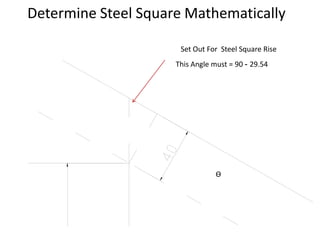
Stairs provide access between floors in buildings and must be designed to carry certain loads. There are various types of stairs including straight run stairs, quarter turn stairs, and spiral stairs, which can be constructed from materials like timber, brick, stone, steel, and reinforced concrete. Key aspects of stair design include the tread, riser, going, flight, and landing. Stairs must also be designed and enclosed appropriately to prevent the spread of fire between floors. Calculation of stair dimensions involves determining the total rise, suitable riser height, and best going based on building code requirements.