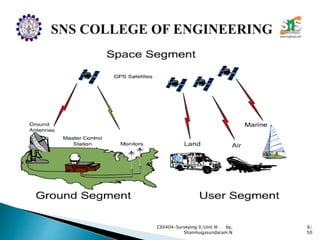
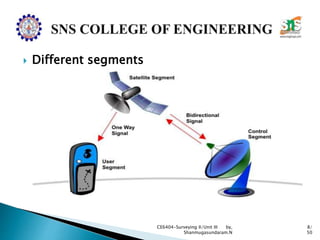
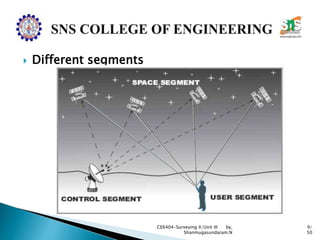
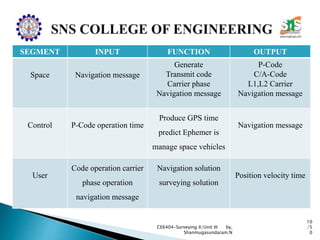
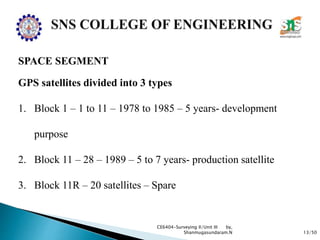
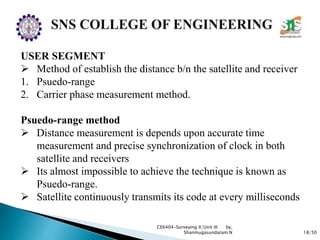
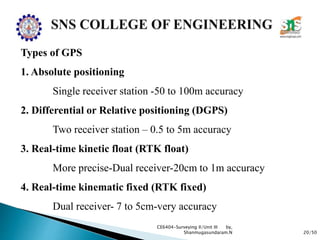
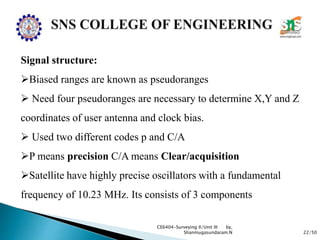
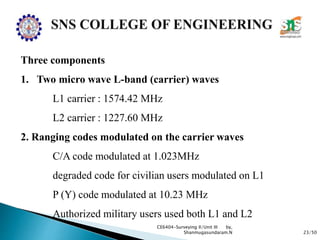
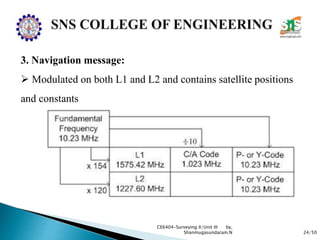
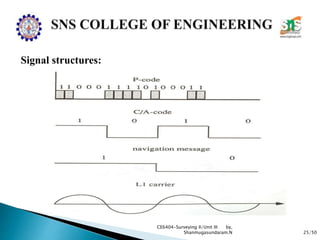
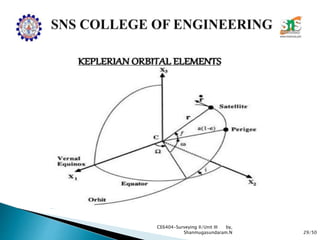
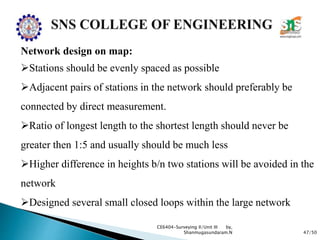
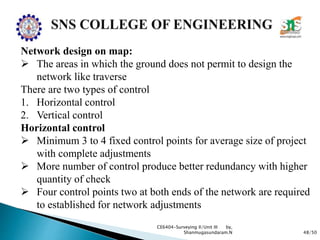
The document discusses the Global Positioning System (GPS). It describes how GPS is a worldwide radio navigation system formed from 24 satellites and their ground stations. It explains the three main segments of GPS: the space segment consisting of the GPS satellites, the control segment which monitors and controls the satellites, and the user segment comprising GPS receivers. It provides details on topics like satellite orbits, signal structure, orbit determination, and different types of GPS receivers.