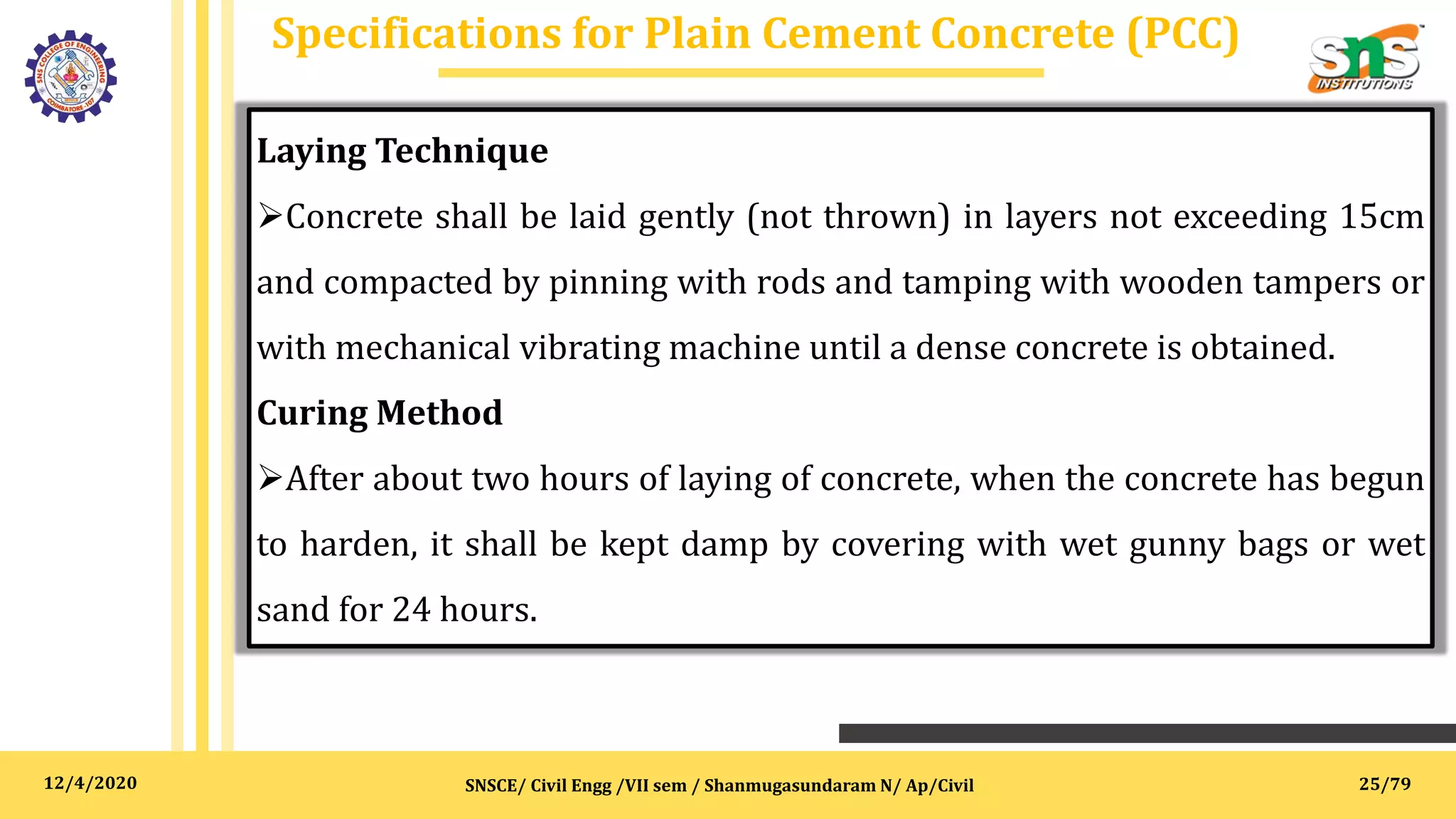
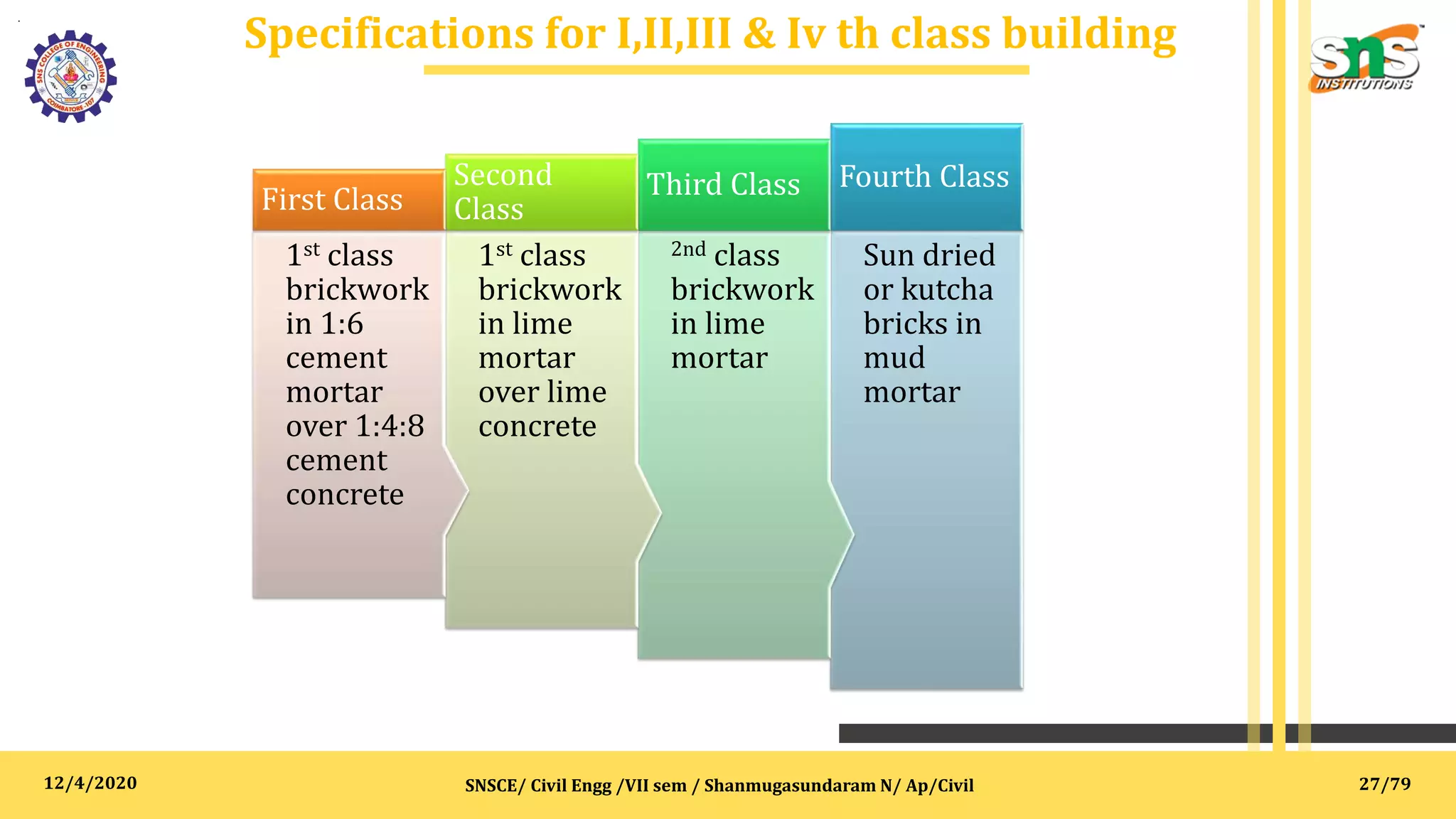
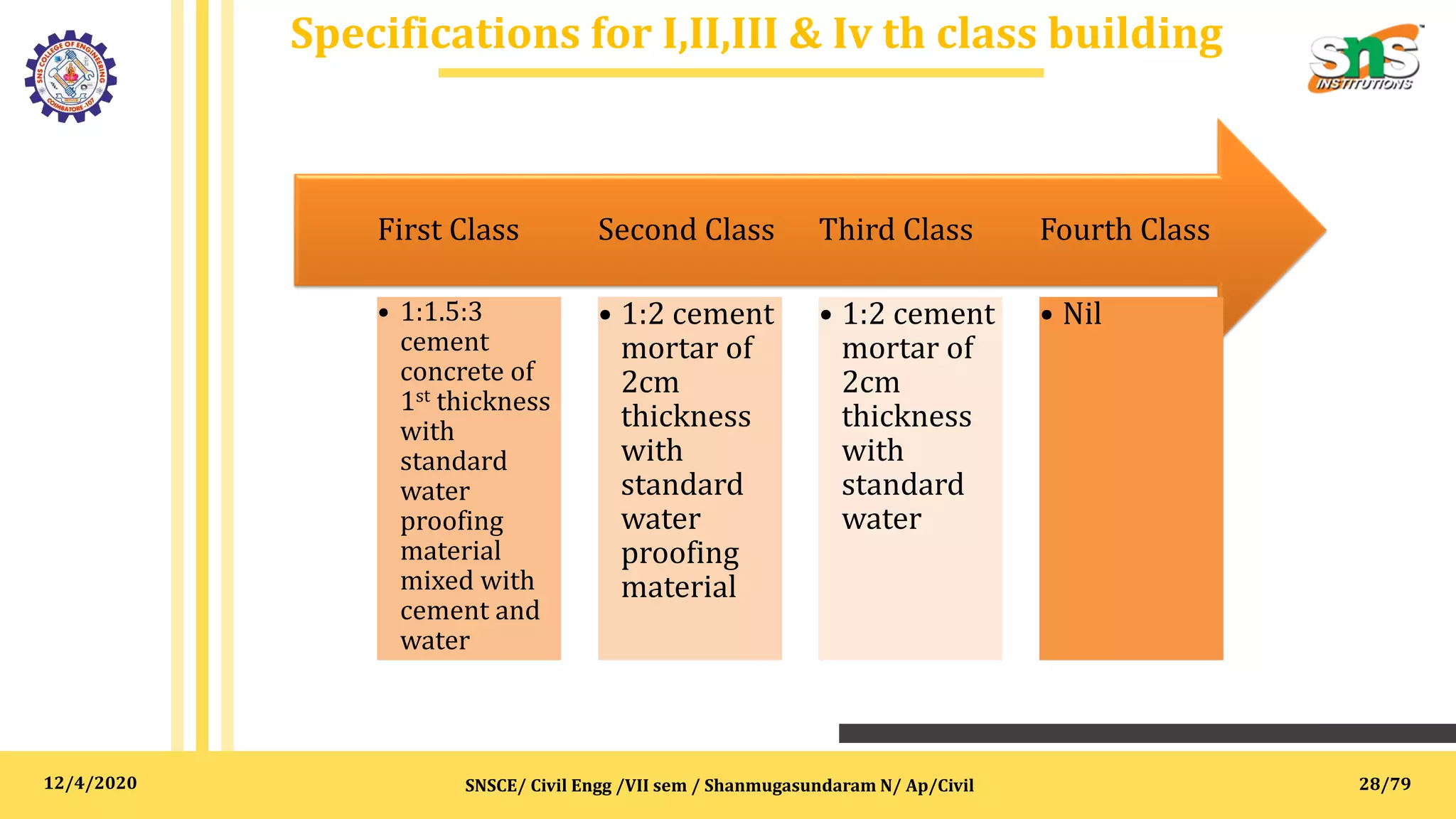
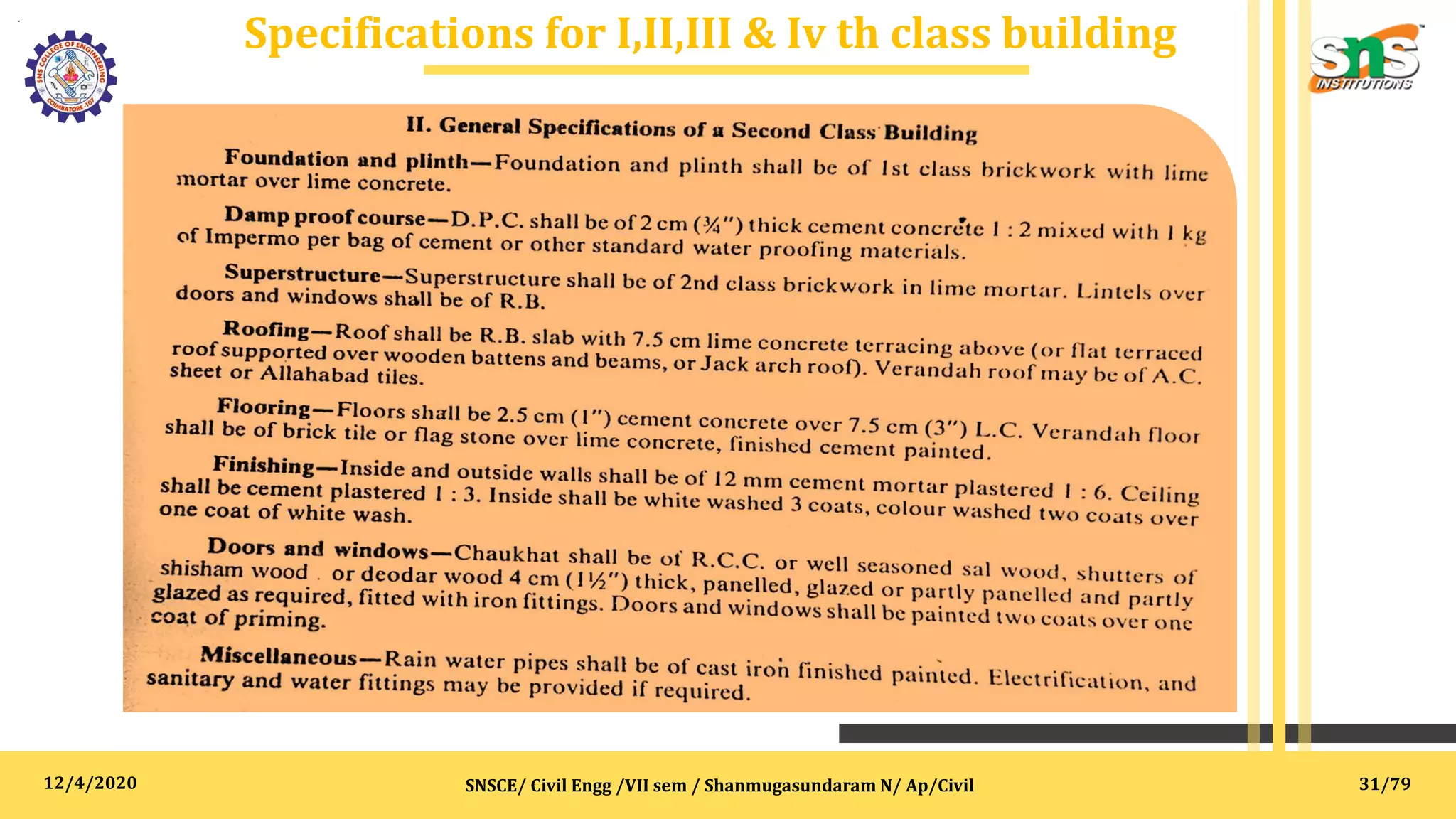
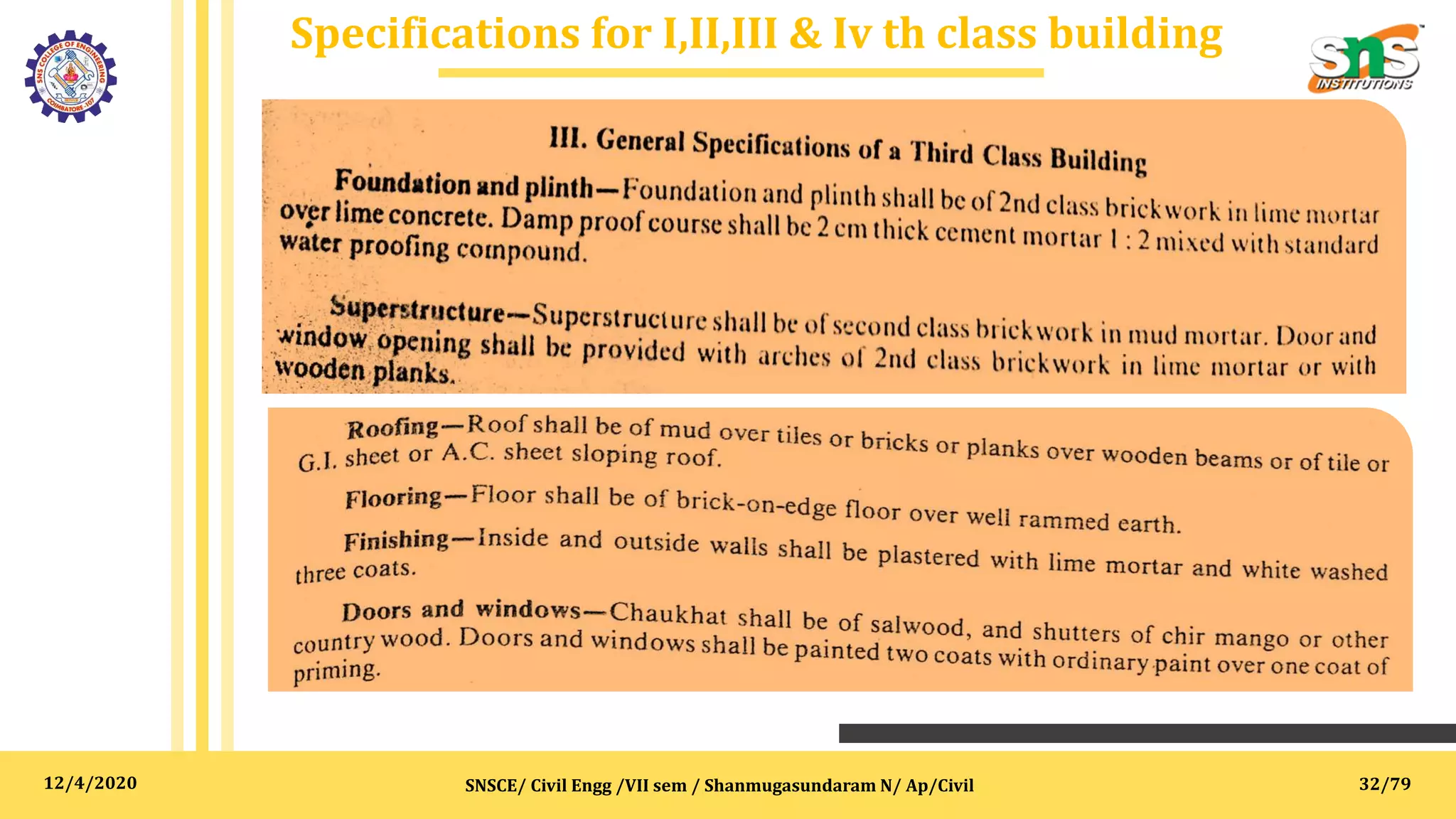
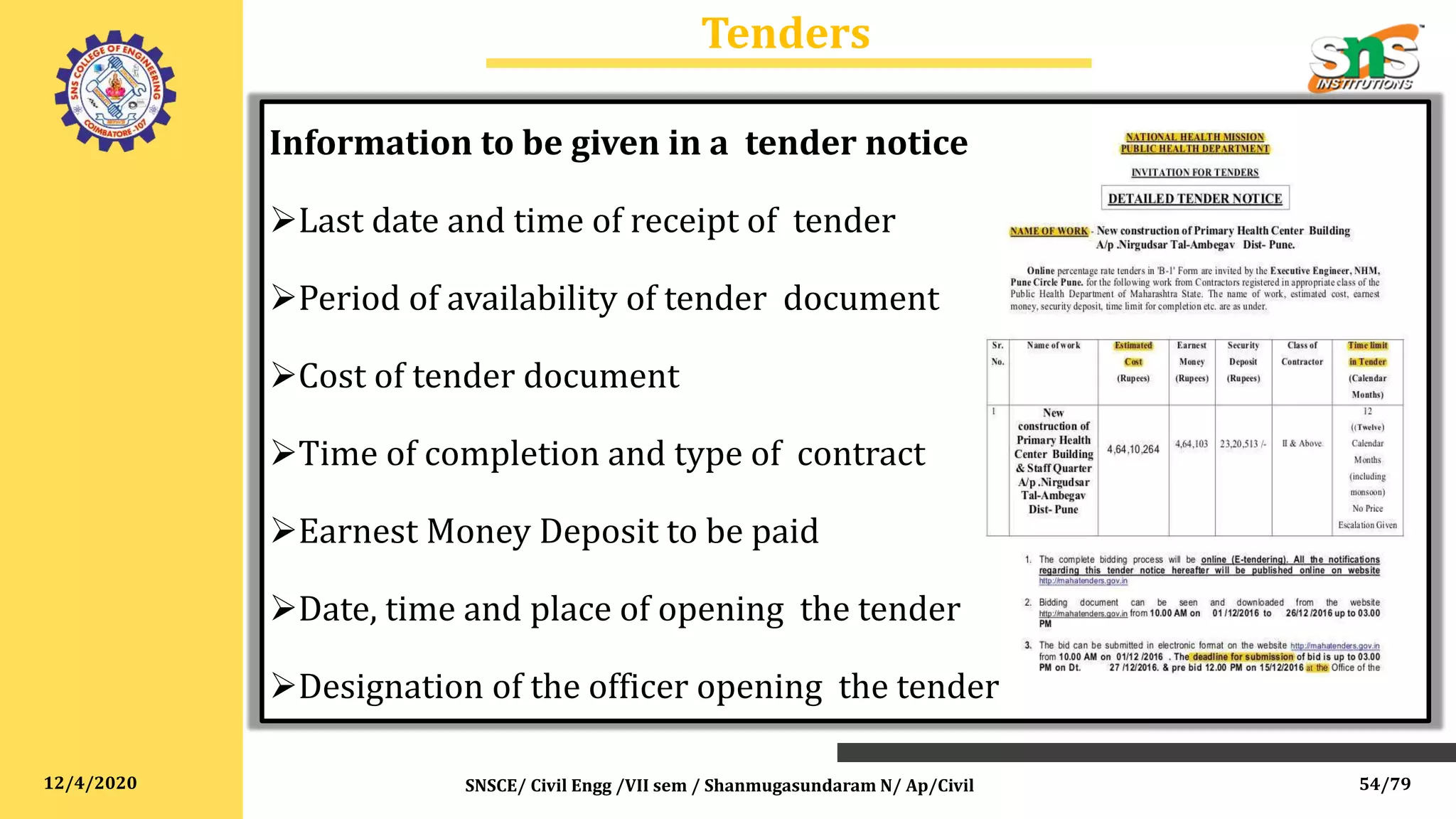
The document outlines specifications, reports, and tender processes relevant to civil engineering, focusing particularly on estimation and costing for construction projects. It details the importance of clear specifications in determining work quality, material requirements, and project costs, along with various materials and construction techniques such as RCC, brick masonry, and plain cement concrete. Furthermore, it includes guidance on drafting tender notices and the necessity of adhering to specifications for project execution and contractor compensation.