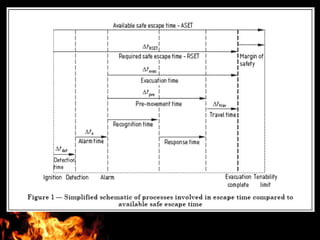
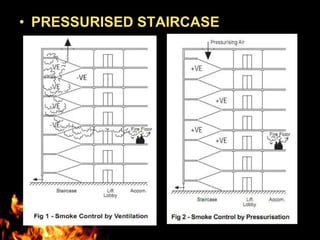
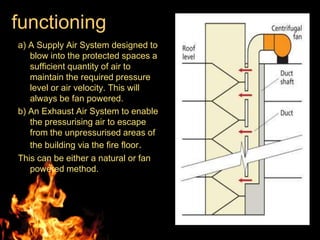
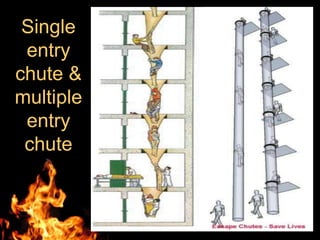
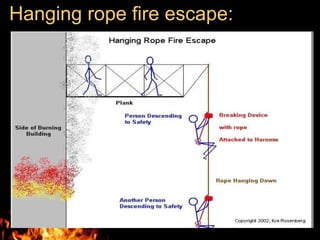
This document discusses fire escape systems and methods of escaping fires. It covers various fire escape designs like pressurized staircases, escape chutes, hanging rope fire escapes, and external fire escaping stairs. It also addresses economic impacts of fires, calculating evacuation times, travel distances, exit widths, and minimum number of exits based on building construction type and occupancy. The document provides details on different vertical and inclined chute designs and residential escape chutes. Overall, it outlines considerations for effective fire escape routes and methods to safely evacuate buildings during fires.