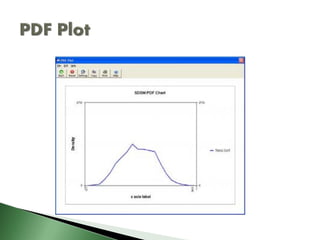
This document discusses statistical downscaling using the Statistical Downscaling Model (SDSM). It describes SDSM as a tool for assessing local climate change impacts that facilitates the development of climate scenarios through empirical relationships between regional predictors from global climate models and local predictands. The document outlines the 7 main steps in SDSM: quality control and data transformation, screening predictor variables, model calibration, weather generation, statistical analysis, scenario generation, and graphing monthly statistics.