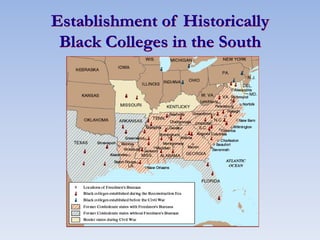
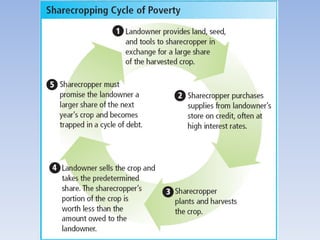
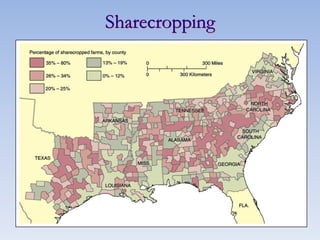
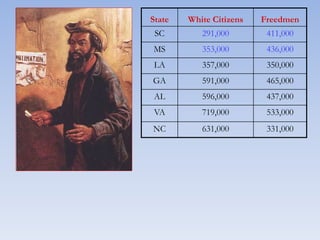
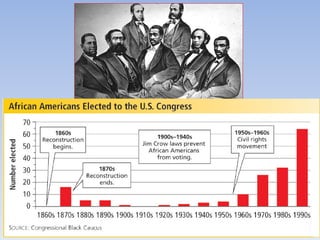
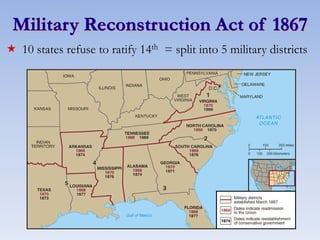
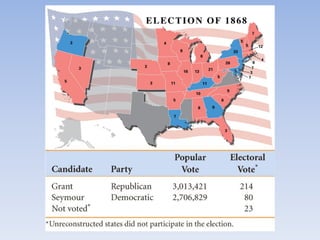
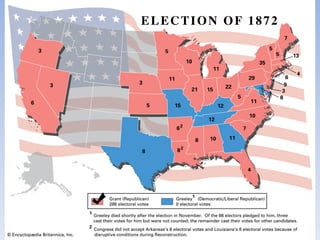
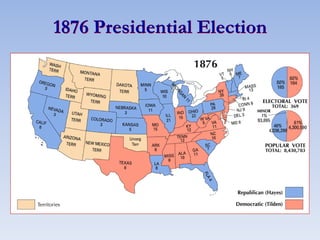
The document summarizes the major events and phases of Reconstruction after the American Civil War from 1865 to 1877. It discusses the debates around rebuilding the South, readmitting Confederate states to the Union, and granting citizenship to freed slaves. It outlines the three phases of Reconstruction under Lincoln, Johnson, and Congressional Republicans. Key events included the passage of the 13th Amendment abolishing slavery, the Black Codes imposed by Southern states, and the ratification of the 14th and 15th Amendments granting citizenship and voting rights to African Americans. Growing corruption and the disputed 1876 presidential election led to the Compromise of 1877 which ended Reconstruction.