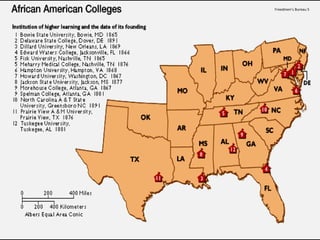
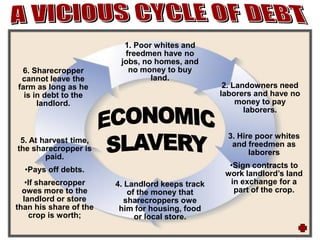
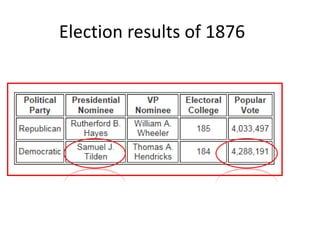
Presidential Reconstruction aimed to quickly readmit southern states to the Union with lenient terms, but it failed to protect the rights of freed slaves. Radical Republican Reconstruction required southern states to rewrite constitutions guaranteeing black rights and ratify the 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments. However, the Compromise of 1877 ended Reconstruction, removing federal troops and protection for freed slaves as the South imposed Jim Crow laws and disenfranchised most black voters.