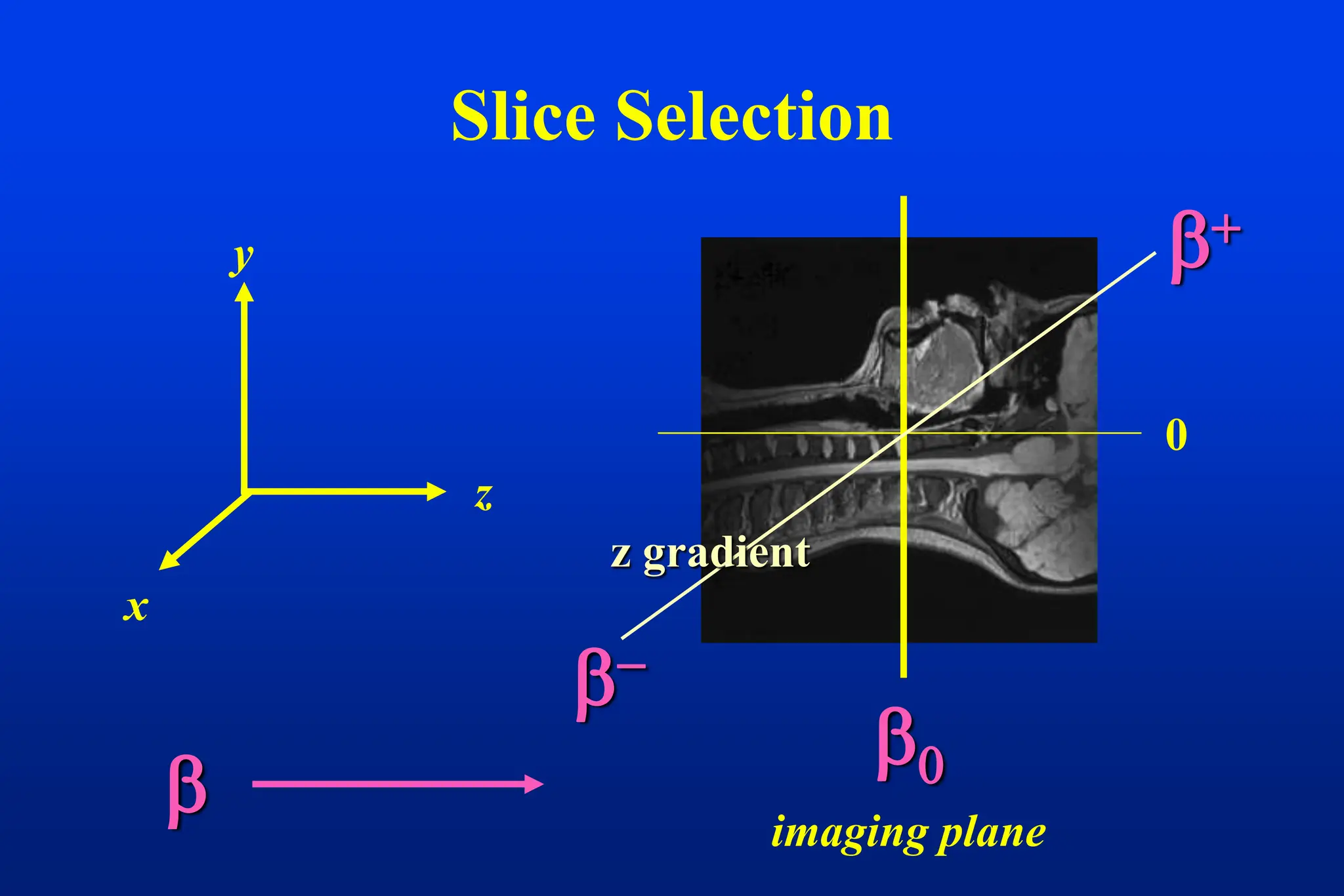
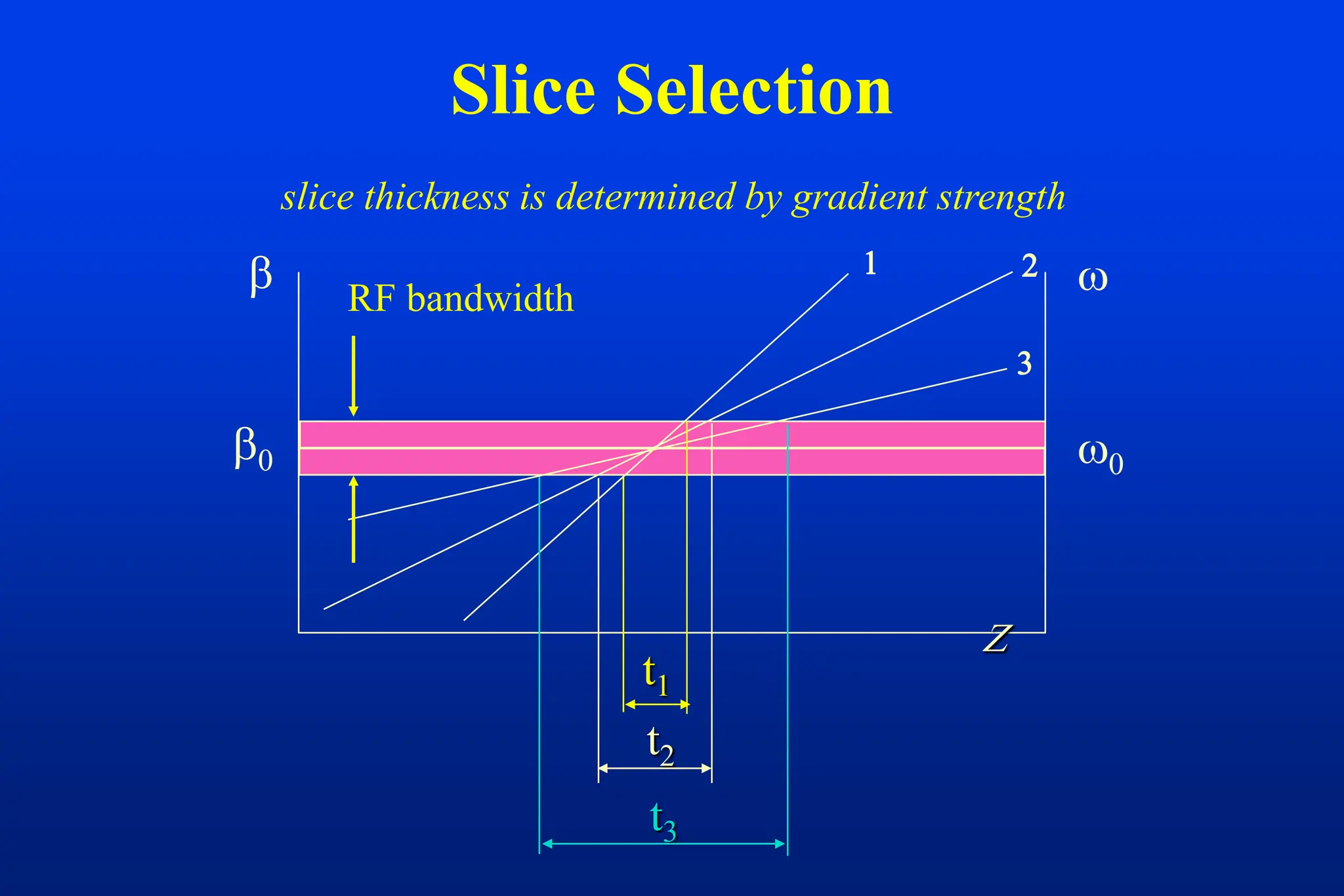
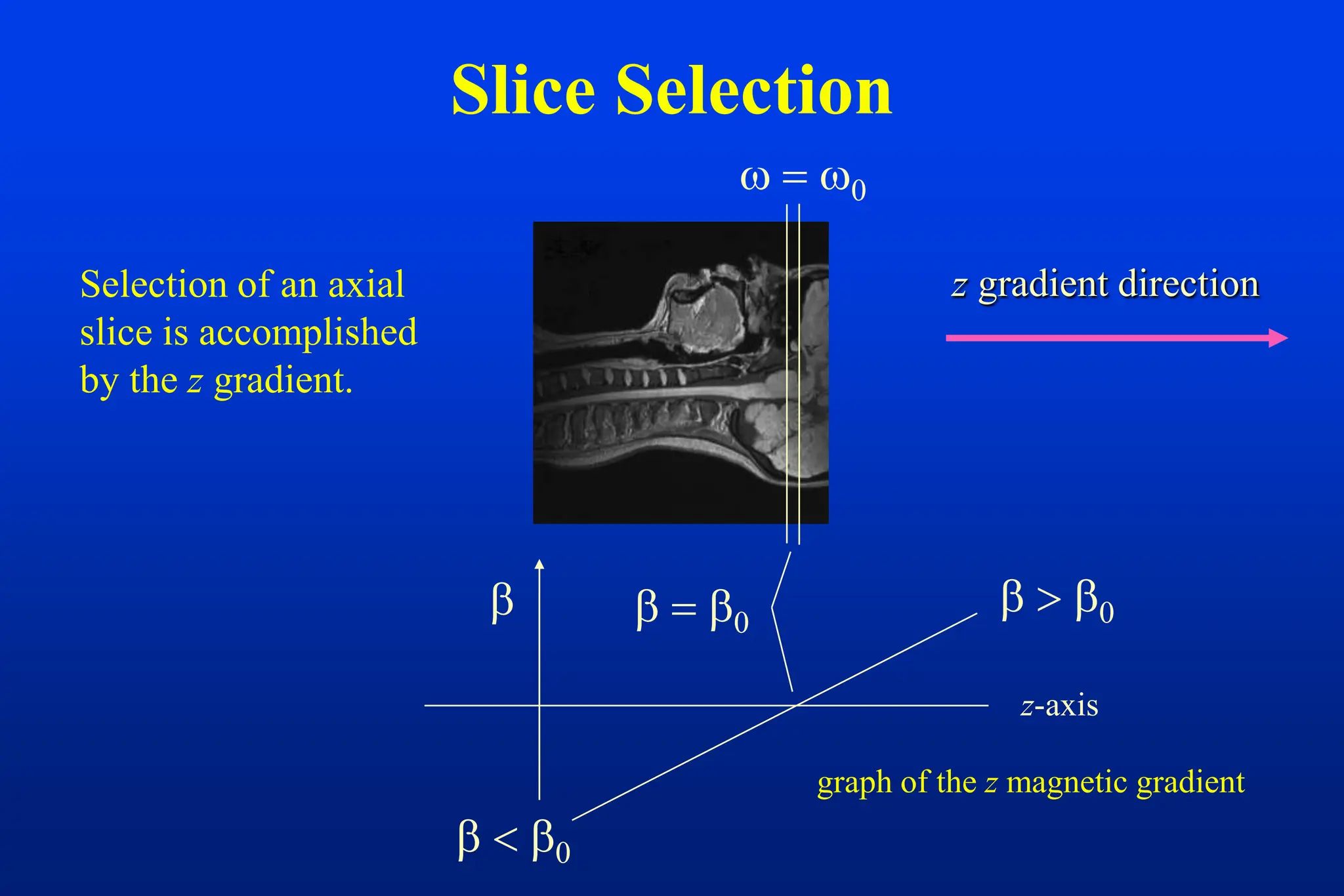
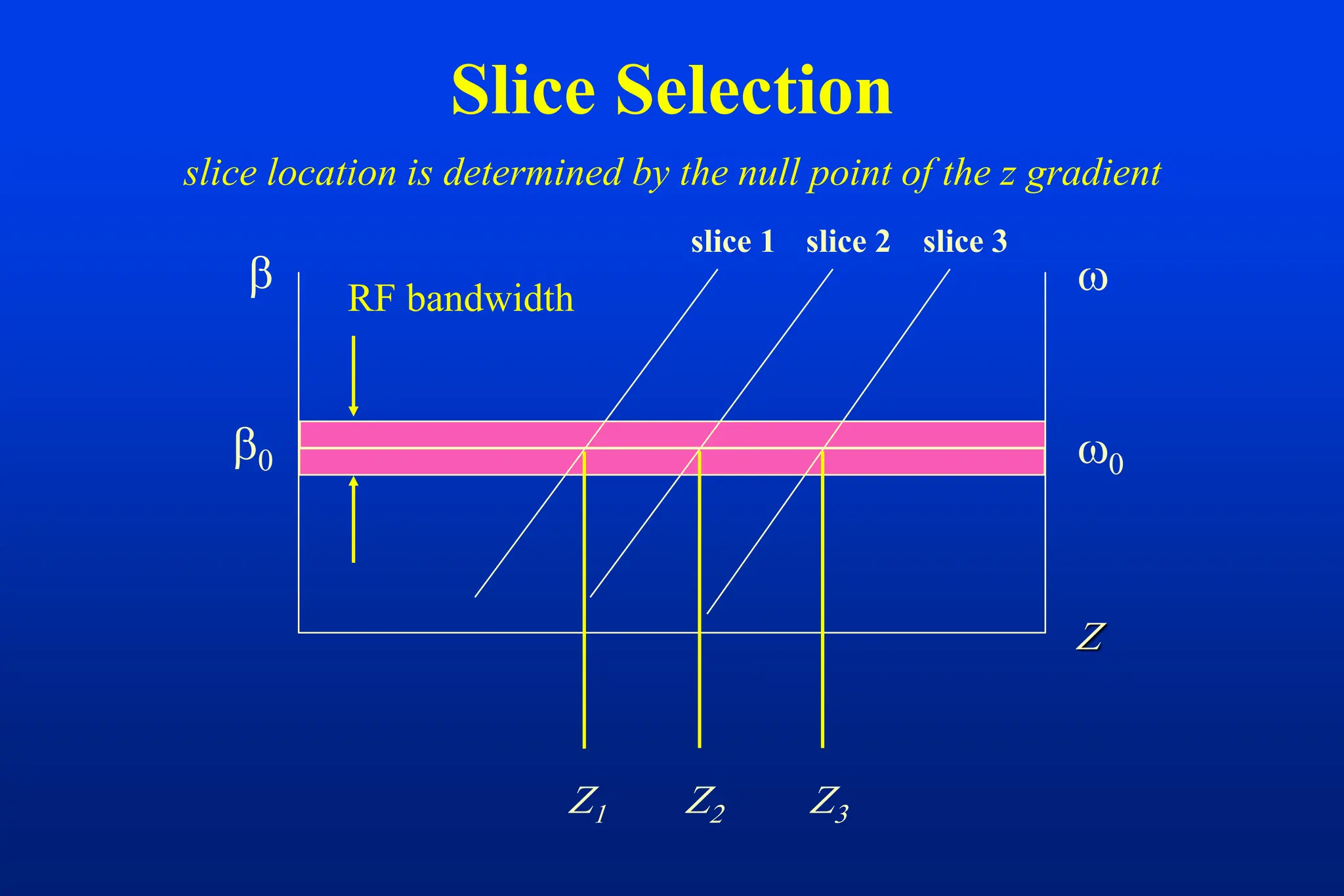
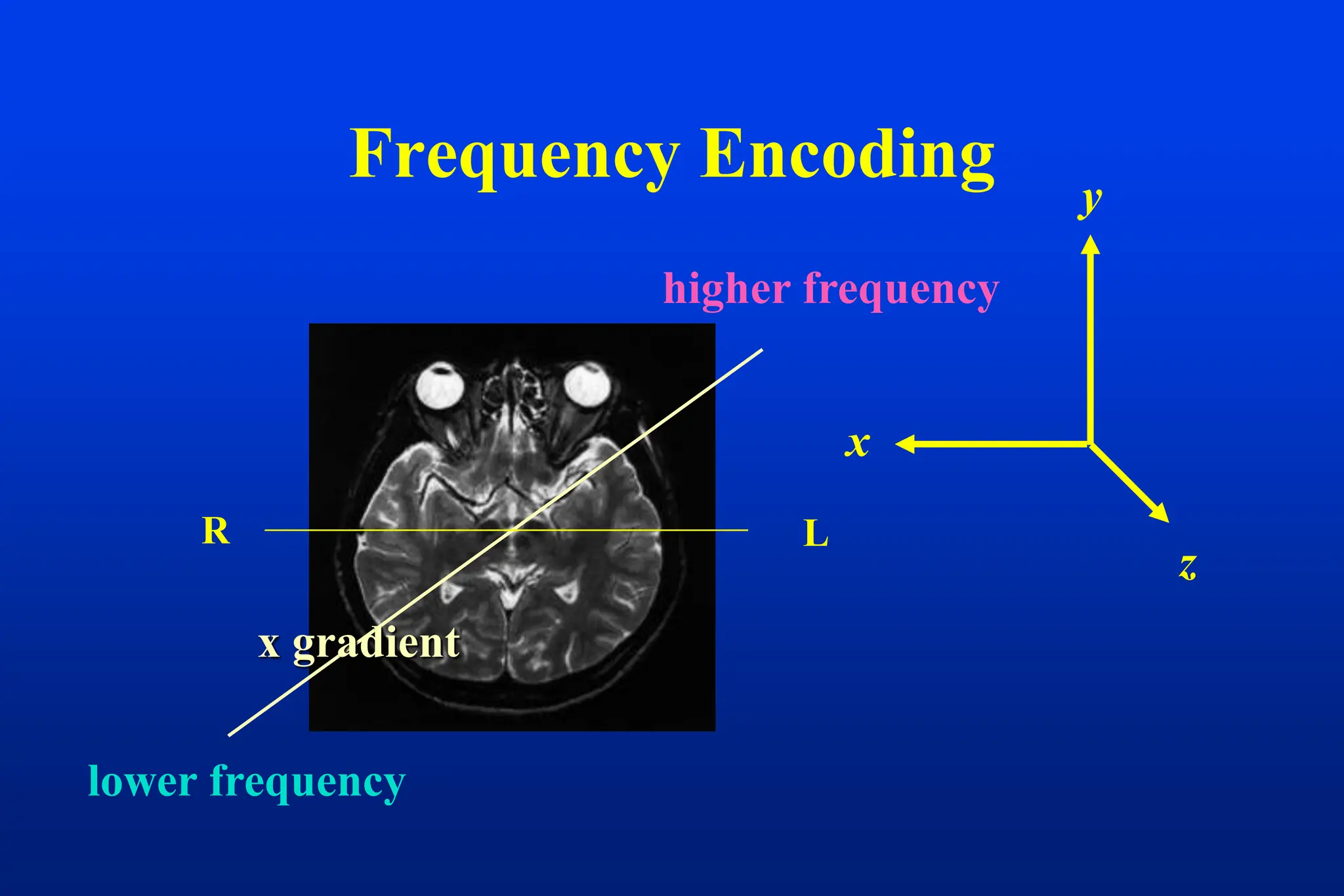
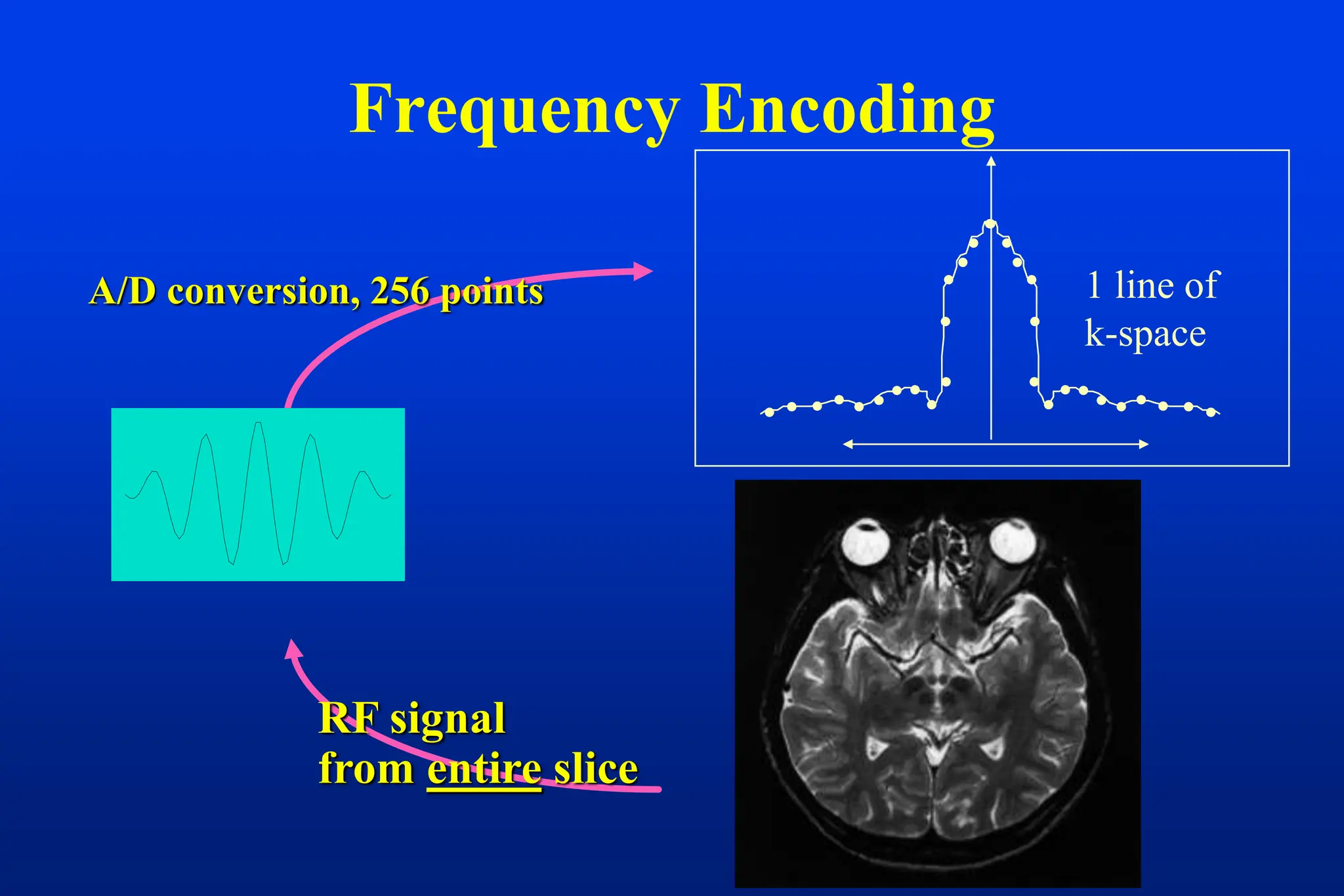
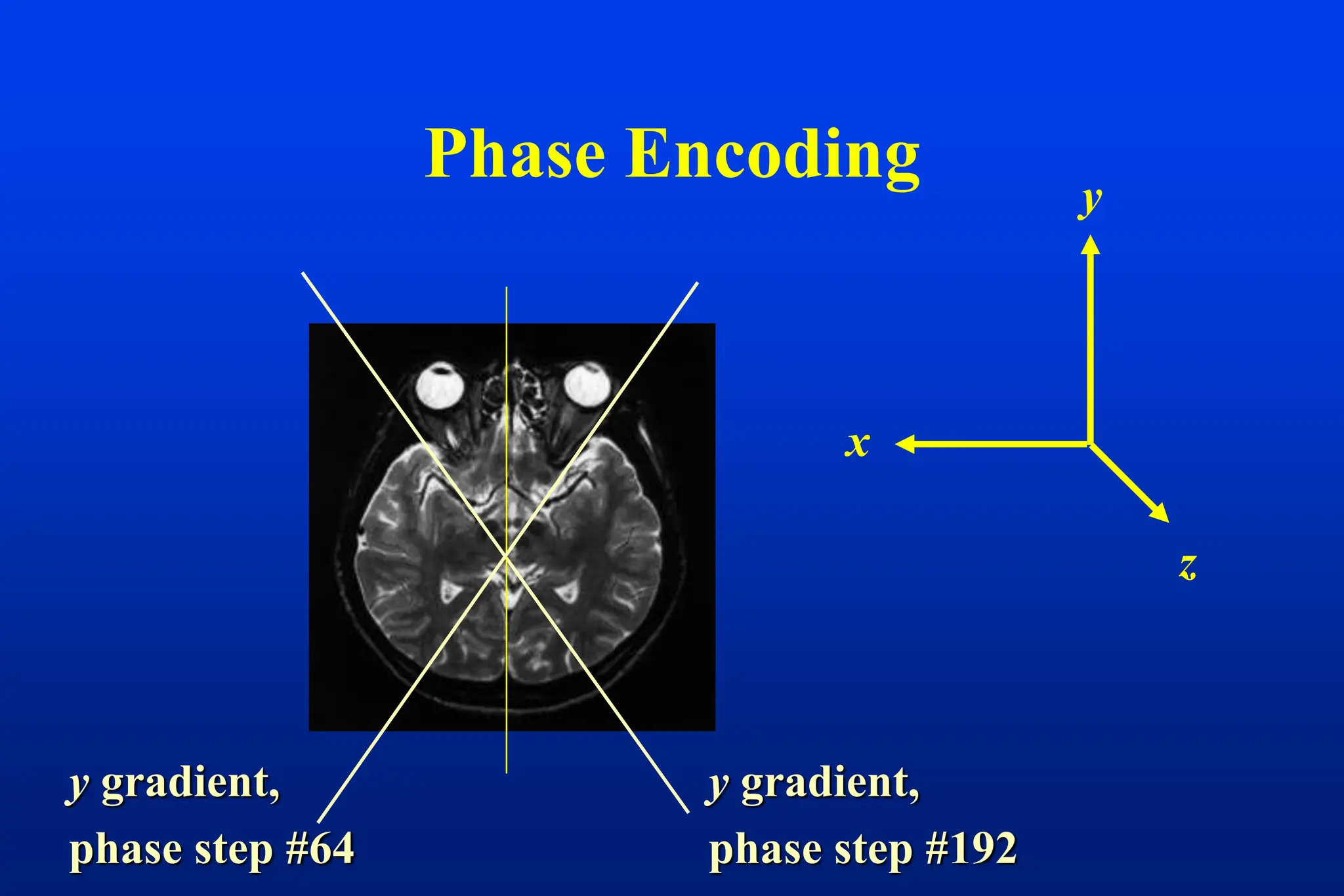
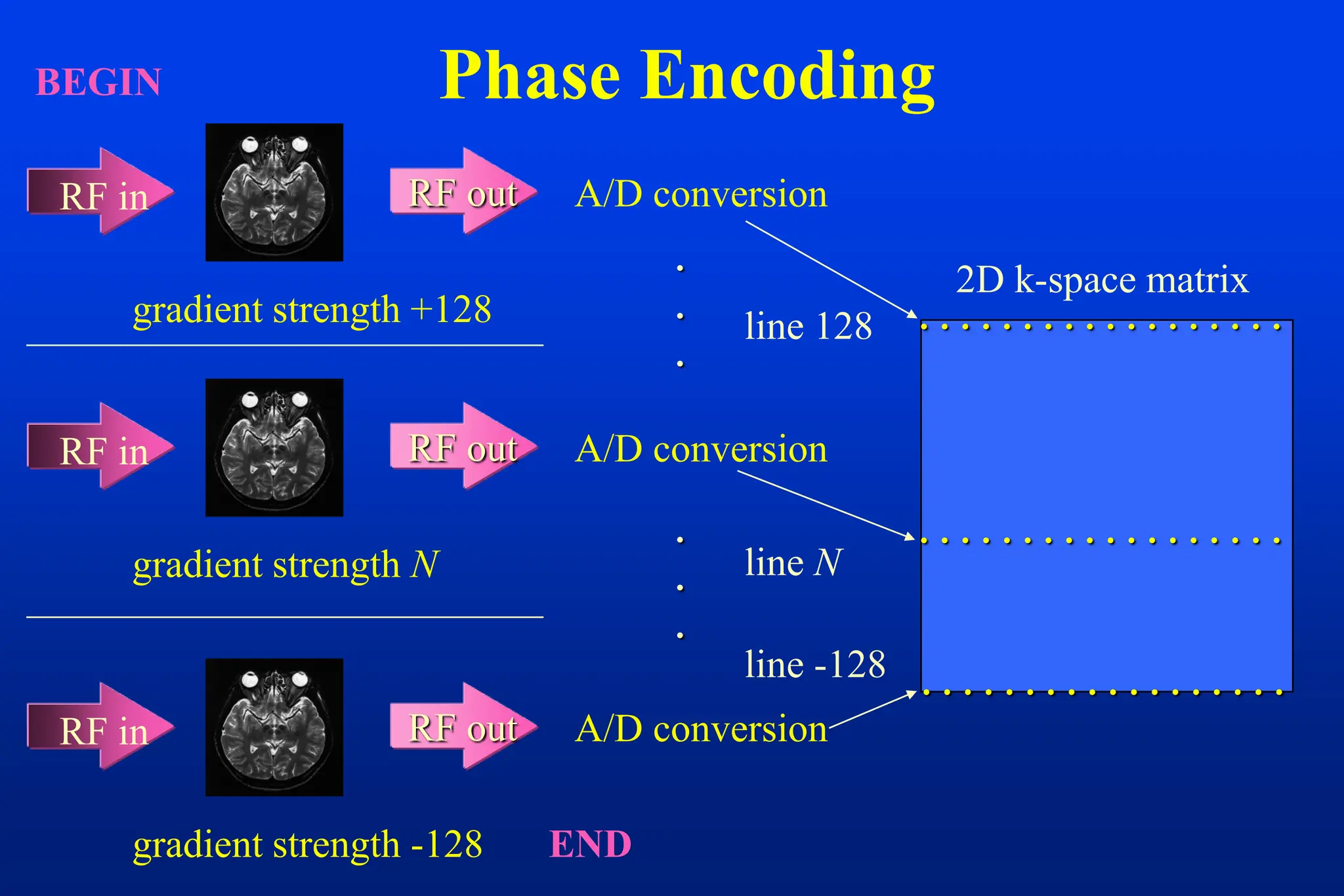
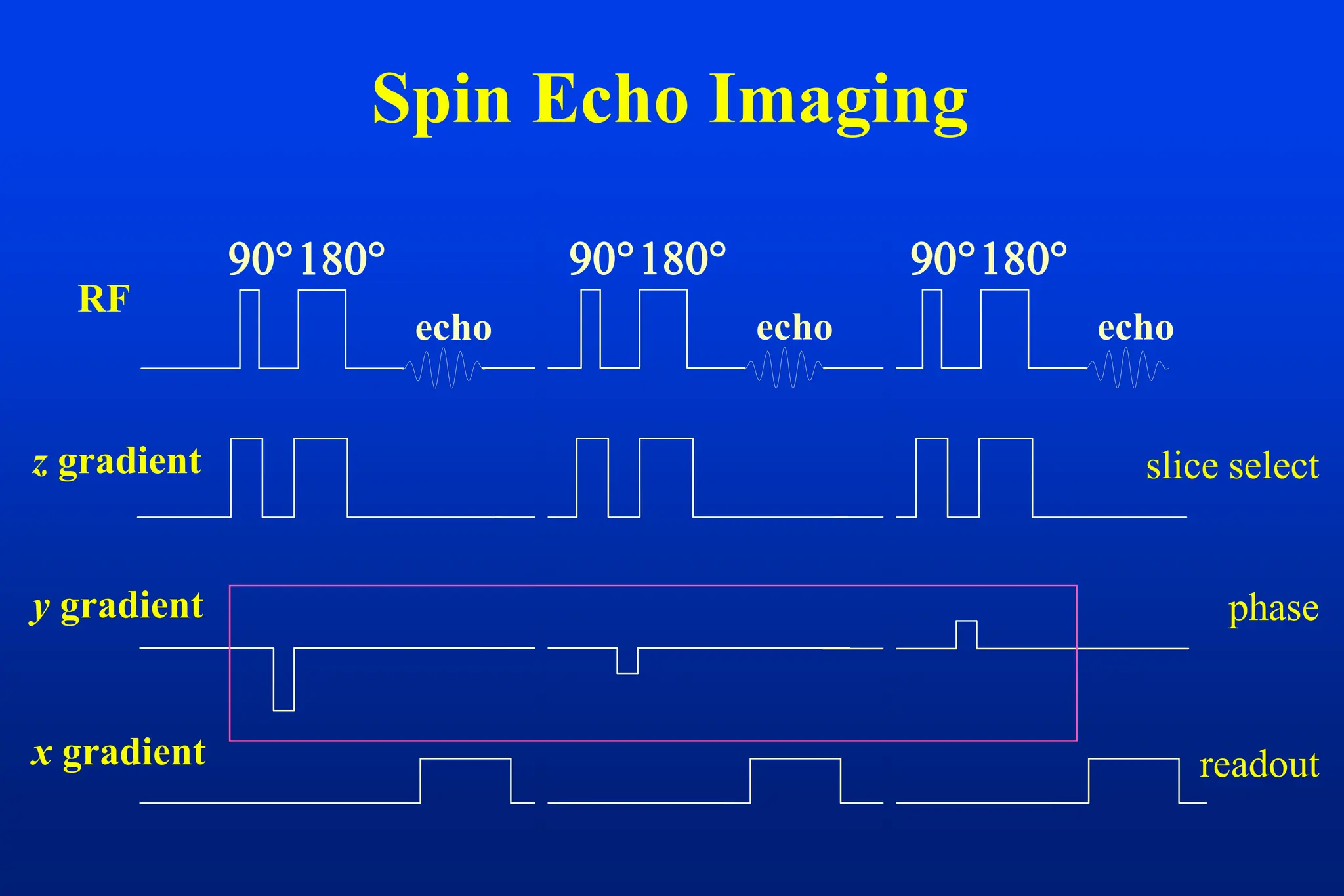
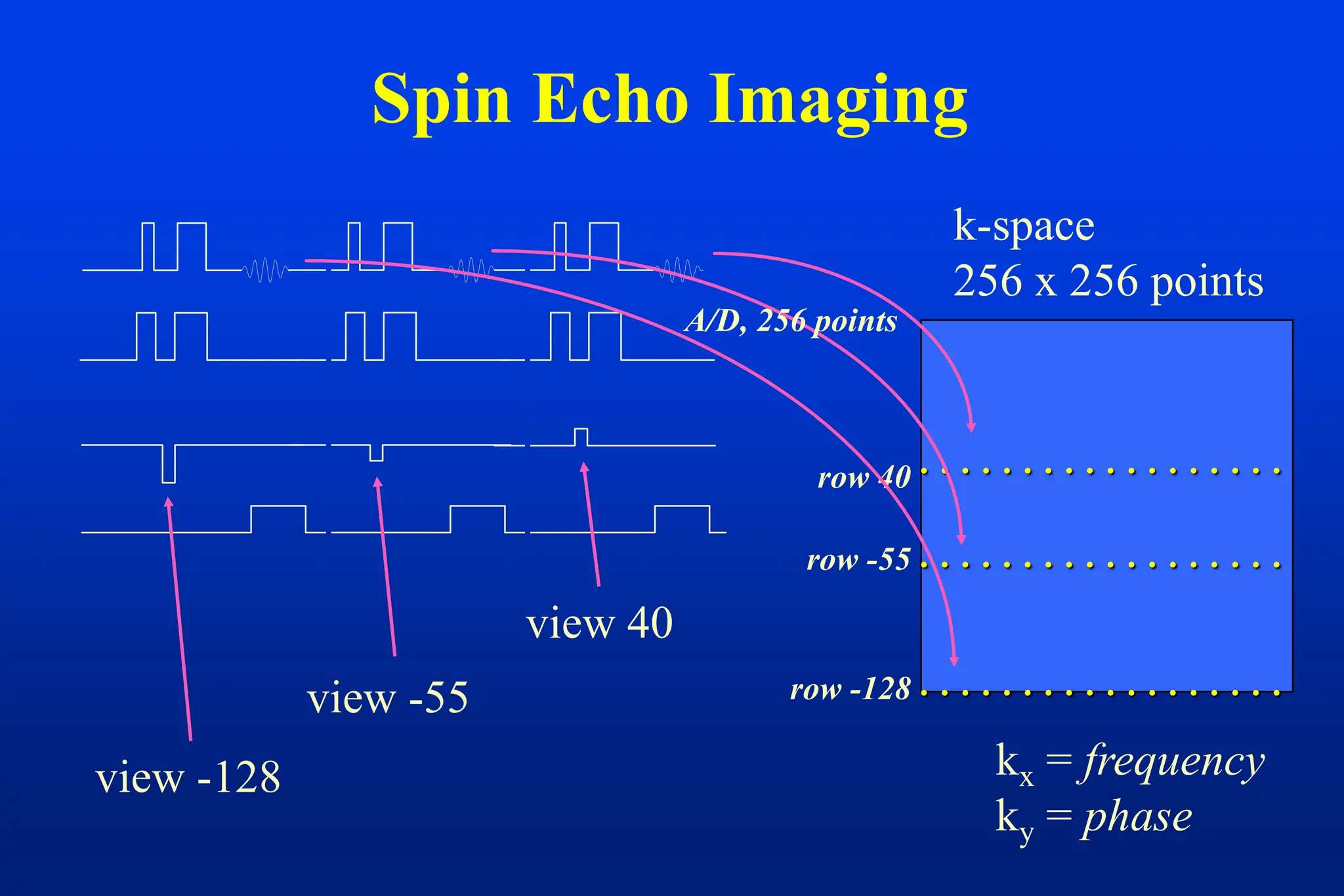
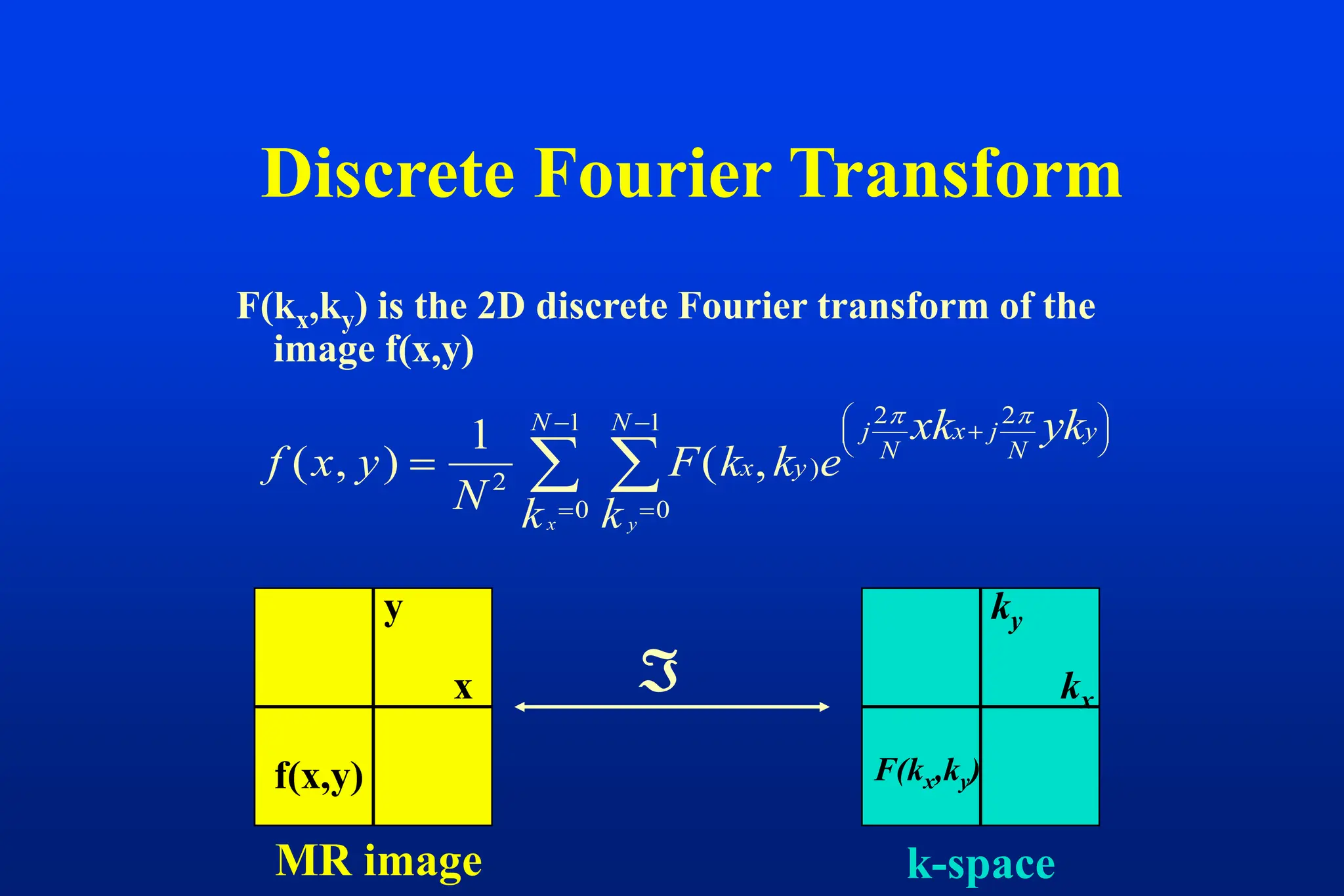
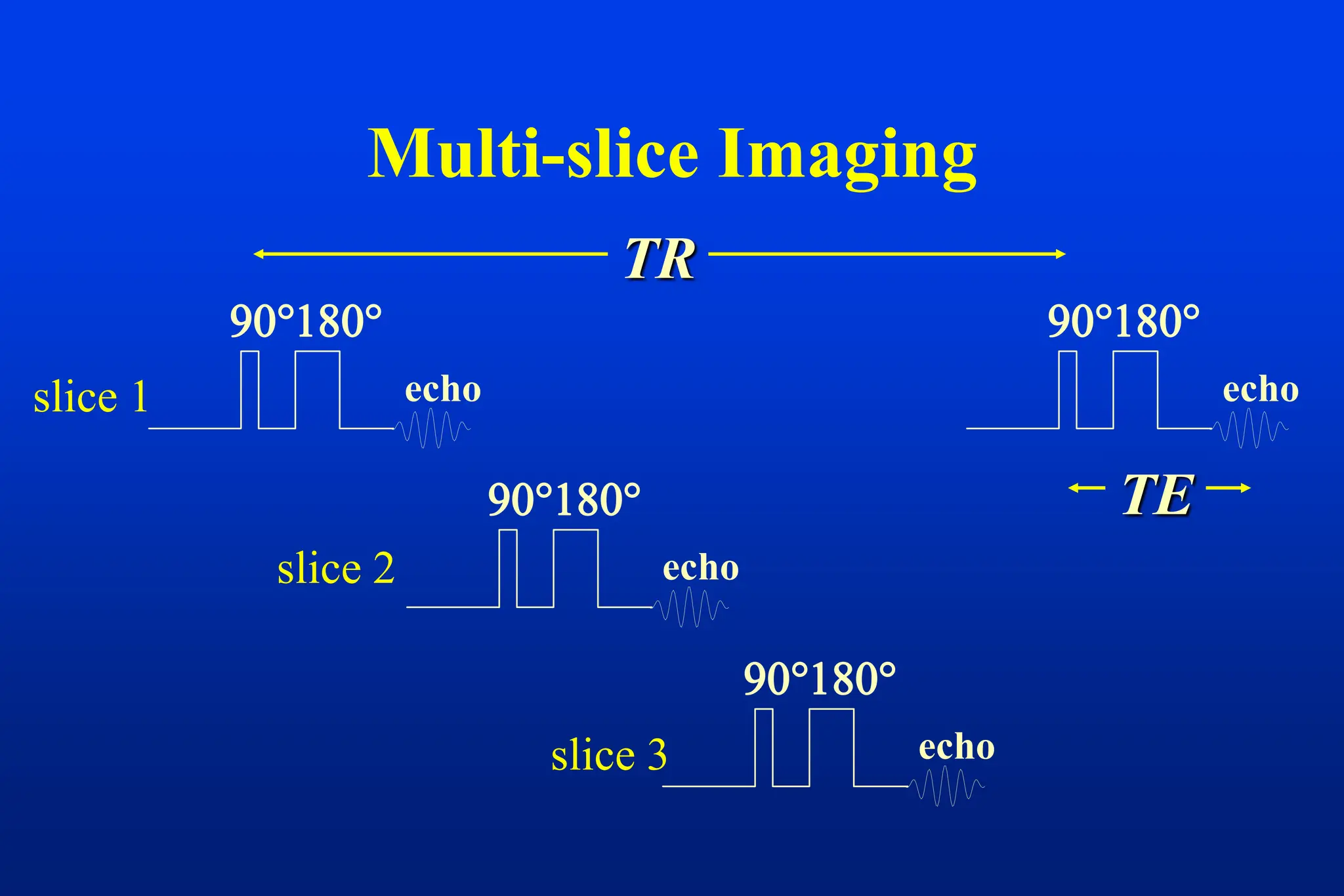
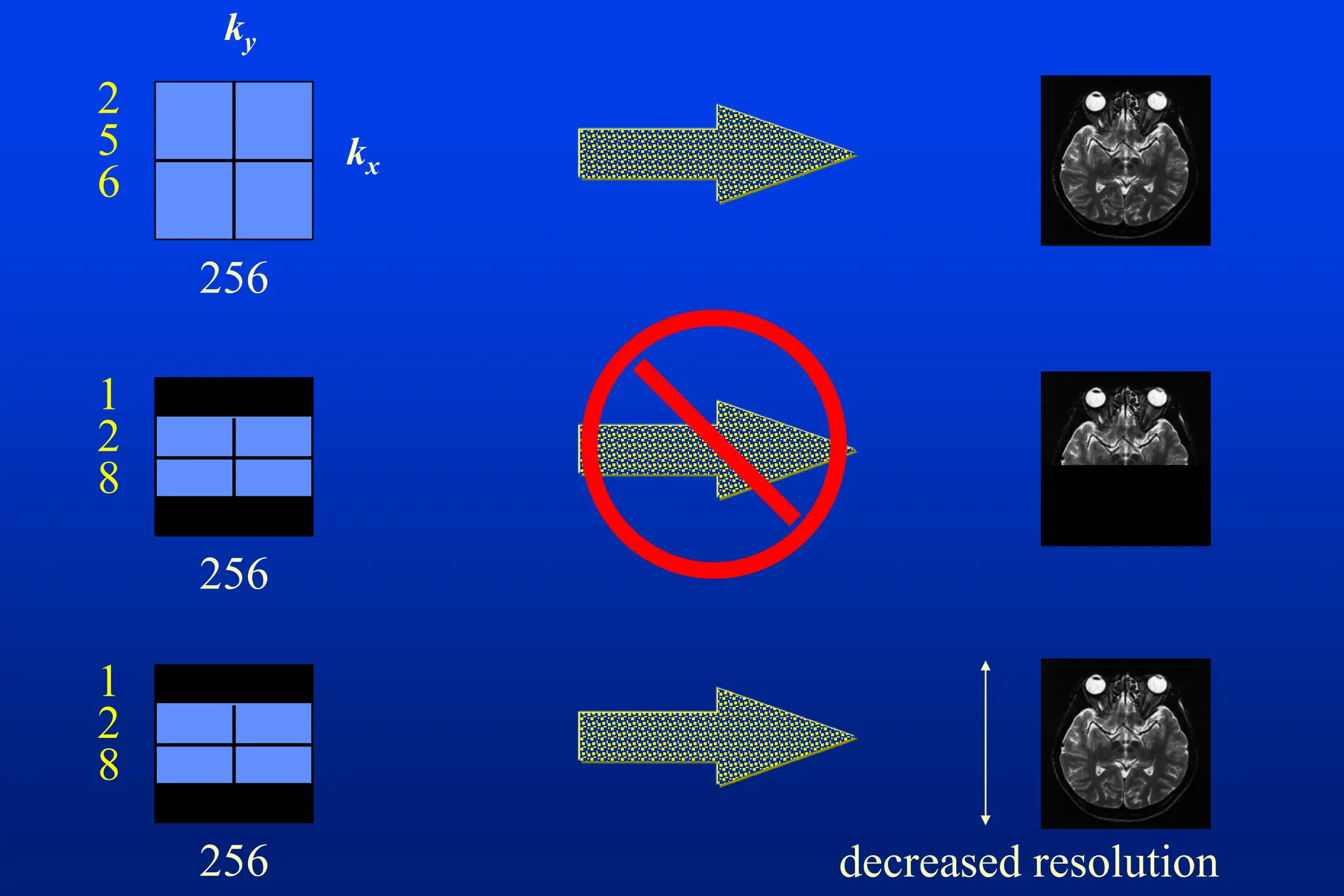
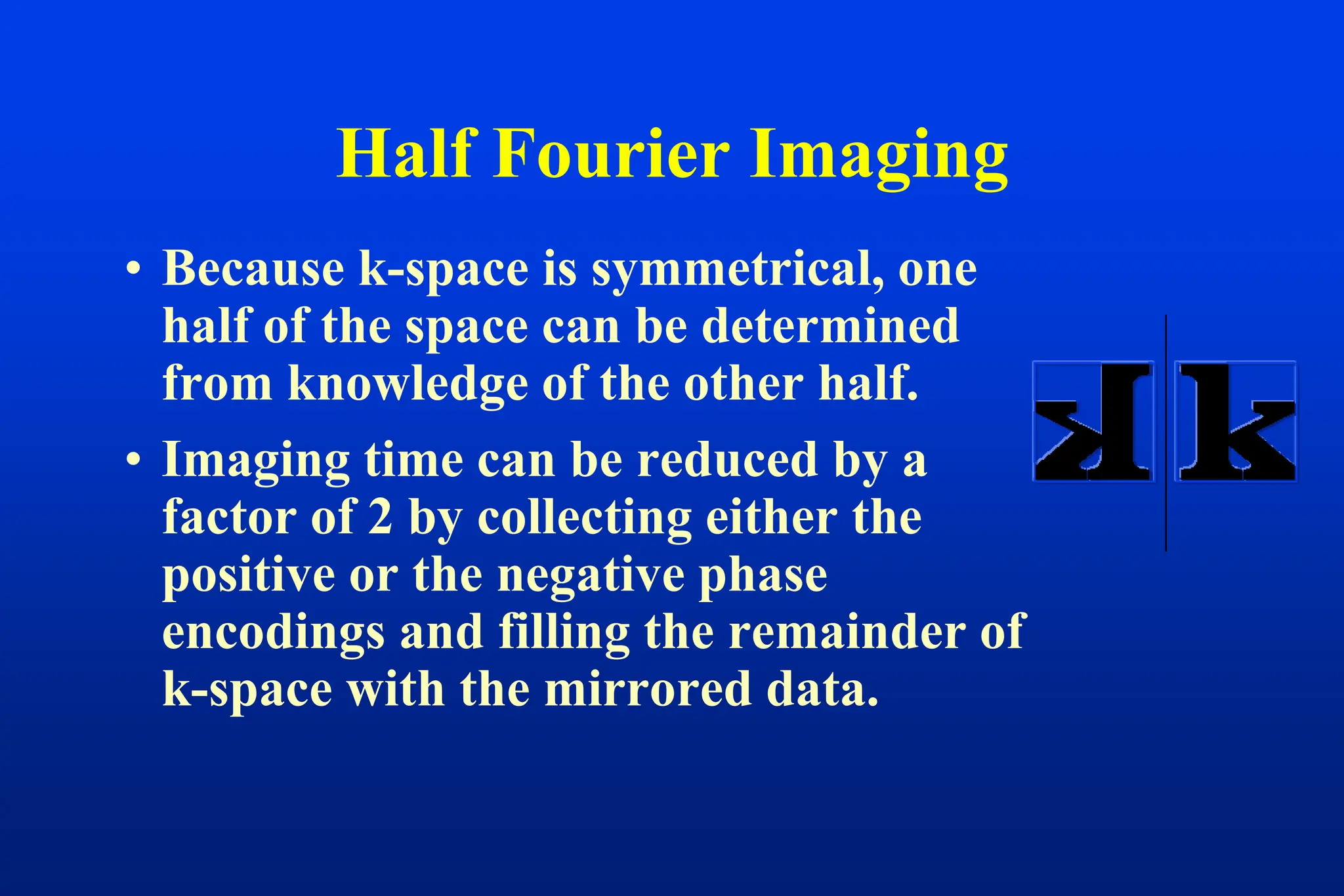
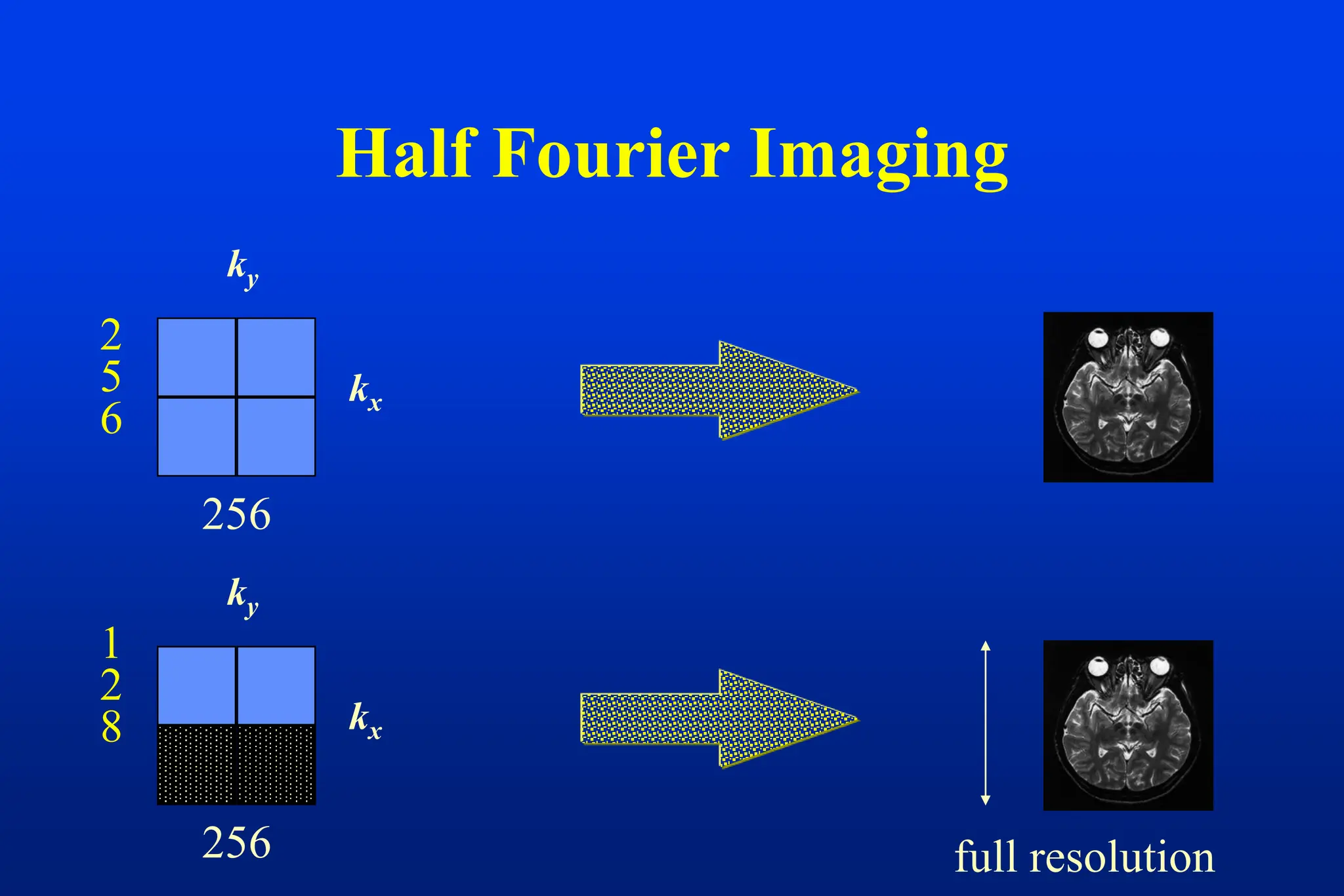
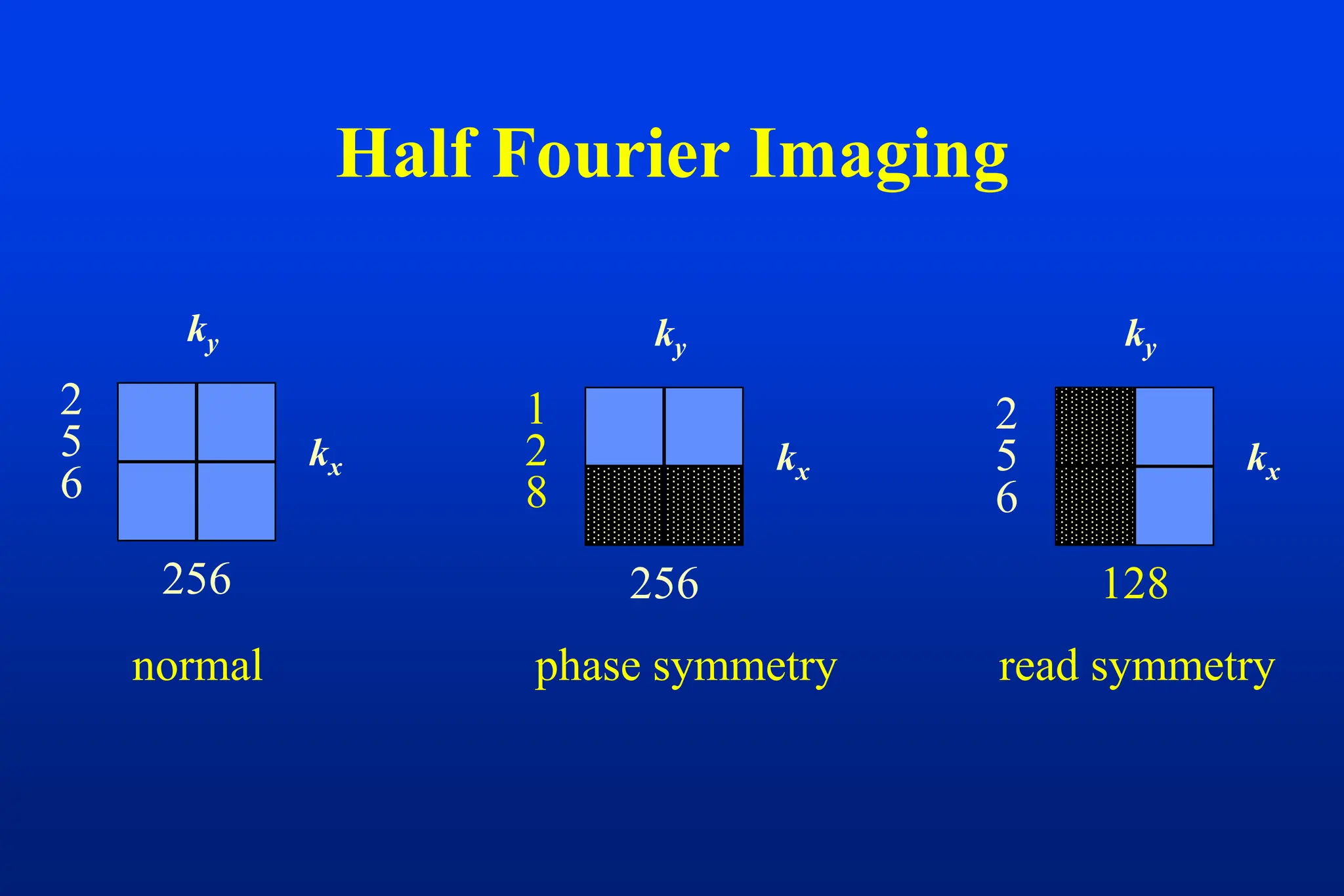
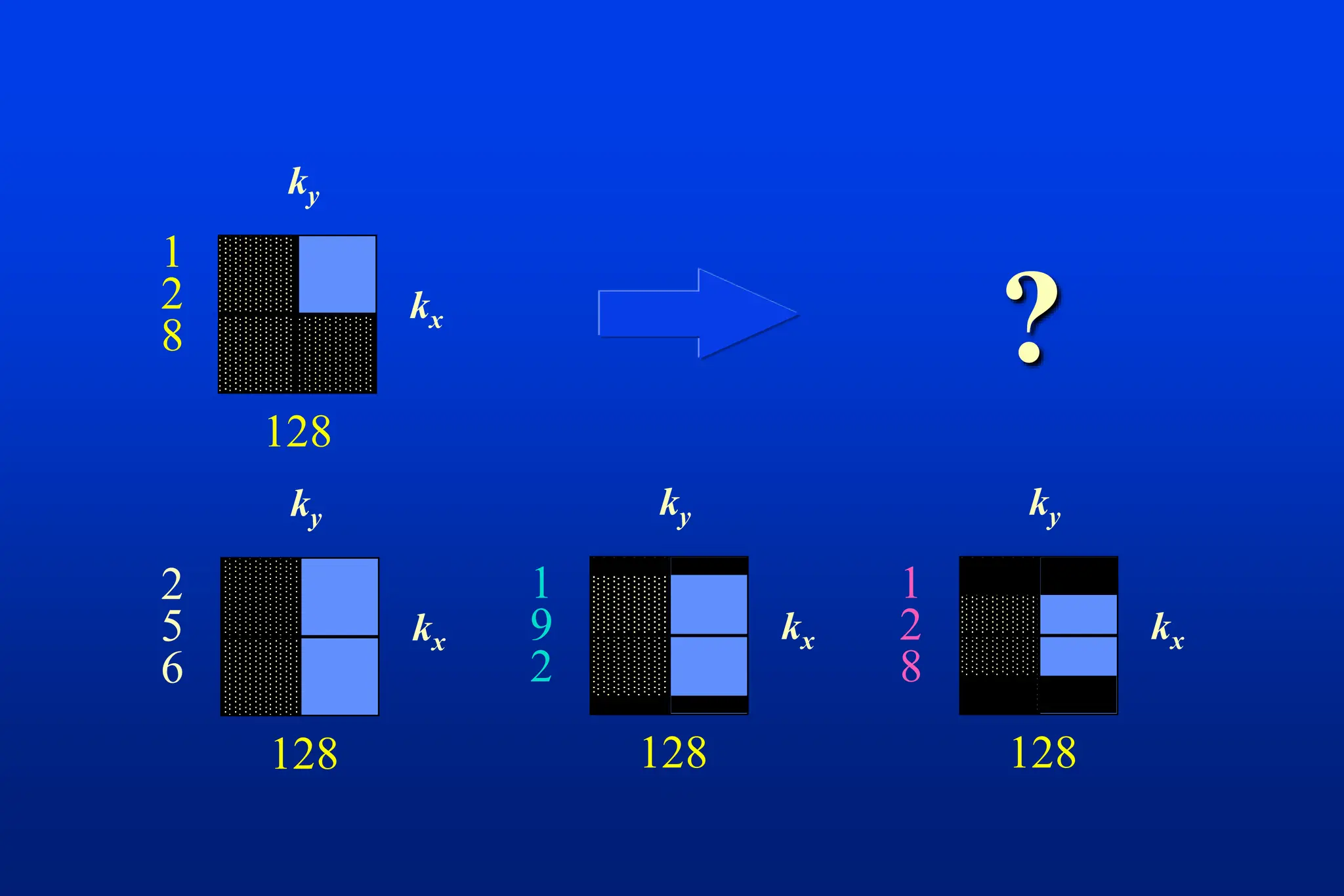
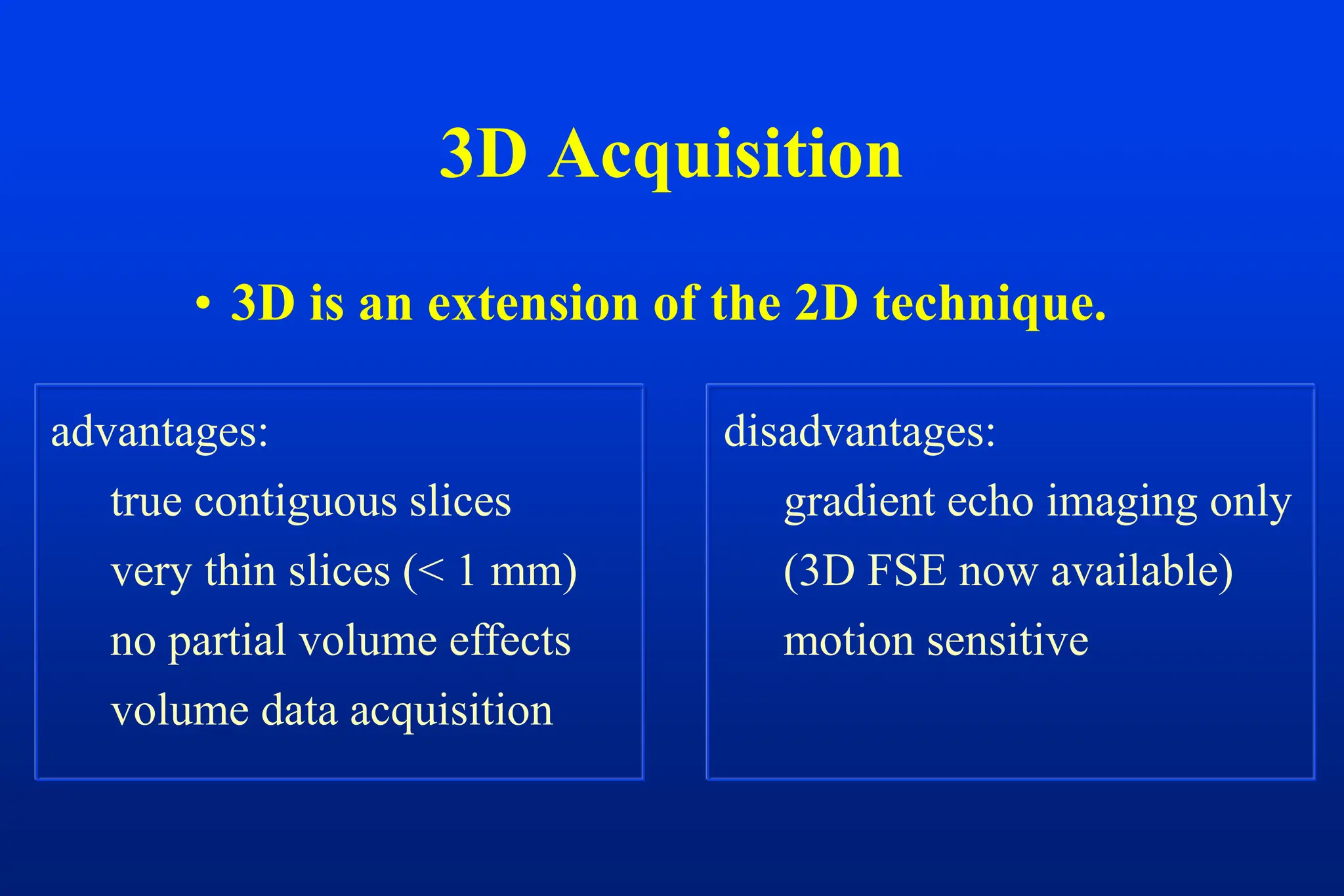
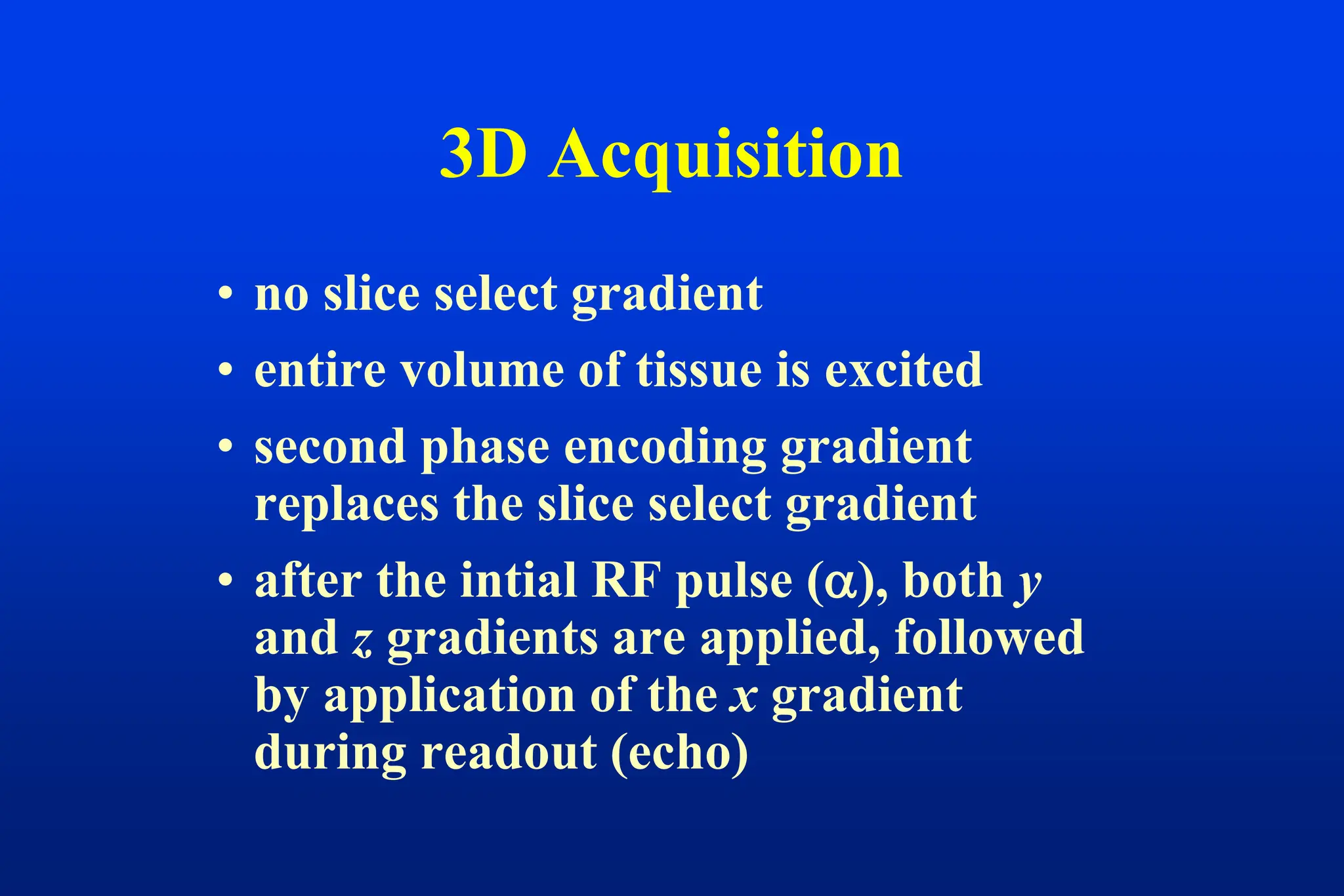
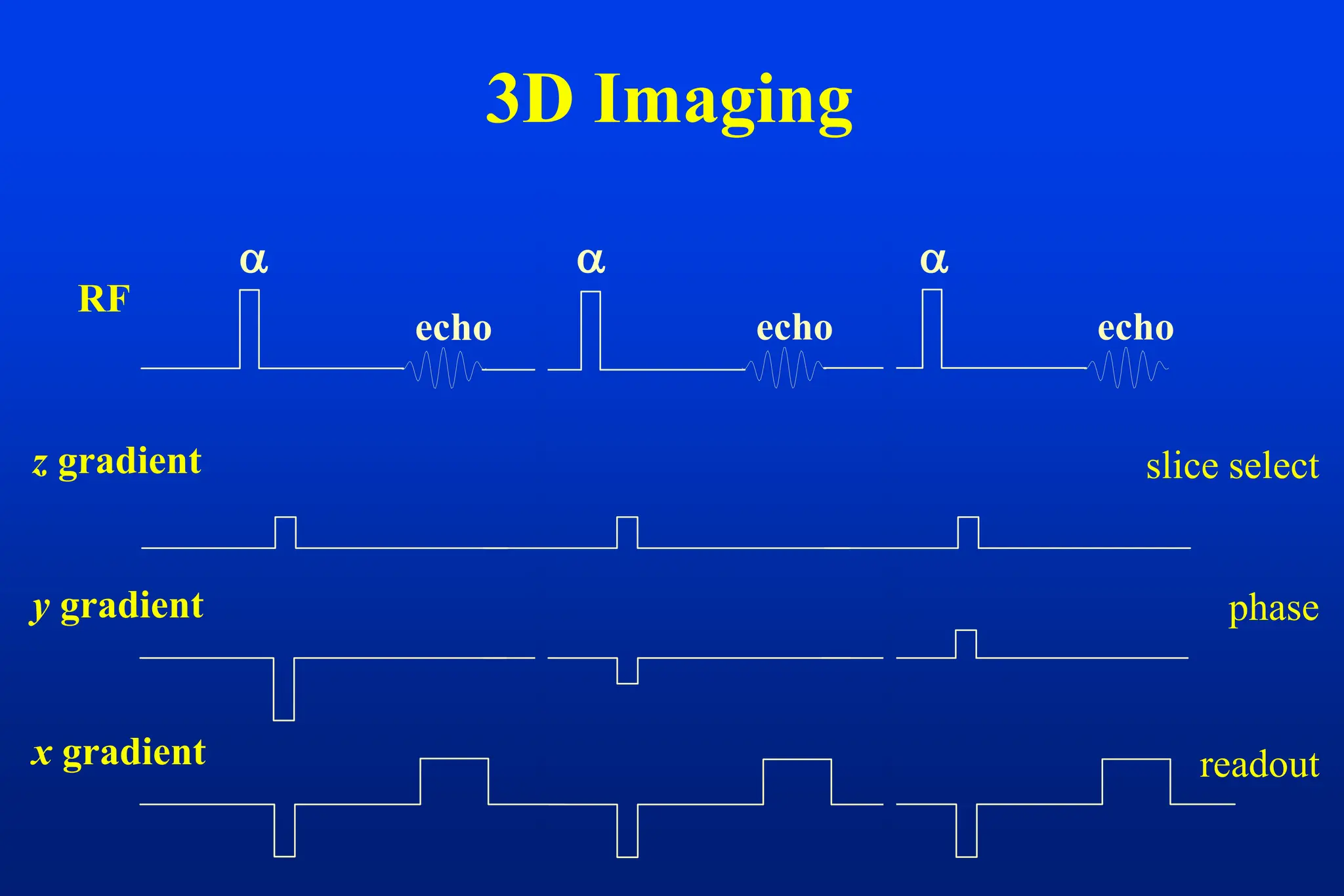
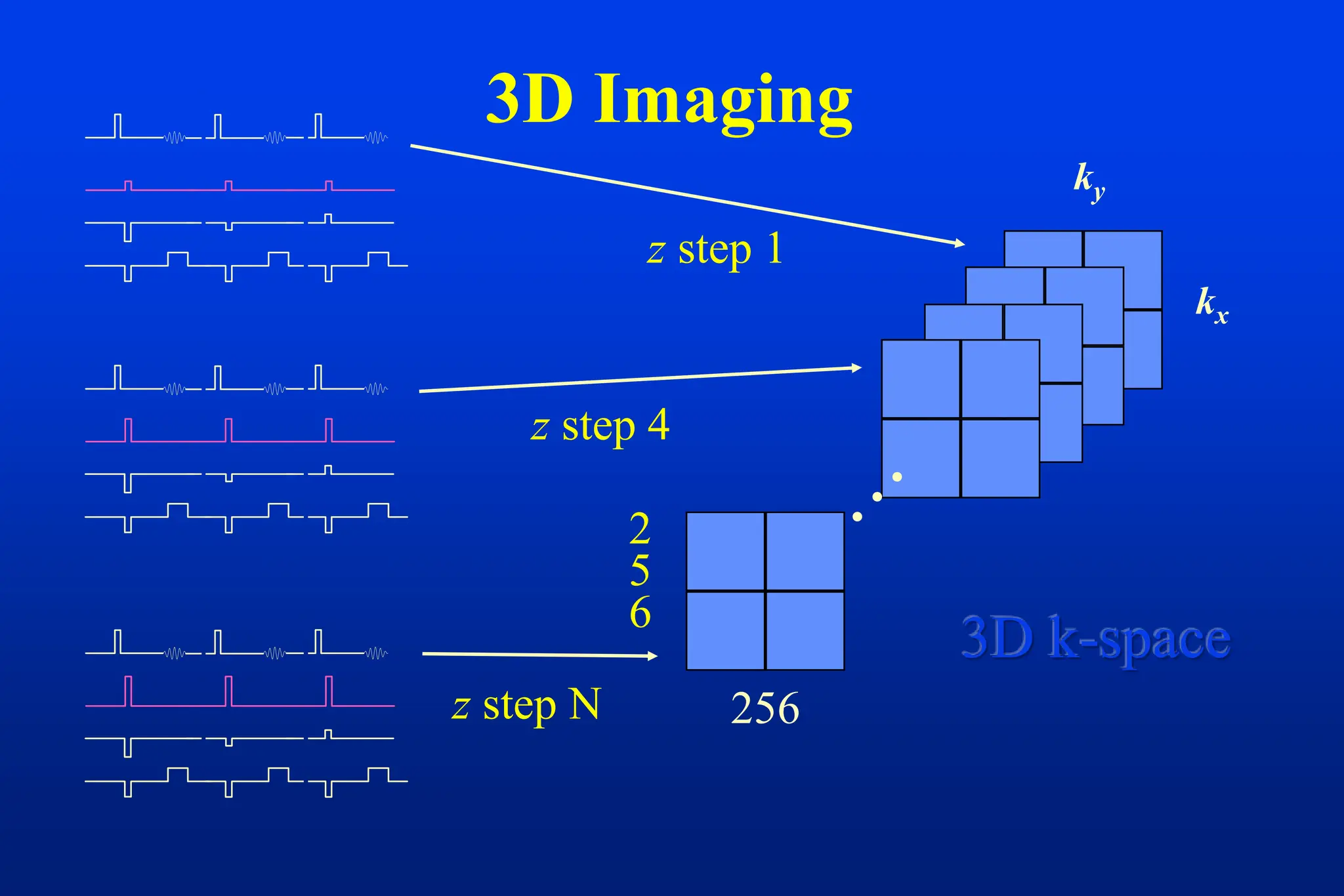
This document discusses techniques for spatial encoding in MRI. Slice selection is performed using a gradient in the z-direction. Within the slice, frequency encoding uses a left-right gradient, while phase encoding with a head-foot gradient fills the remaining direction of k-space. Multiple slices can be acquired simultaneously using interleaved acquisition between RF pulses. Resolution can be reduced and speed increased using half Fourier and parallel imaging techniques. Three-dimensional imaging excites the entire volume and uses two phase encoding gradients.