The document summarizes web security considerations and technologies like SSL, TLS, and SET.
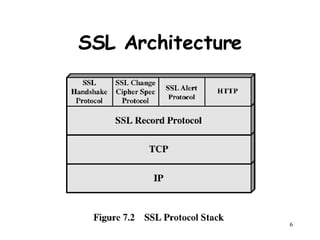
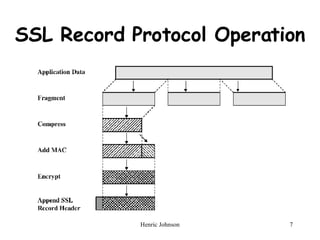
SSL and TLS provide encryption and authentication to secure data transmission between a client and server on the web. The handshake protocol allows servers and clients to authenticate each other and negotiate encryption before transmitting application data.
SET is an open encryption specification that protects credit card transactions on the internet. It provides security protocols and formats to ensure confidentiality, integrity of data, cardholder authentication, and merchant authentication for online payments. The sequence of events for transactions using SET is described briefly.
![Chapter 7 WEB Security Henric Johnson Blekinge Institute of Technology, Sweden http://www.its.bth.se/staff/hjo/ [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter-ns7-7548/85/Web-Security-in-Network-Security-NS7-1-320.jpg)