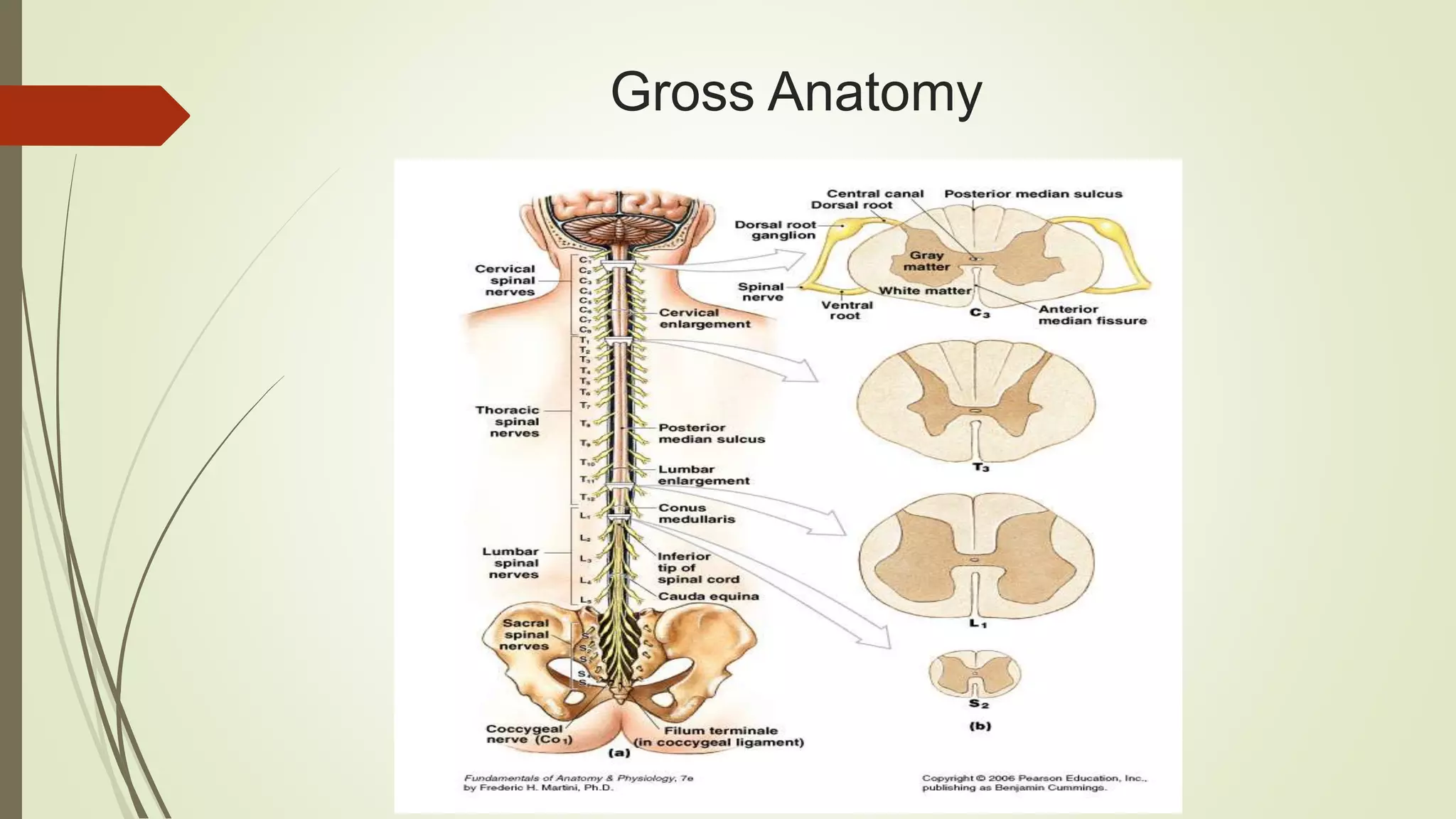
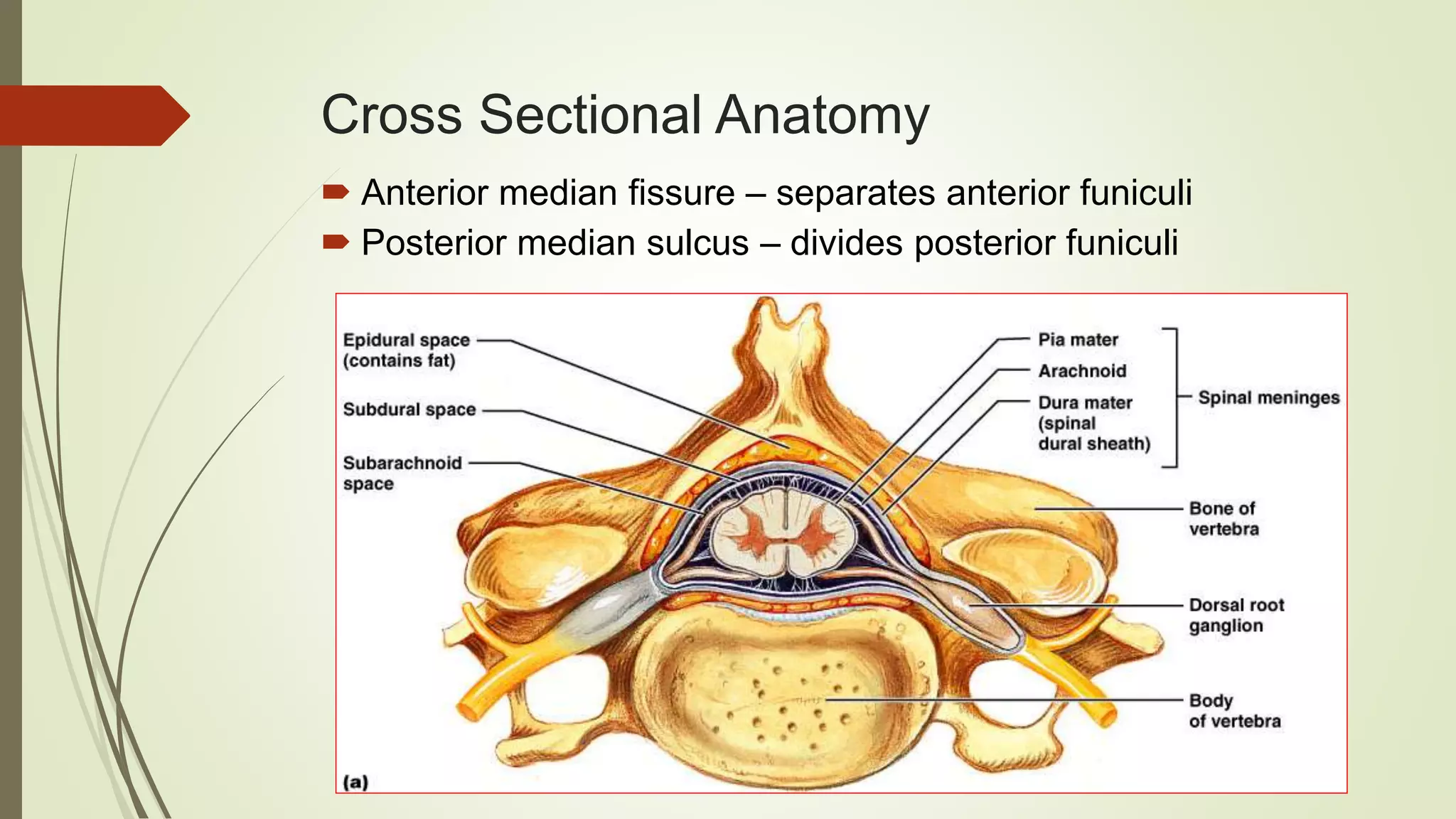
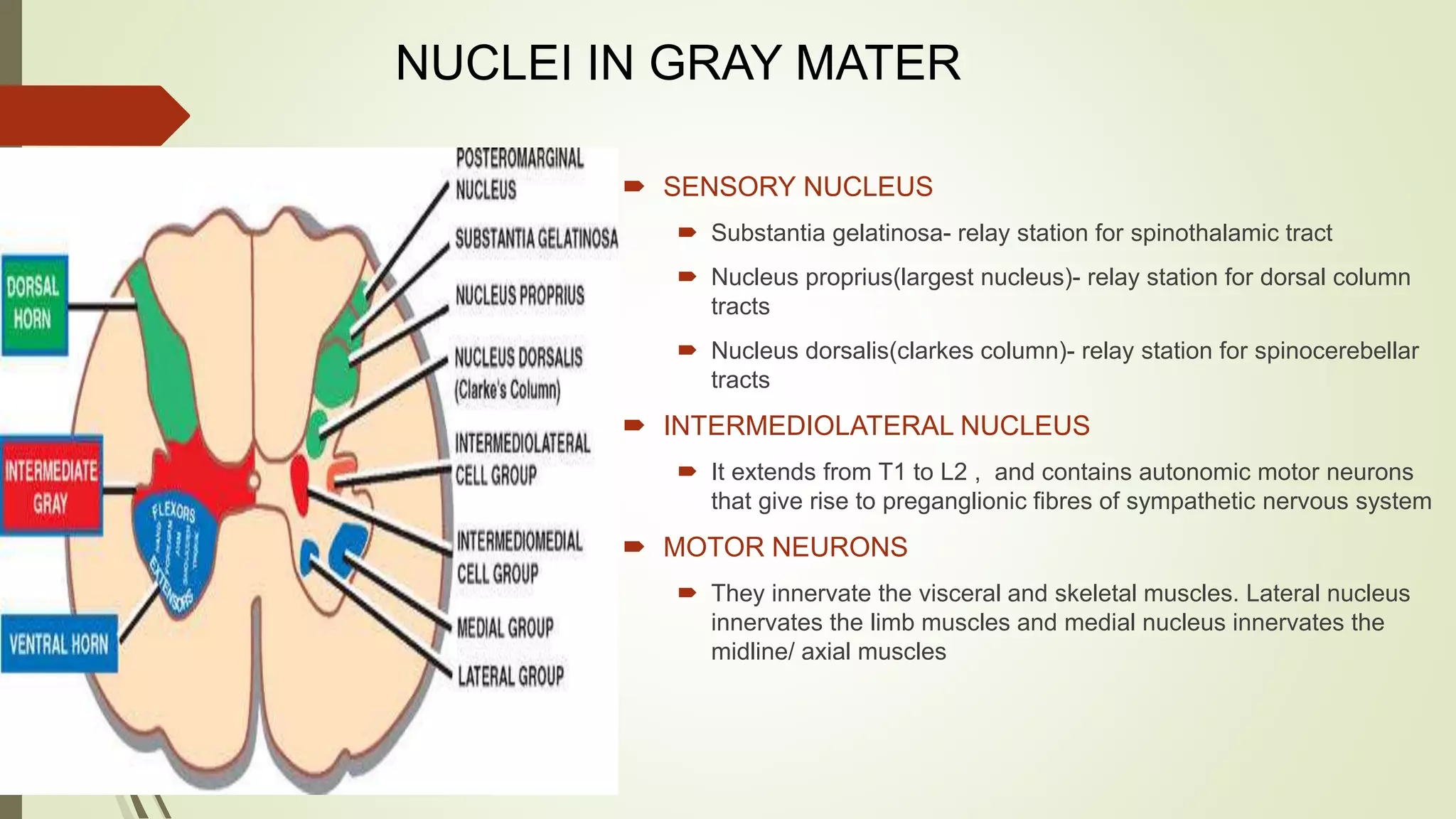
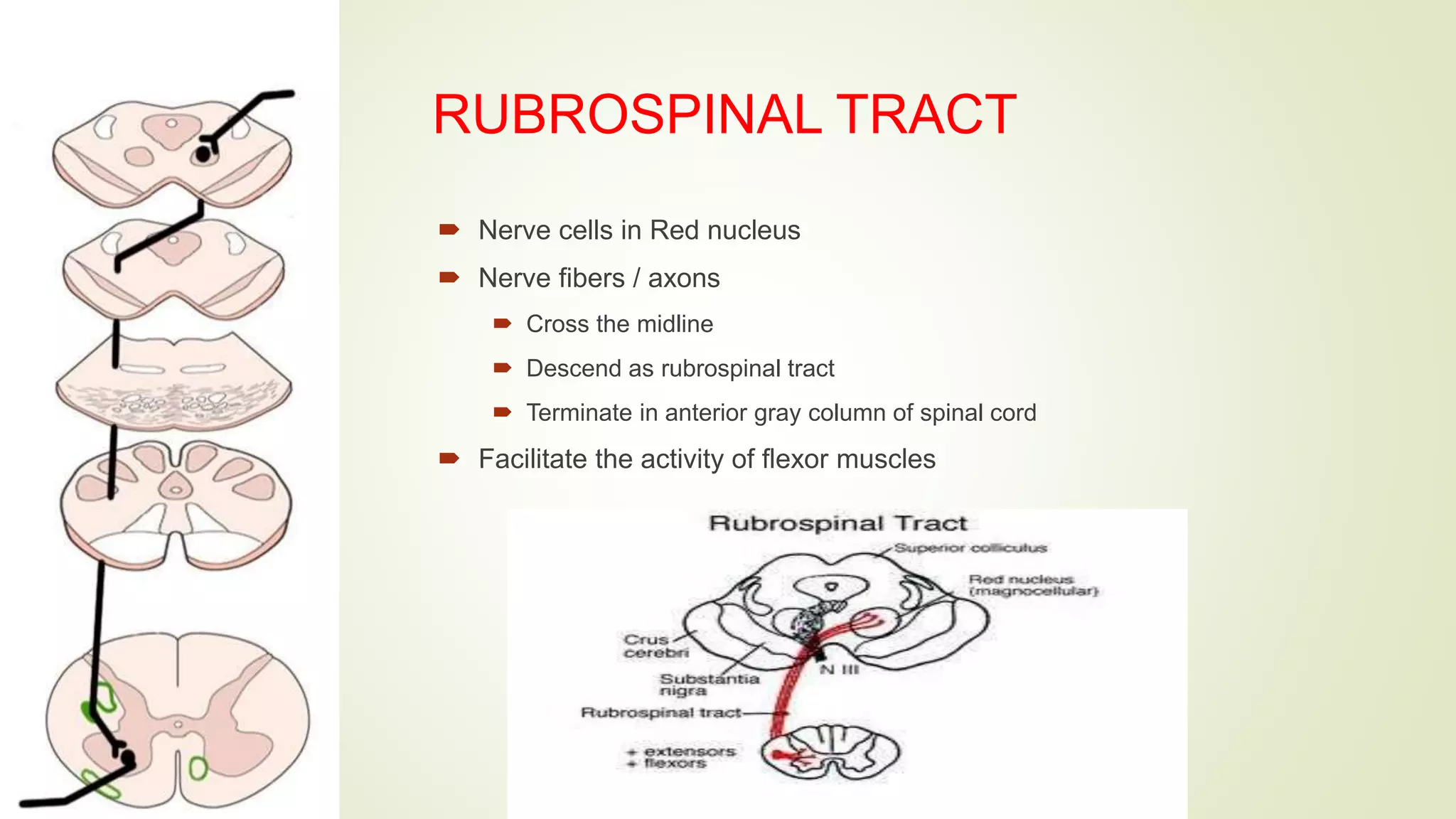
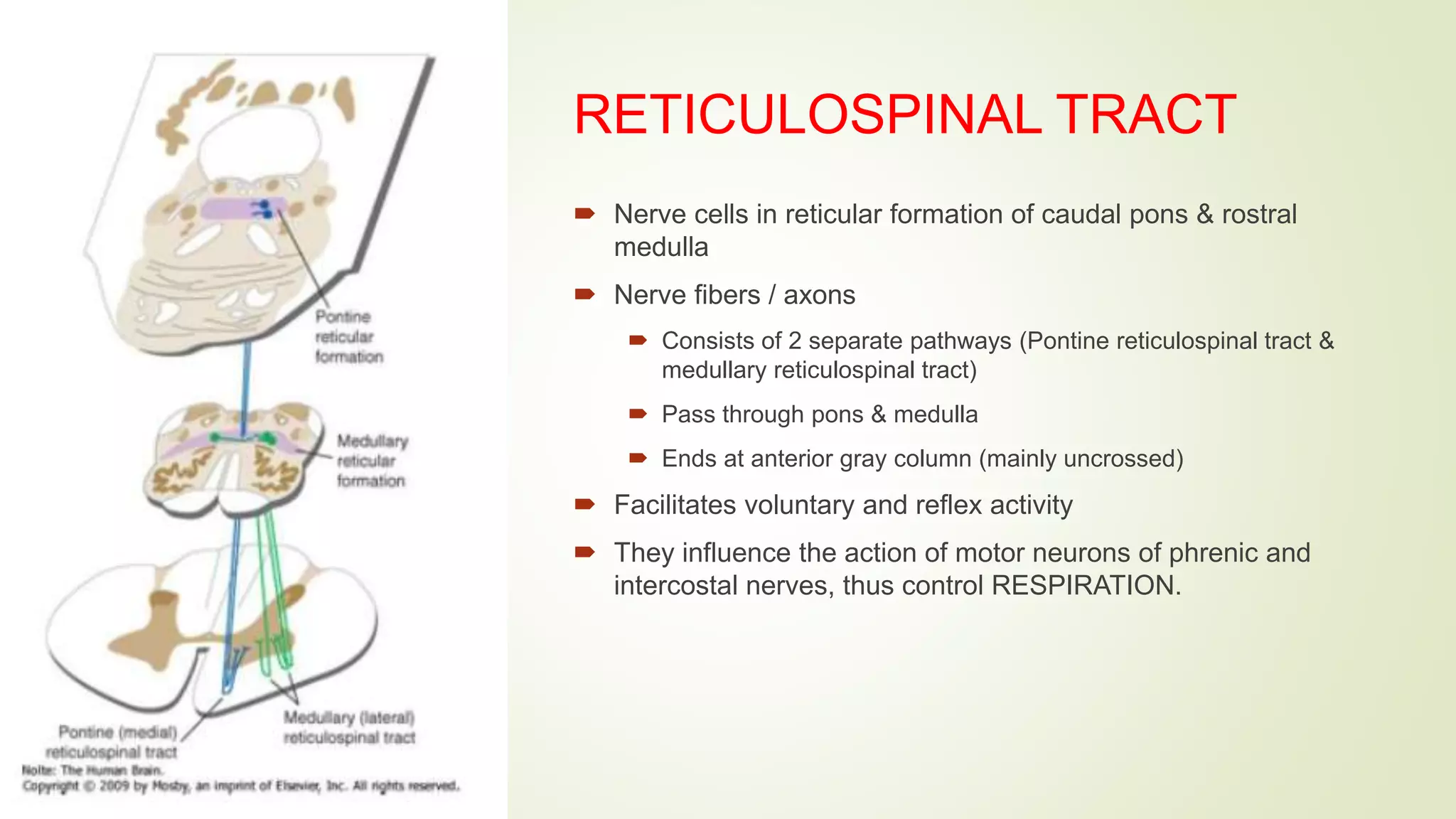
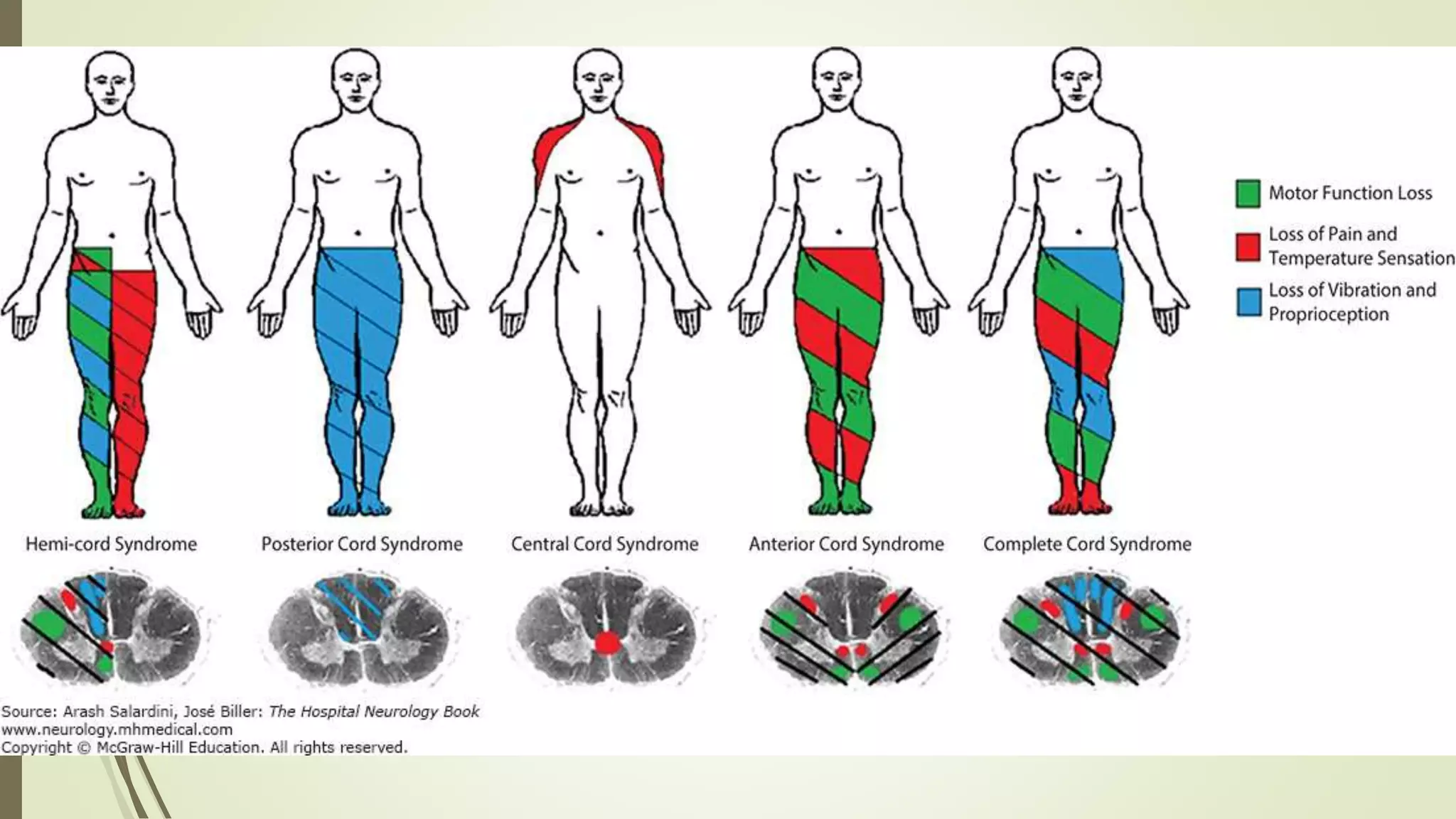
The document presents an overview of the neuroanatomy of the spinal cord, including its gross and cross-sectional anatomy, the surrounding meninges, and blood supply. It details the structure of spinal cord gray and white matter, the anatomy of ascending and descending tracts, and their clinical implications related to various injuries or diseases. Additionally, it discusses the arterial and venous supply to the spinal cord and its clinical relevance, particularly regarding ischemic conditions.