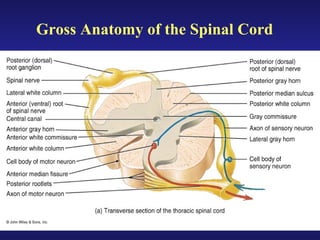
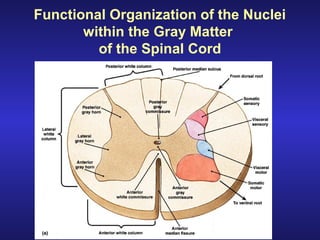
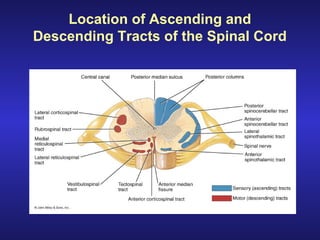
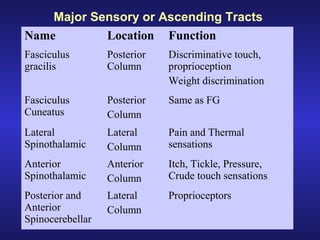
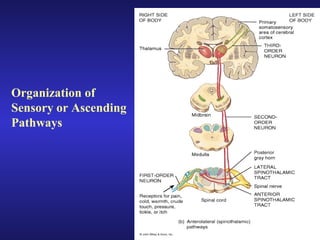
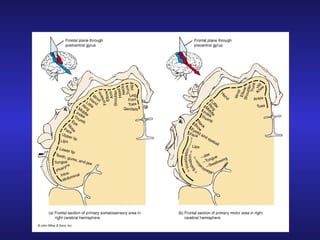
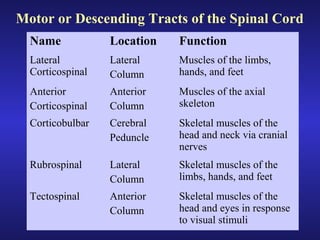
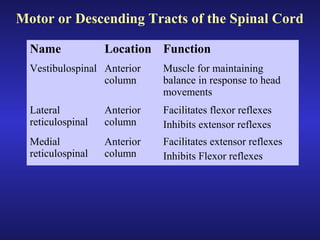
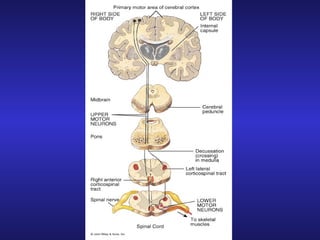
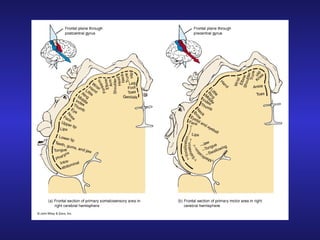
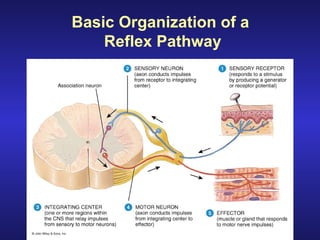
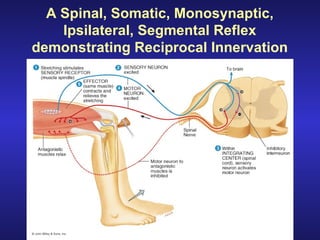
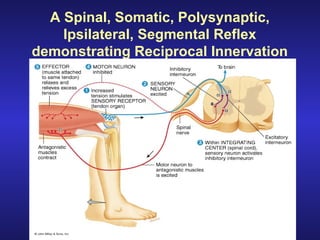
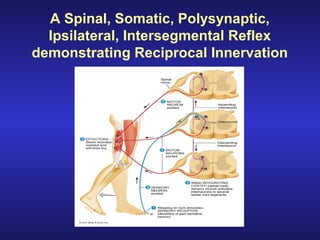
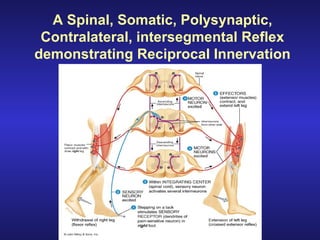
The document summarizes the gross anatomy and functional organization of the spinal cord. It describes the location and functions of ascending tracts that transmit sensory information and descending tracts that control motor signals. The organization of sensory and motor pathways within the spinal cord and definitions of various reflex pathways are provided, including examples of monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflexes.