The document provides information about standard work for managers, including:
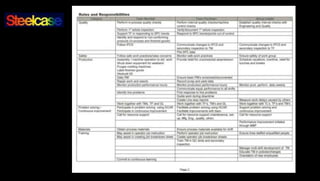
1) It discusses the need to define all manager activities as standard processes and document them using a "Standardized Work for Supervisor" sheet.
2) It lists the five qualities of an effective leader: knowledge of work, knowledge of responsibilities, skills in instructing, skills in improving methods, and leadership skills.
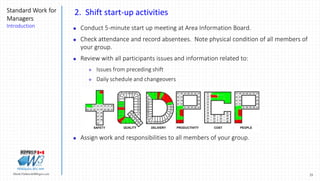
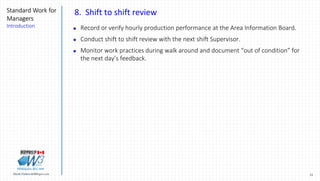
3) It presents examples of how to structure a supervisor's daily activities into 10 time elements including pre-shift activities, shift start-up activities, and post start-up activities.


















![20Marek.Piatkowski@Rogers.com
Standard Work for
Managers
Introduction
Thinkingwin, Win, WIN
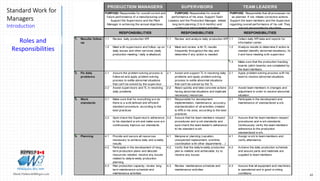
Roles of General Supervisors and Shop Floor Managers
Must have practical knowledge of all Standardized Work for Supervisor activities
Must be able to provide On-the-Job [OJT] Training to all Supervisors
Coach, advise and support
Discipline - adhere to standards [one best way]
Structured daily walk about, review if Standardized Work is being followed - “Show
me”
Continuously simplify and improve Standardized Work for Supervisors](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stdwformanagersandsupervisors-october2016-161113191902/85/Stdw-for-managers-and-supervisors-october-2016-20-320.jpg)