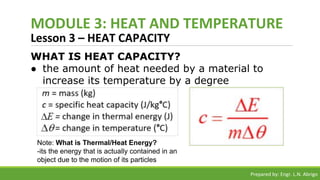
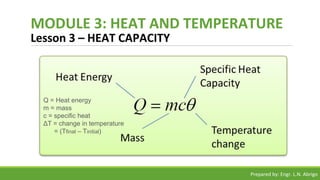
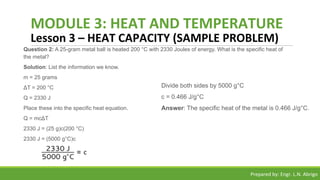
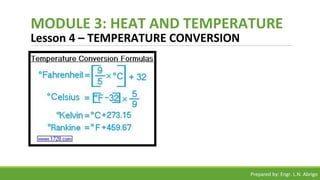
The document provides a comprehensive overview of heat and temperature for grade 8 science, explaining the concepts, measurements, and calculations related to thermal energy. Key topics include the difference between heat and temperature, heat capacity, and example problems illustrating specific heat calculations. Prepared by Engr. L.N. Abrigo, the module serves as an educational resource for understanding fundamental principles of heat transfer and temperature dynamics.