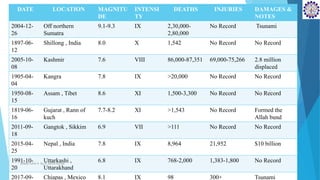
1) The document summarizes 10 major earthquakes that have occurred in India based on their magnitude, intensity, deaths, and damages. The deadliest earthquake struck off the coast of Sumatra in 2004 with a magnitude of 9.1-9.3 resulting in 230,000 to 280,000 deaths.
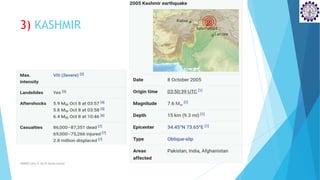
2) The Shillong earthquake of 1897 in Meghalaya had a magnitude of 8.0 and caused 1,542 deaths. The Kashmir earthquake of 2005 had a magnitude of 7.6, causing 86,000-87,351 deaths and displacing 2.8 million people.
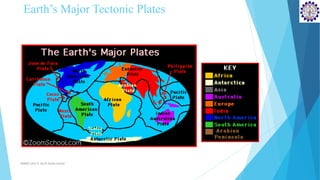
3) Major earthquakes are often caused by the collision of the Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates