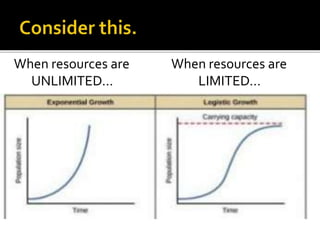
This document discusses biodiversity and population ecology. It defines biodiversity as the variety of life forms in an ecosystem. Organisms have economic, ecological, and aesthetic value. They are important for ecosystem balance and provide goods like food, medicine, clothing, and energy. The document also discusses population size, birth and death rates, carrying capacity, and factors that influence populations like resources, natural disasters, competition, predation, and diseases. It notes that the Philippines has high biodiversity but it is threatened by habitat loss and overexploitation of resources.