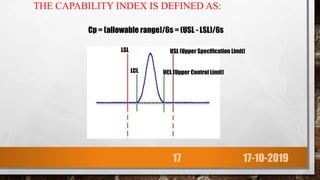
This presentation discusses statistical control charts which are tools used in pharmaceutical manufacturing to determine if a process is in statistical control. It defines control charts and explains that they provide a visual representation to monitor a process and identify instances where the process may be going out of control. The presentation covers the objectives, principles, types of control charts including variable and attribute charts, their characteristics and benefits such as improving quality, productivity and reducing defects. It also discusses using control charts to evaluate process capabilities.