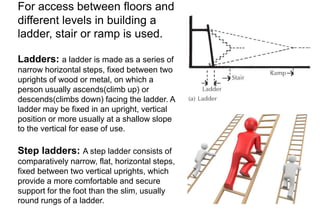
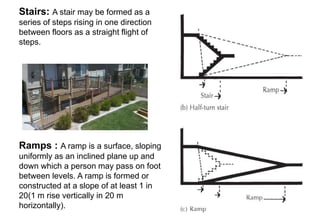
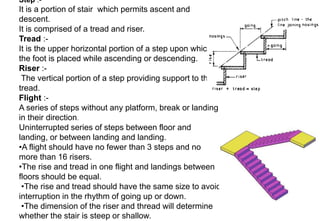
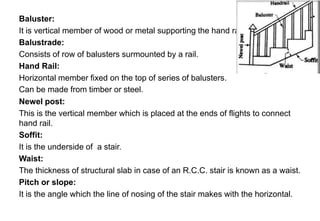
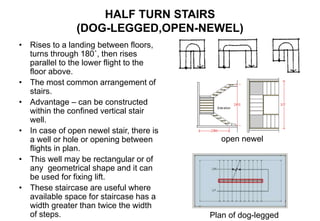
Stairs provide access between different floors and levels of a building. They consist of steps arranged in flights with landings between. Stairs can be made of various materials like timber, metal, stone, reinforced concrete, or brick. Common types include straight stairs, quarter turn stairs, half turn stairs, and spiral/circular stairs. Stairs must meet functional requirements of strength, safety, and fire safety to support loads and allow escape. Proper dimensions of treads, risers, headroom, and handrails are important for safe use of stairs in a building.