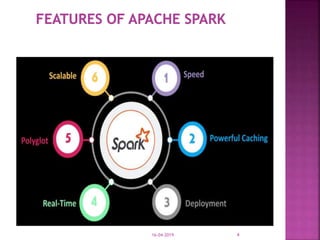
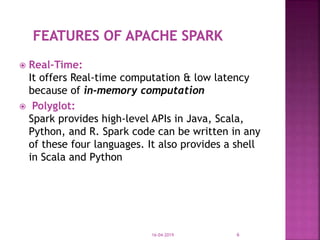
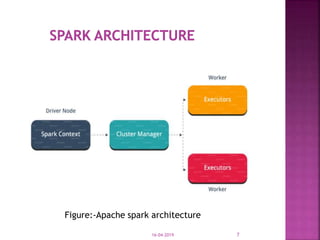
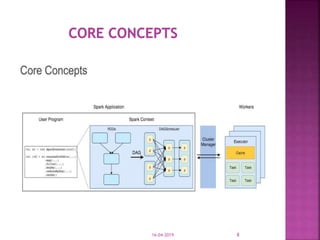
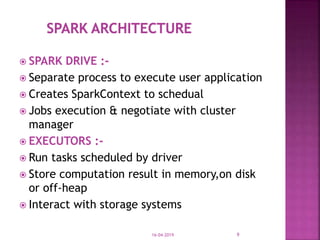
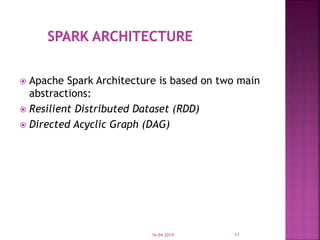
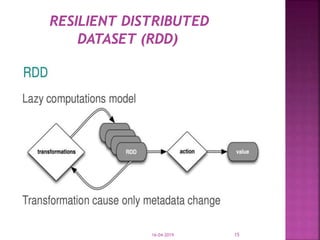
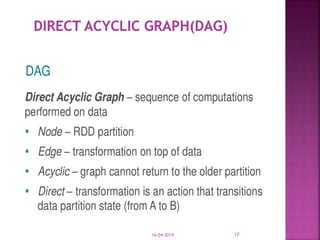
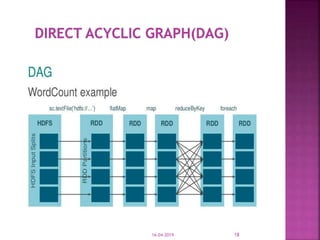
The document discusses Apache Spark, an open source cluster computing framework for real-time data processing. It notes that Spark is up to 100 times faster than Hadoop for in-memory processing and 10 times faster on disk. The main feature of Spark is its in-memory cluster computing capability, which increases processing speeds. Spark runs on a driver-executor model and uses resilient distributed datasets and directed acyclic graphs to process data in parallel across a cluster.