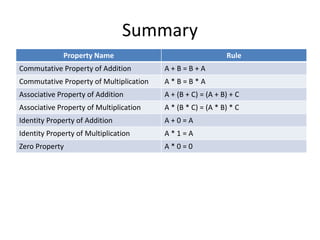
The document explains key mathematical properties including commutative, associative, identity, zero, and distributive properties. It provides definitions, examples, and the rules associated with each property, illustrating how they apply to addition and multiplication. It emphasizes that these properties hold true for all real numbers but may not apply beyond that set.