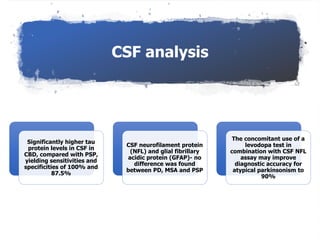
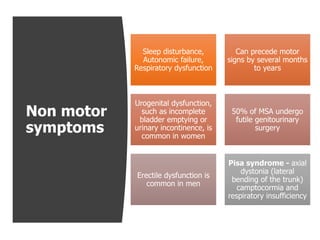
This document provides an overview of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP) and Multiple System Atrophy (MSA). It defines PSP and MSA as neurodegenerative diseases characterized by selective neuronal dysfunction and loss associated with pathologically altered proteins. The document discusses the pathophysiology, clinical features, subtypes, diagnostic criteria and investigations for PSP and MSA. Key points include that PSP is the second most common cause of parkinsonism after IPD, and involves characteristic tau protein deposits in the brain. Clinical features of PSP include early falls, vertical gaze palsy, speech and swallowing problems, and frontal cognitive deficits. The MDS criteria aim to improve diagnosis of early and variant






























































![MSA
Two main clinical phenotypes
• MSA parkinsonian type
[MSA-P]
• MSA cerebellar type [MSA-C]
• MSA pure autonomic [MSA-
A]
Median age of onset for MSA is 58 years of
age, which is younger than that of PSP and
CBD
Median survival is 9 years with incidence of
0.6 cases 1.00.000 population](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pspmsappt-190421121222/85/Progressive-supranuclear-palsy-and-multiple-system-atrophy-64-320.jpg)





















![Autonomic Function
Testing
• Tilt-table testing, 24-hour ambulatory blood
pressure and heart rate monitoring
• Supine blood pressure with heart rate, then
standing blood pressure and heart rate after 3
minutes
• Sweat testing (eg, quantitative sudomotor
axon reflex test [QSART]) and gastric emptying
study (for gastroparesis)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pspmsappt-190421121222/85/Progressive-supranuclear-palsy-and-multiple-system-atrophy-87-320.jpg)







