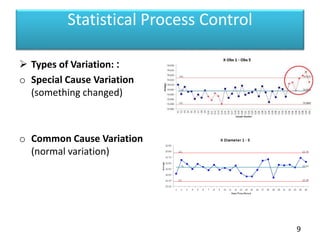
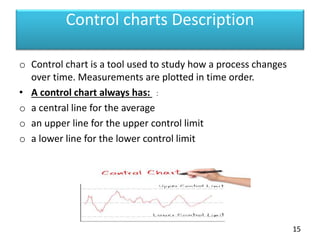
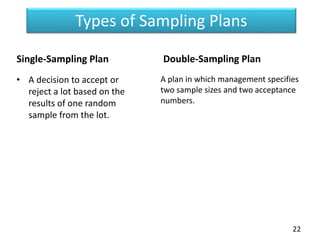
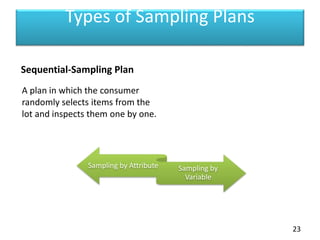
This document discusses statistical process control (SPC) and control charts. It defines SPC as a method for monitoring, controlling, and improving a process through statistical analysis. Control charts are a key tool in SPC and are used to monitor how a process changes over time by plotting measurements on a chart showing average lines and control limits. The document outlines the basic steps in using SPC, including planning, data collection, analysis, and taking action if needed to improve the process based on the results.