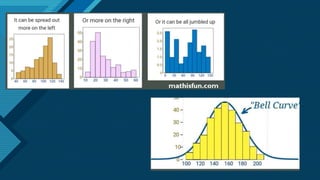
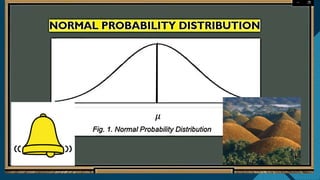
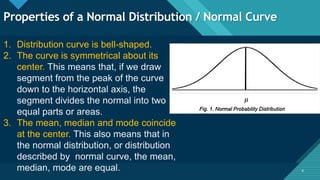
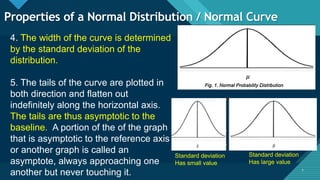
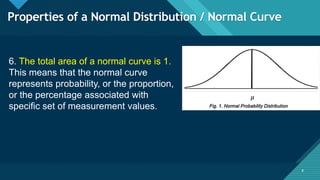
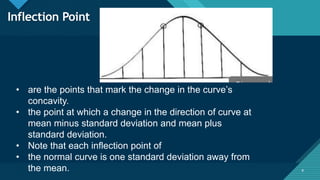
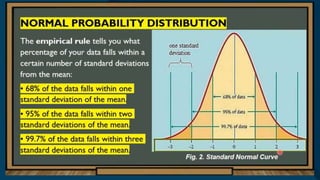
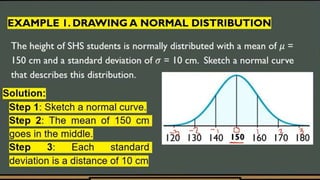
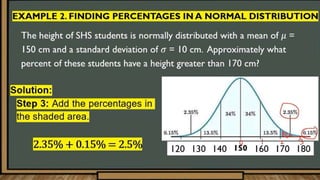
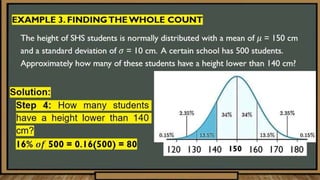
The document discusses the normal distribution and its key properties. It describes how the normal distribution is a bell-shaped curve that is symmetrical around the mean. It also notes that the mean, median, and mode are equal at the center of the distribution. Additionally, it explains how the standard deviation determines the width of the curve and that the total area under the curve is 1.