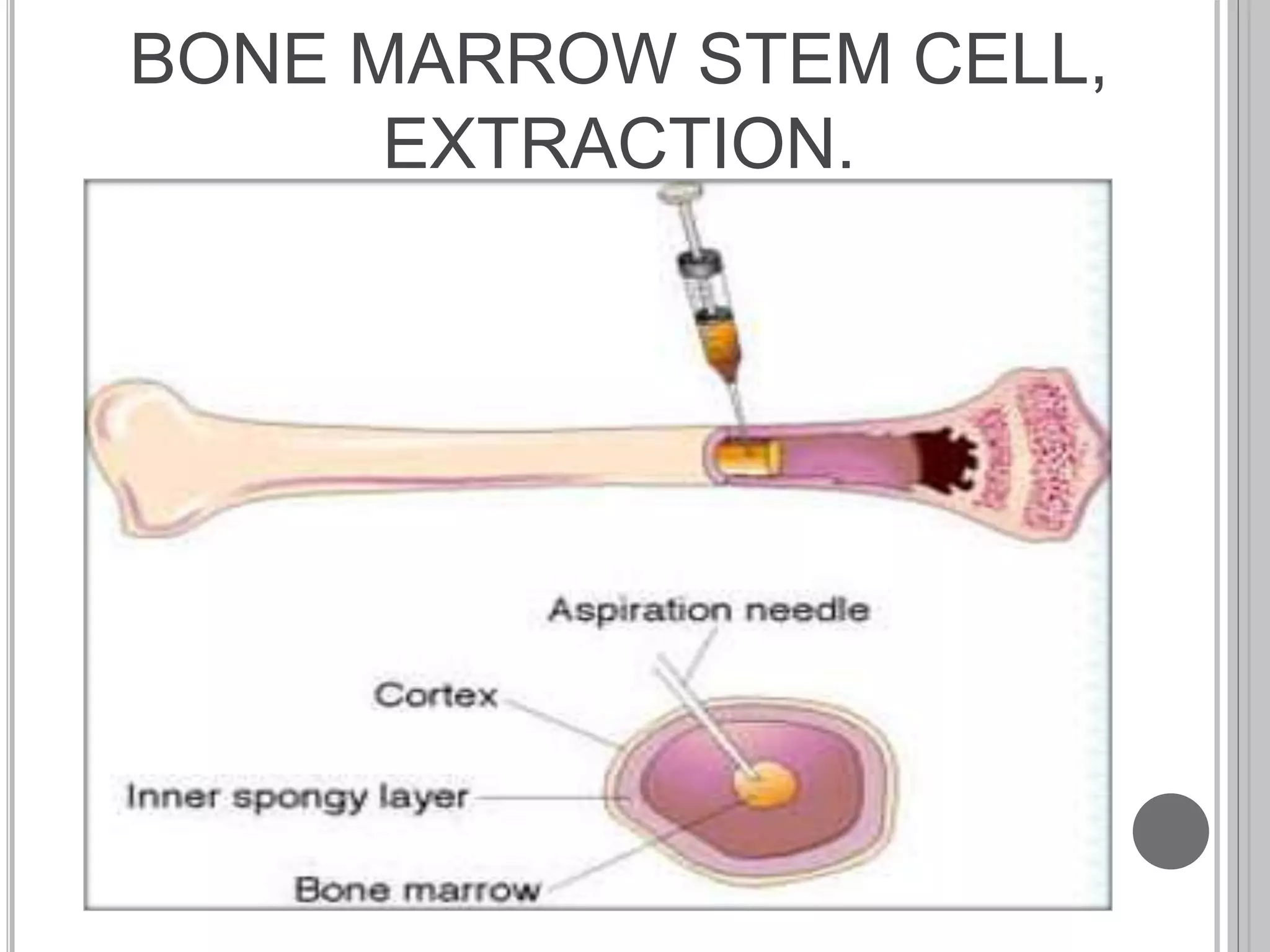
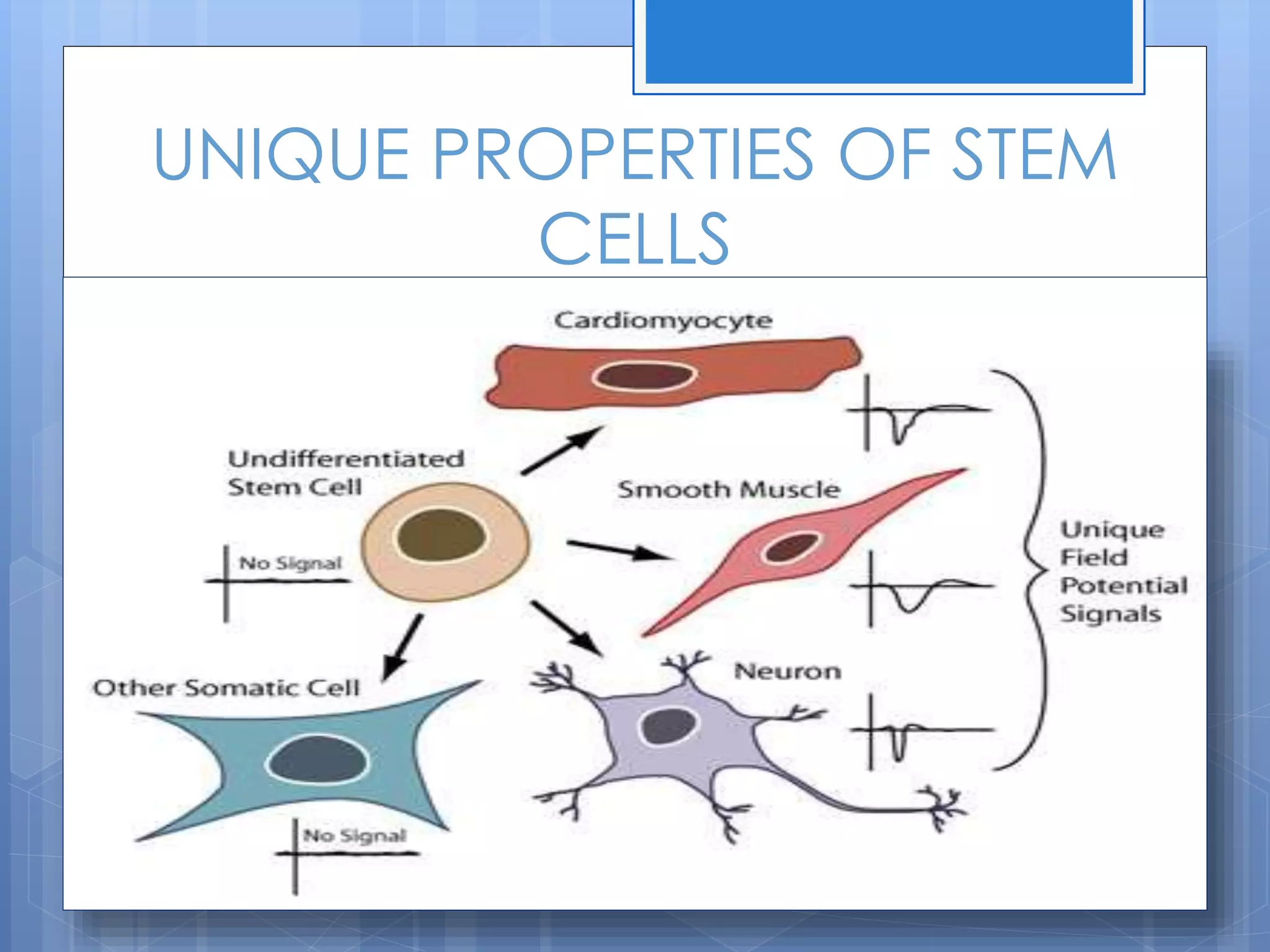
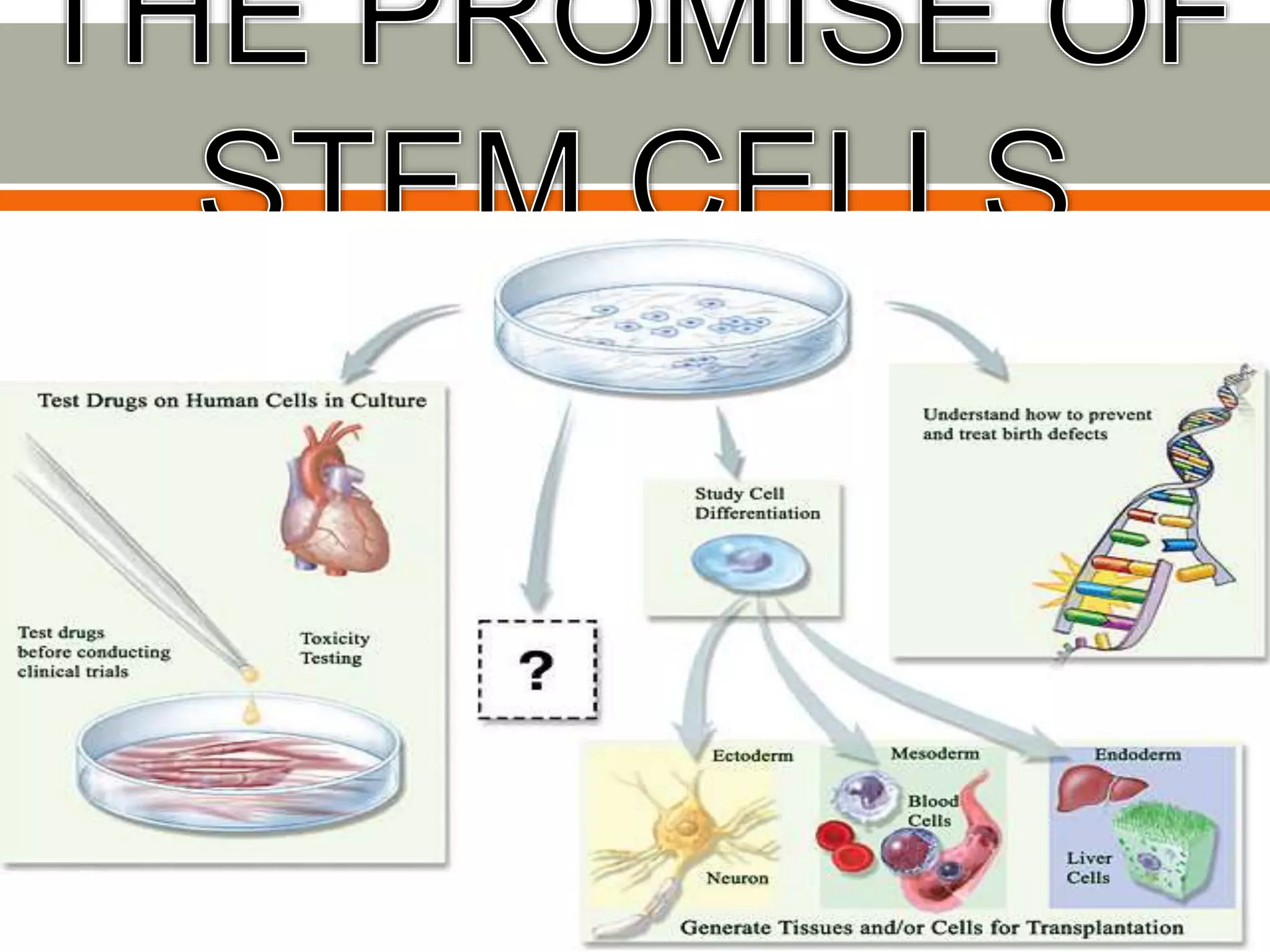
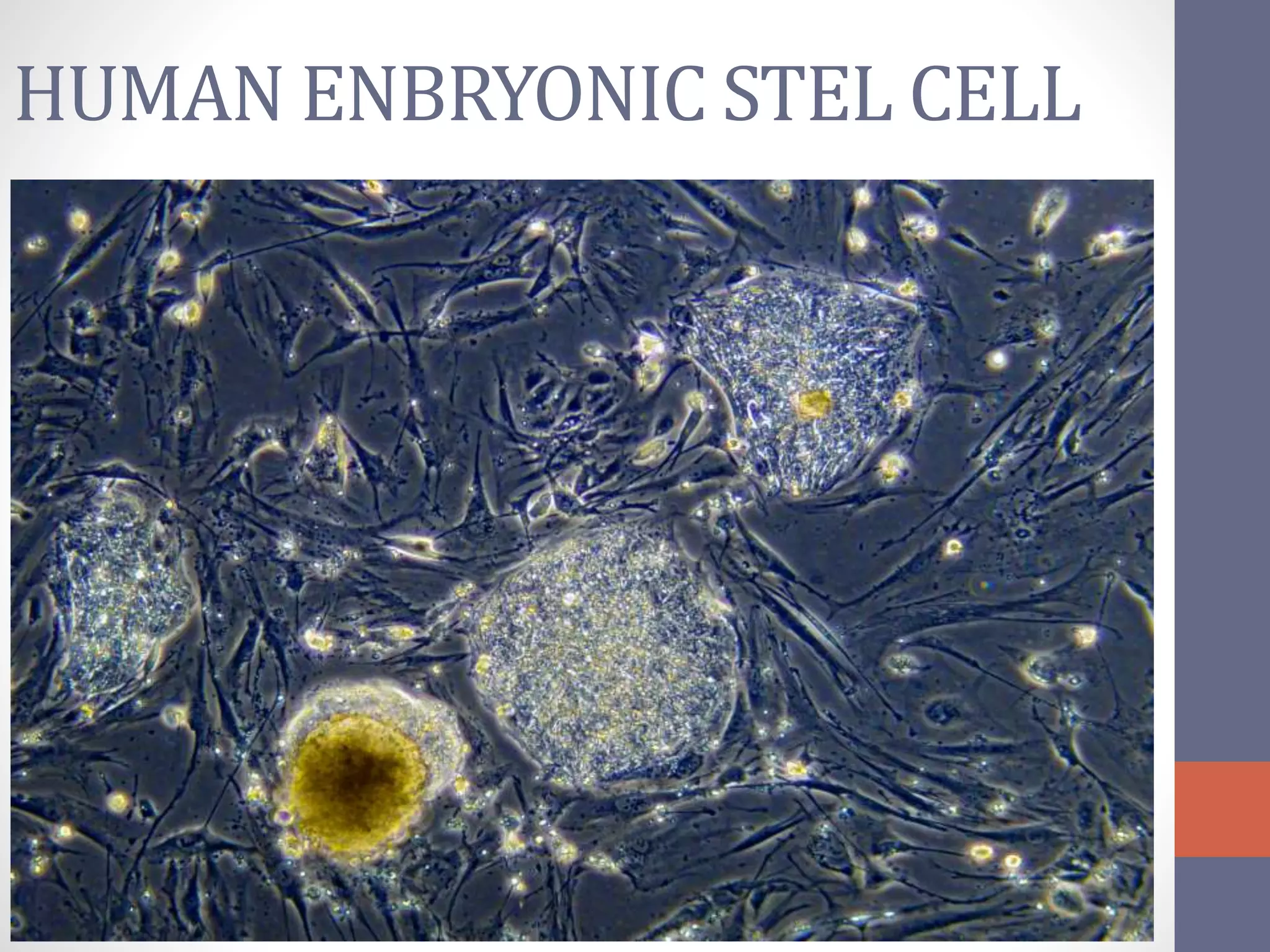
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can differentiate into specialized cells and divide to produce more stem cells. There are two main types - embryonic stem cells isolated from blastocysts and adult stem cells found in tissues. Adult stem cells act as a repair system, replenishing tissues. Stem cells can be extracted from bone marrow, adipose tissue, and blood. They are characterized by their ability to self-renew and differentiate into other cell types. Embryonic stem cells are derived from embryos and cultured on feeder layers where they can proliferate indefinitely. Stem cells have potential uses in research, drug testing, and regenerative cell therapy for conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and spinal cord injury.