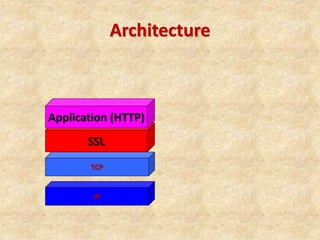
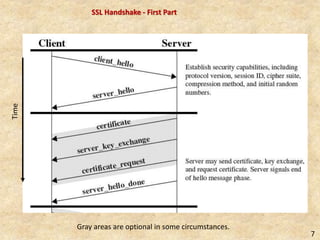
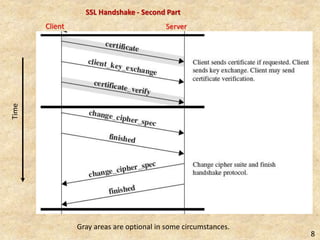
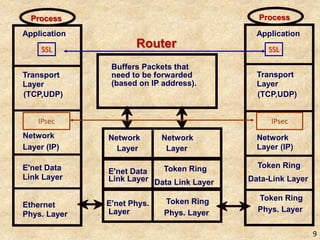
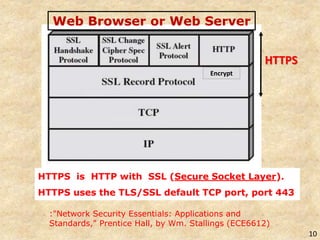
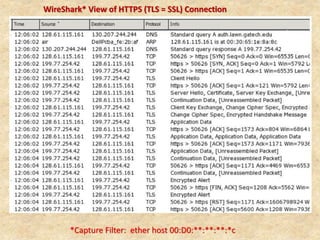
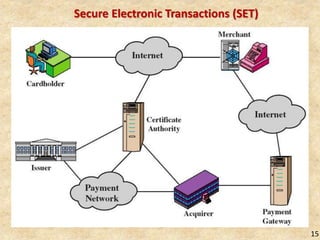
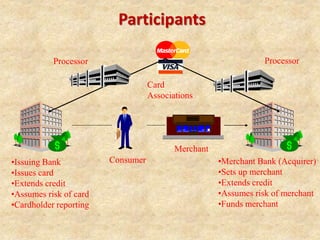
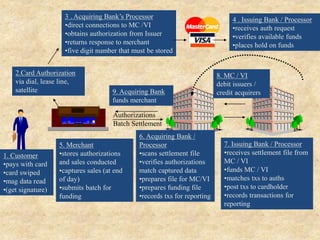
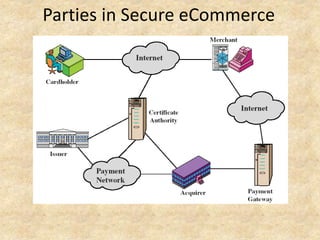
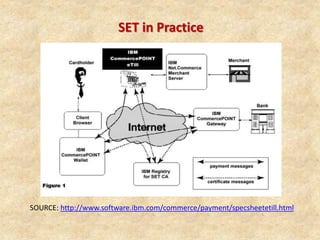
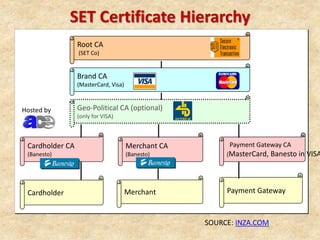
SSL/TLS provides encryption and authentication for secure internet communications. It originated from efforts by IETF, ANSI, and Netscape in the 1990s. SSL/TLS establishes a secure channel through a handshake to negotiate encryption keys before data transfer. SET builds on SSL/TLS to provide additional privacy, authentication, and integrity specifically for online credit card transactions through the use of digital signatures and certificates. It establishes separate encryption for payment and order information that is only revealed to authorized parties.