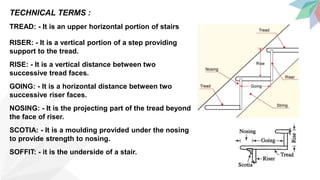
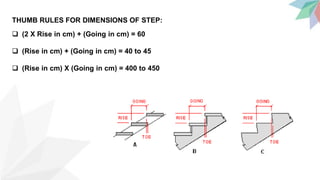
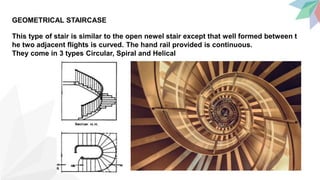
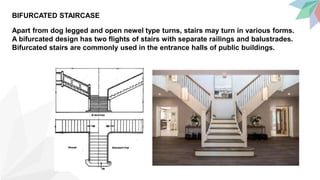
Stairs provide access between floors and are a means for fire to spread. The key components of stairs are treads, risers, going, nosing, and handrails. Good staircases are wide enough for comfortable use, have 3-12 steps, and adequate lighting and ventilation. Stair dimensions follow thumb rules regarding the relationship between rise, going, and their product. Common staircases include straight, quarter turn, dog-legged, open well, geometrical, bifurcated, and spiral configurations. Stairs can be constructed from materials like metal, concrete, stone, glass, and timber.