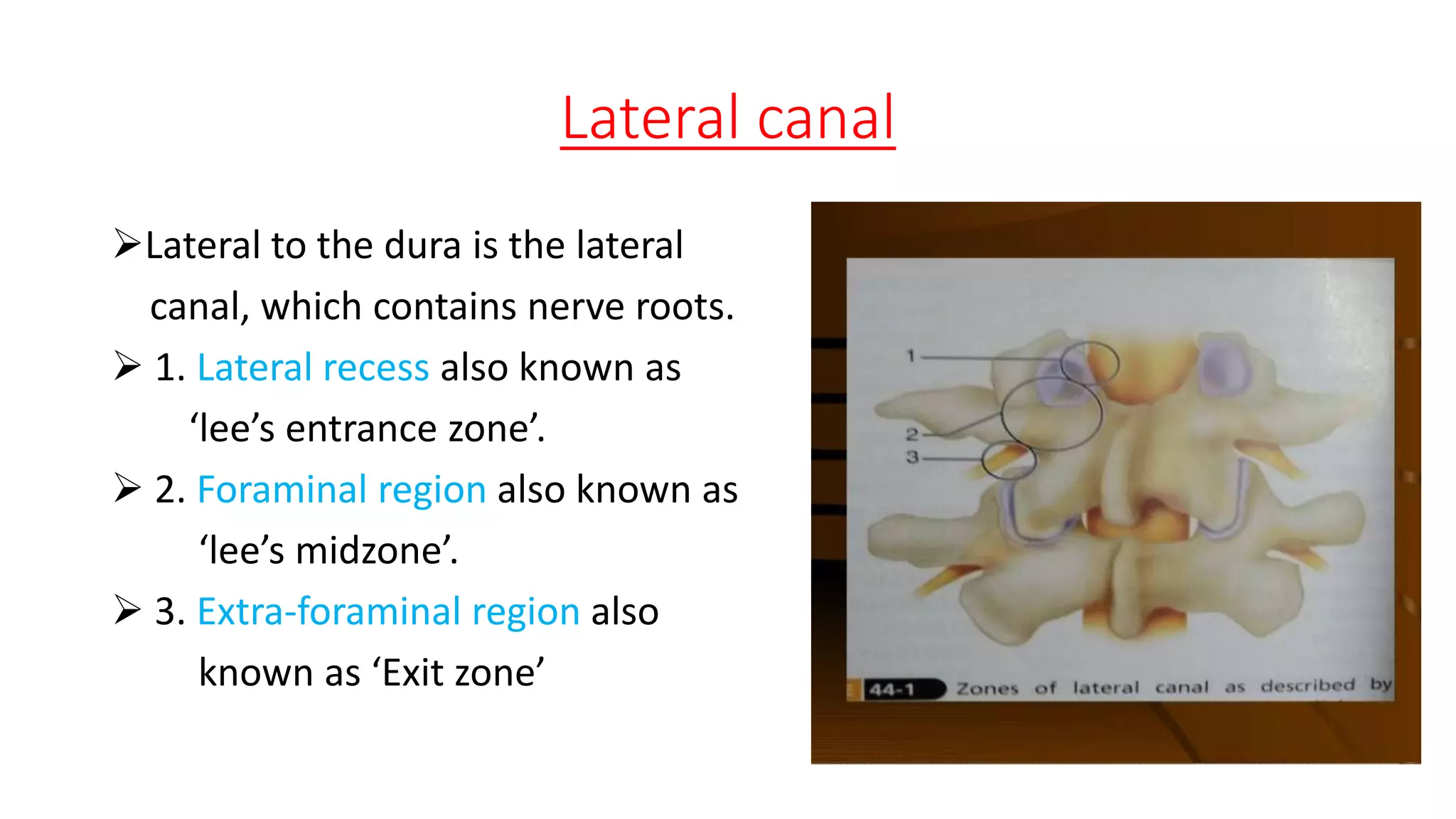
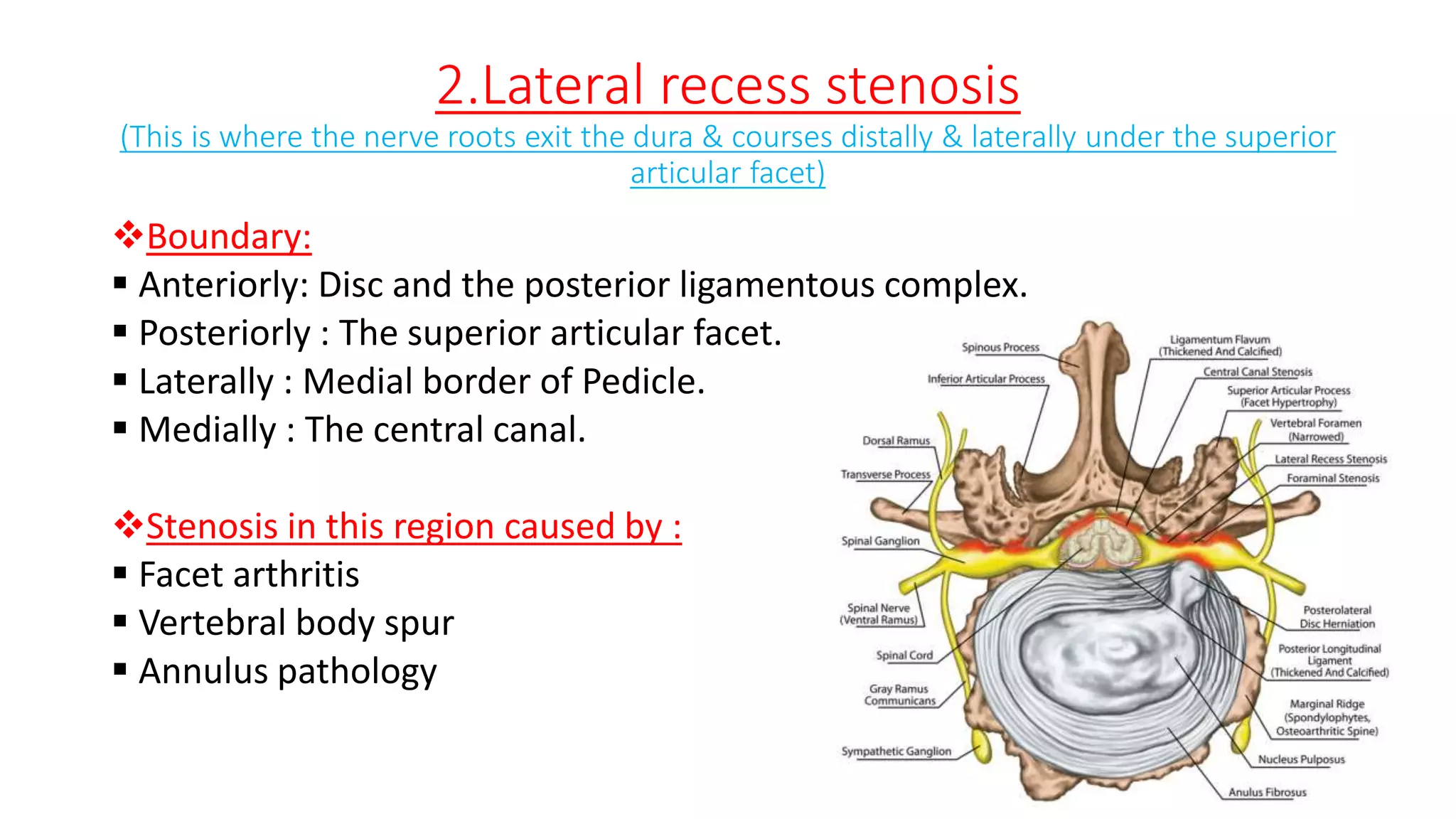
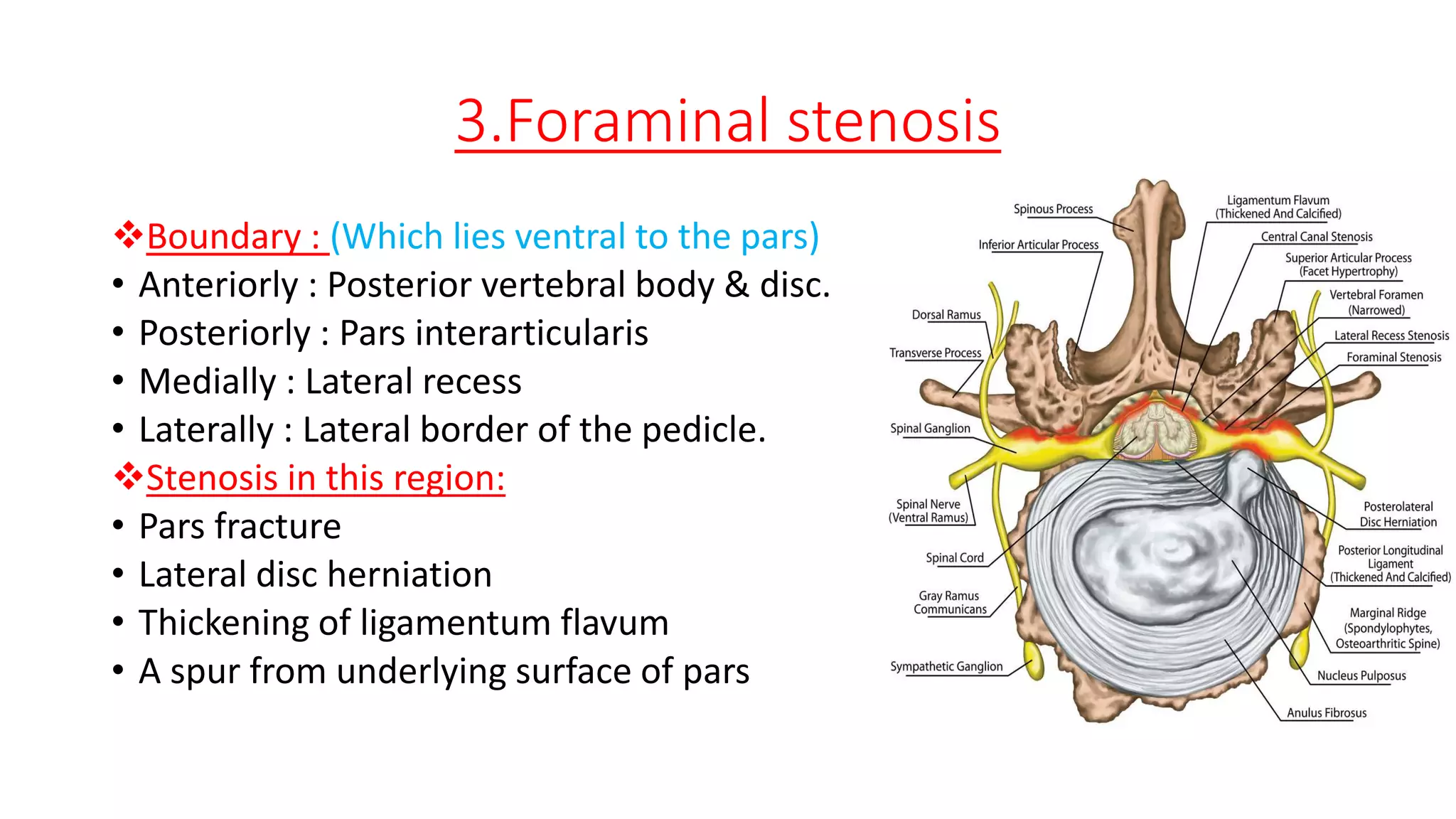
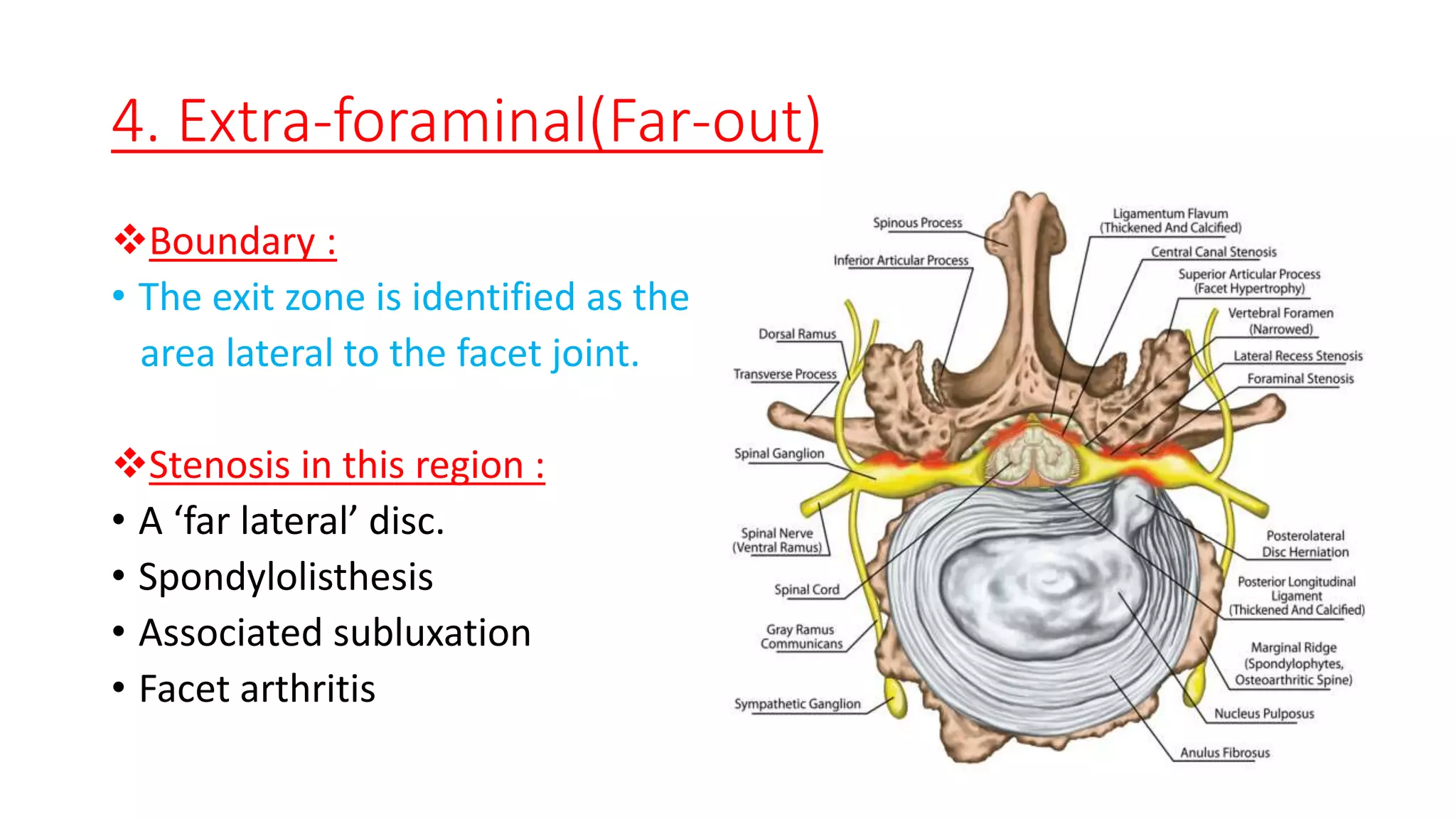
The document discusses spinal canal stenosis, including:
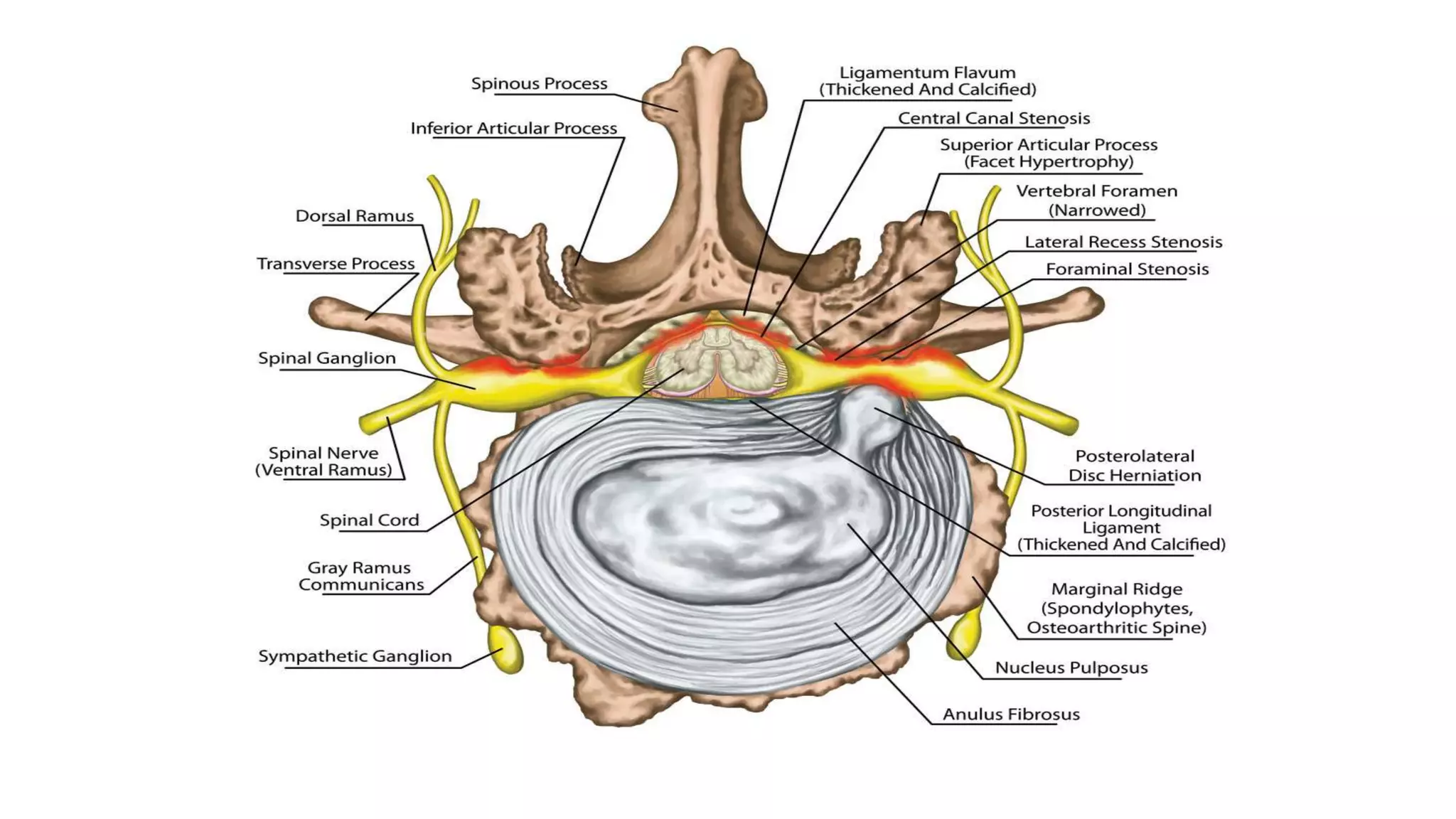
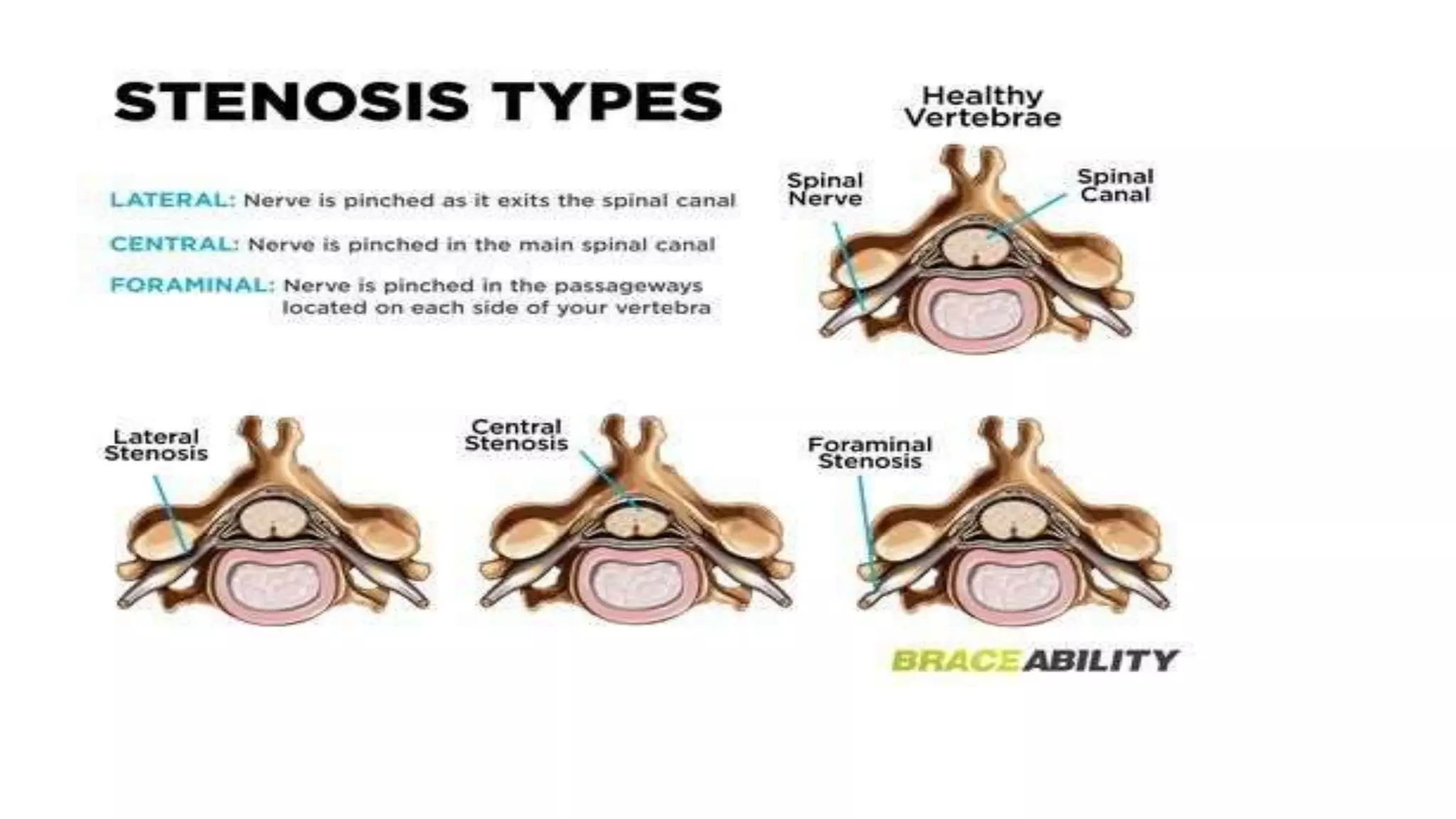
1. It describes spinal canal stenosis as the narrowing of the spinal canal and compression of the spinal cord and nerve roots, most commonly occurring in the lumbar vertebrae.
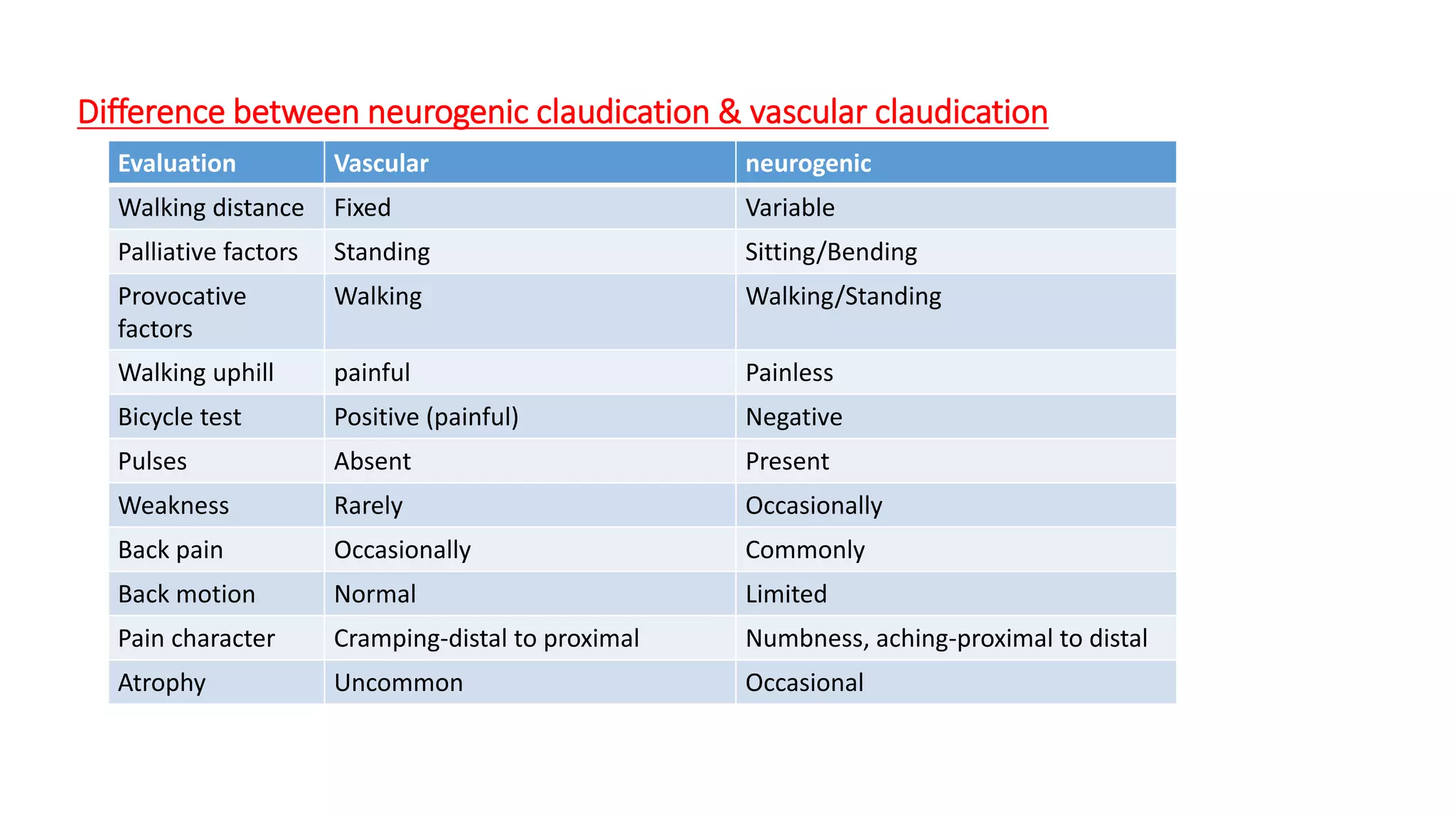
2. Symptoms include back pain radiating into the legs, numbness, and weakness that is relieved by bending forward and made worse by standing upright or walking.
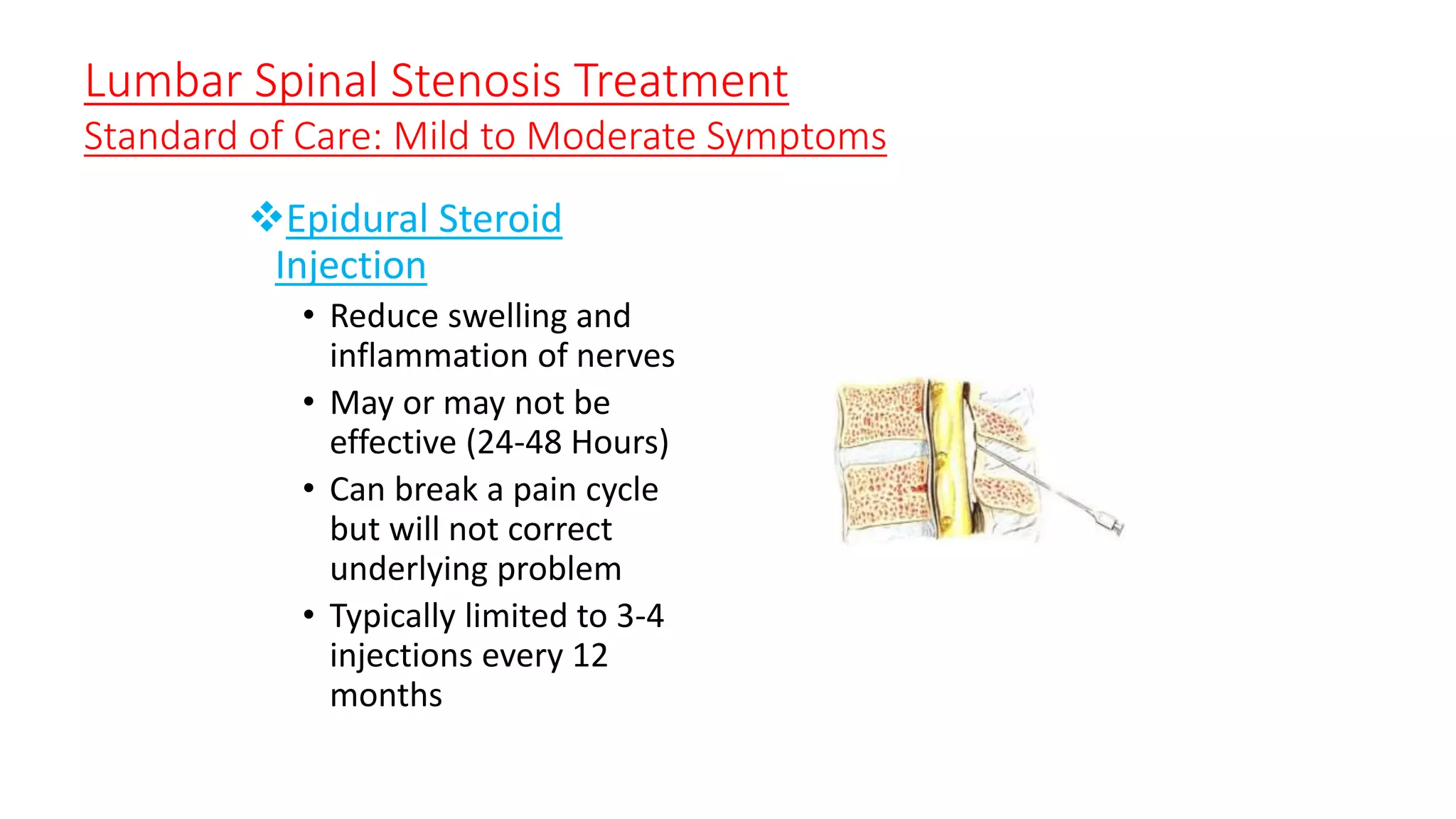
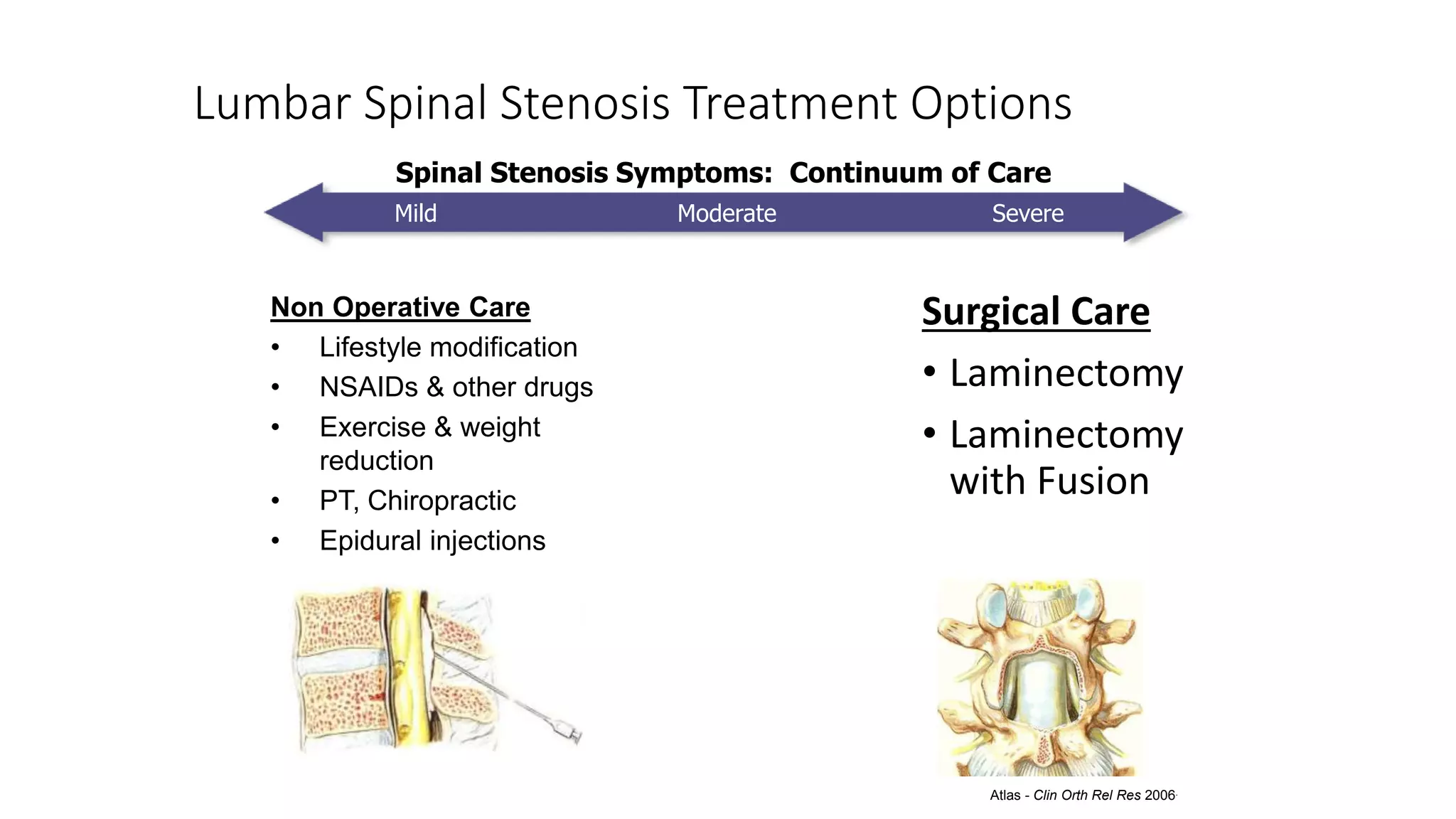
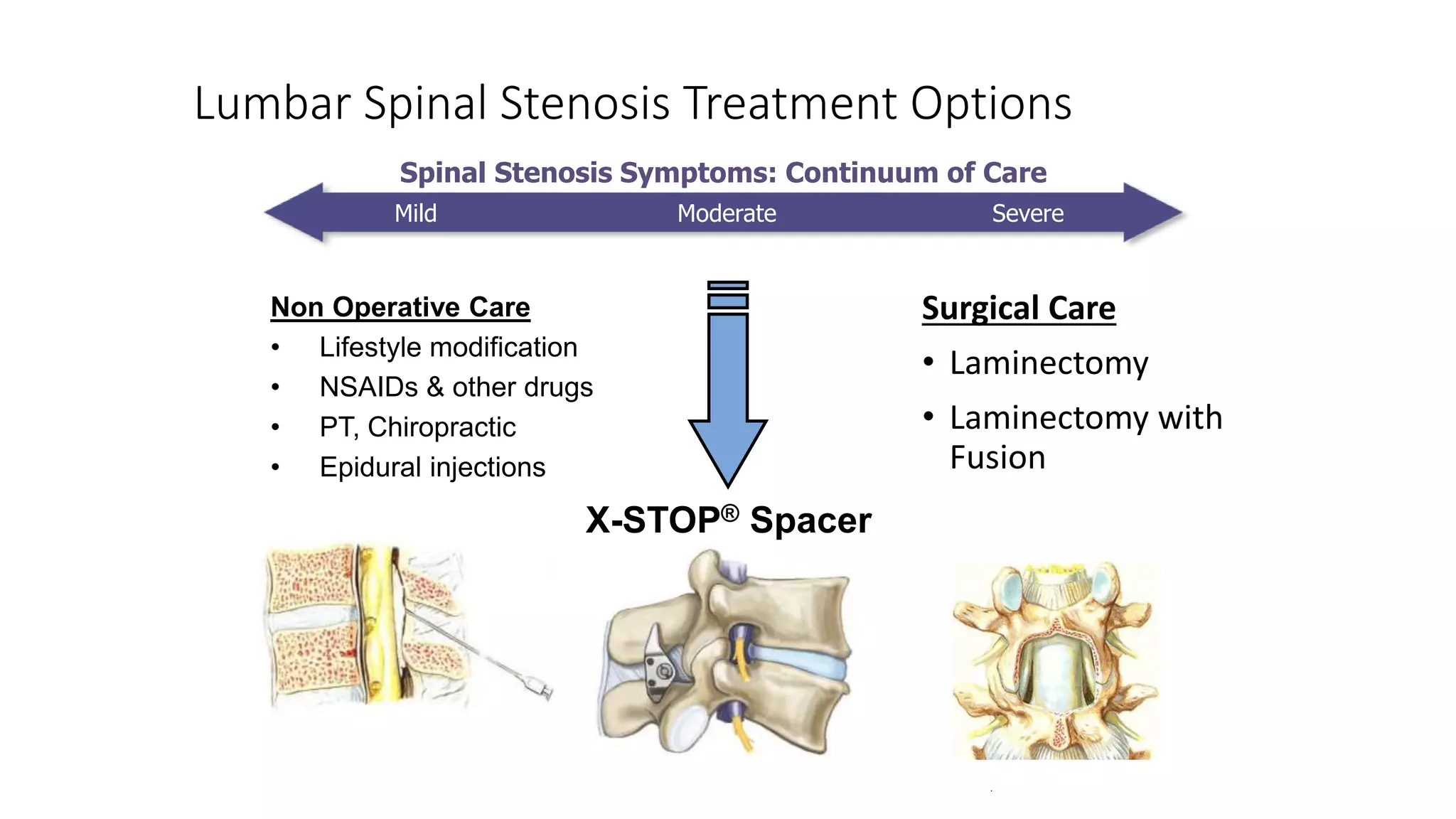
3. Treatment options range from non-surgical approaches like medication, physical therapy, and epidural injections for mild-to-moderate cases to surgical decompression like laminectomy or the X-STOP implant for more severe cases.