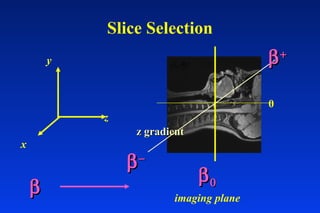
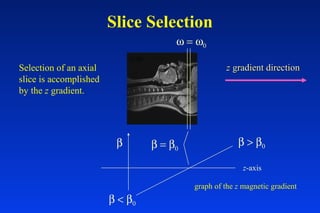
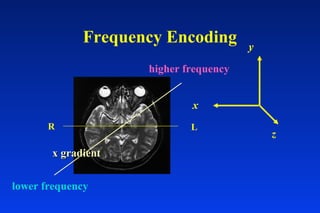
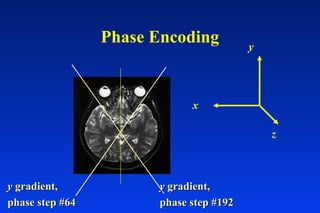
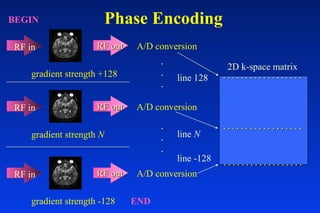
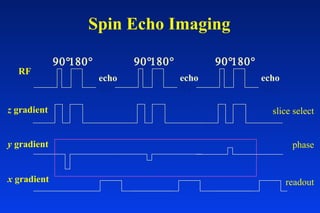
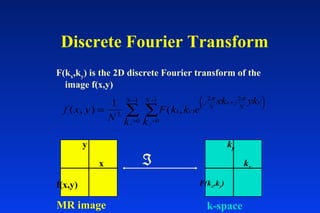
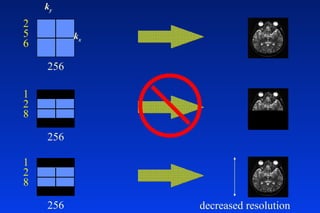
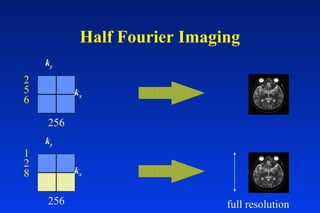
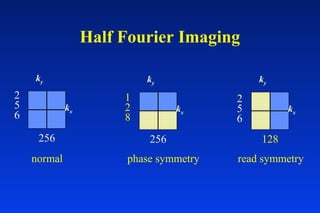
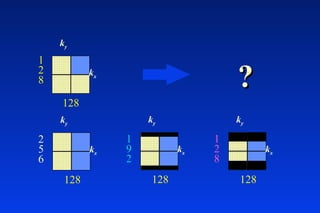
1. MRI uses spatial encoding gradients and radiofrequency pulses to selectively excite slices of tissue and encode spatial information in the MRI signal. 2. Frequency encoding gradients encode left-right spatial information, while phase encoding gradients are applied in the orthogonal direction to fully spatially encode each image slice. 3. Fourier transformation is used to reconstruct images from the spatially encoded MRI data.