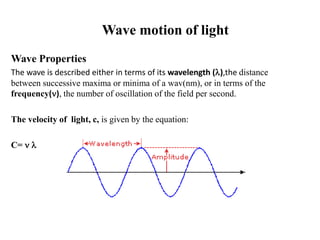
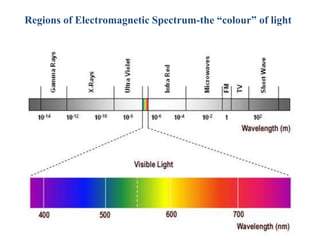
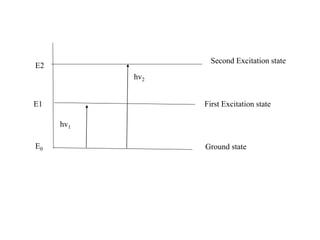
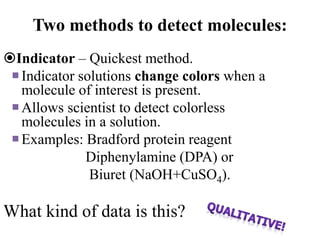
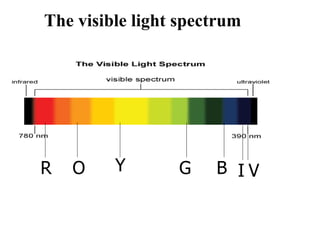
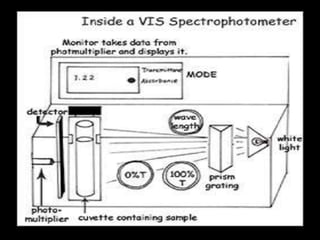
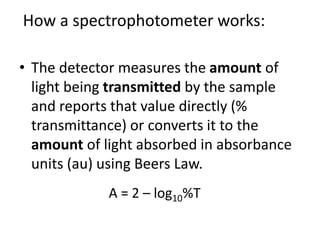
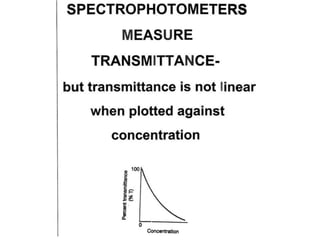
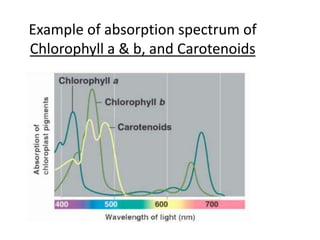
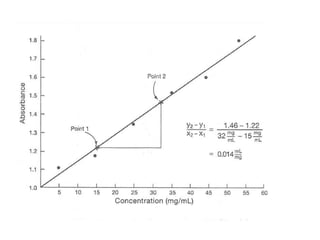
The document provides a detailed overview of spectrophotometry and its applications in measuring solute concentration in solutions by analyzing light absorption. It discusses the properties of electromagnetic radiation, the interaction of light with matter, different types of spectrophotometers, and the methods for detecting molecules. Additionally, it highlights the significance of constructing standard curves for determining unknown concentrations based on absorbance data.