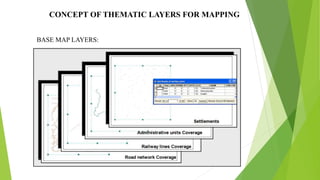
The document discusses the preparation of ground water prospects maps for the Rajiv Gandhi National Drinking Water Mission project, using remote sensing and GIS to identify potential groundwater sources in rural habitations. It outlines the project's objectives, methodologies for ground water exploration, and the significance of these maps in selecting suitable recharge structure locations and improving water supply coverage. The document also clarifies the scope and limitations of these maps in terms of accuracy and variable yields.