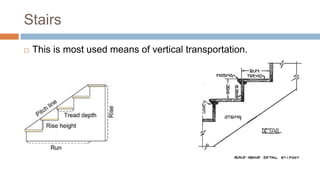
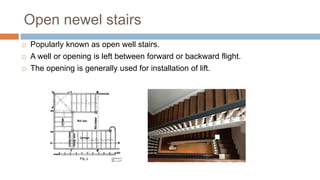
There are four main types of vertical transportation: stairs, lifts, escalators, and ramps. Stairs can be straight, dog-legged, geometric, circular, or involve quarter or full turns. Escalators are powered continuous moving stairways used to transport people between floors in places like malls and airports. Ramps provide a sloped surface for transportation between floors, especially for large numbers of people or vehicles. Elevators use guided cars or platforms to lift people and materials vertically between levels in buildings over four stories tall, and can be traction, hydraulic, roped hydraulic, or holeless hydraulic.