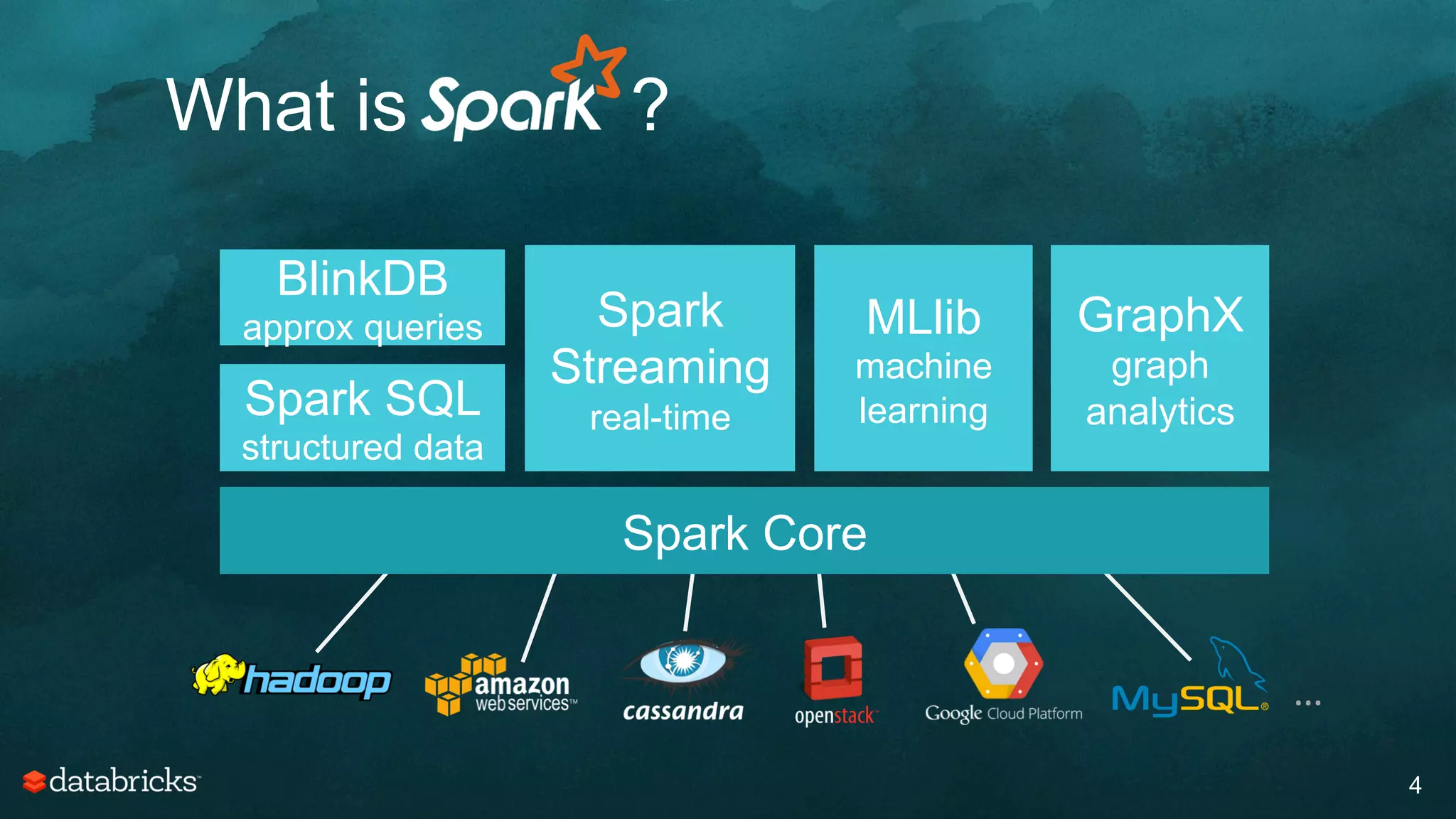
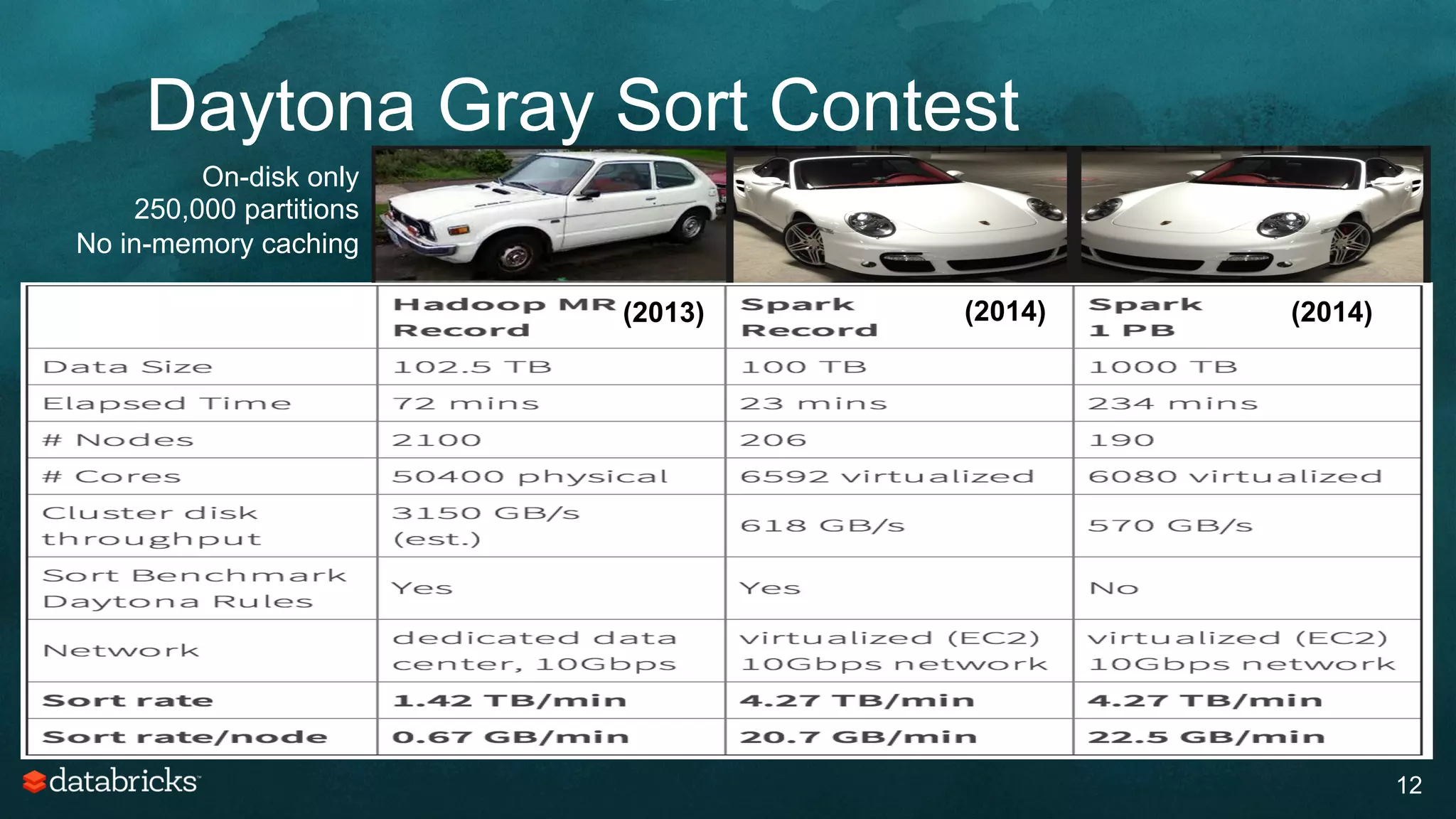
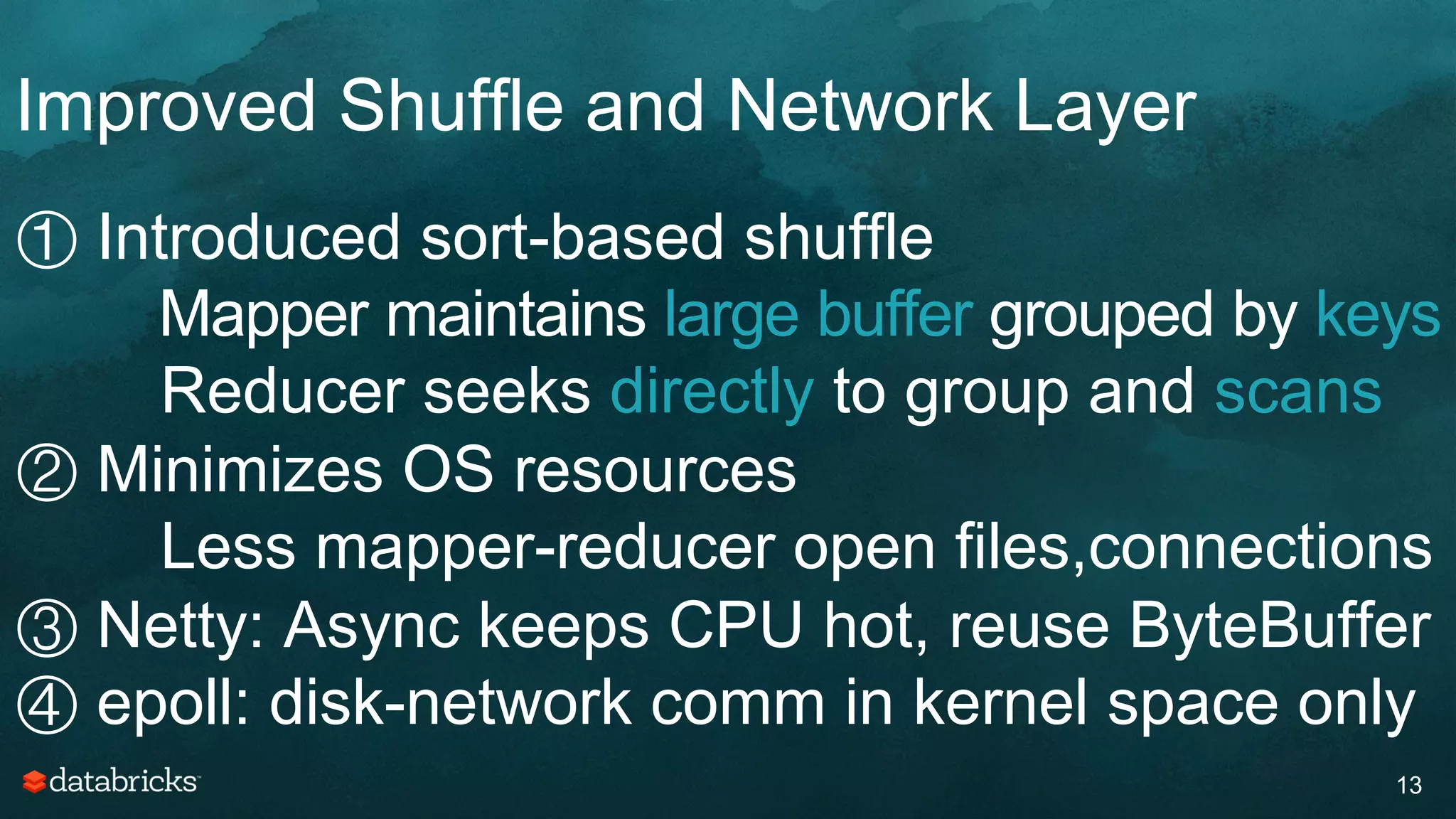
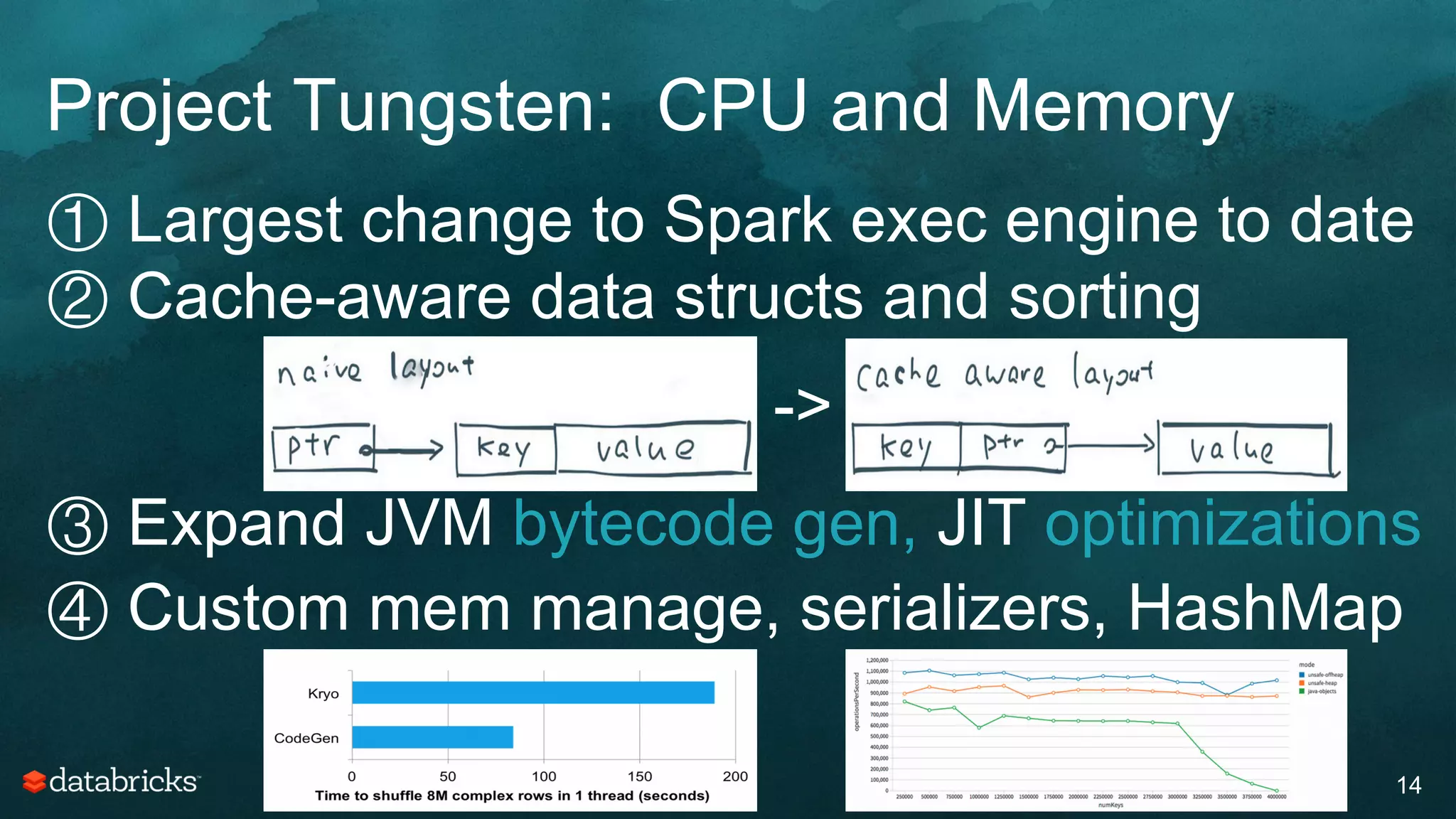
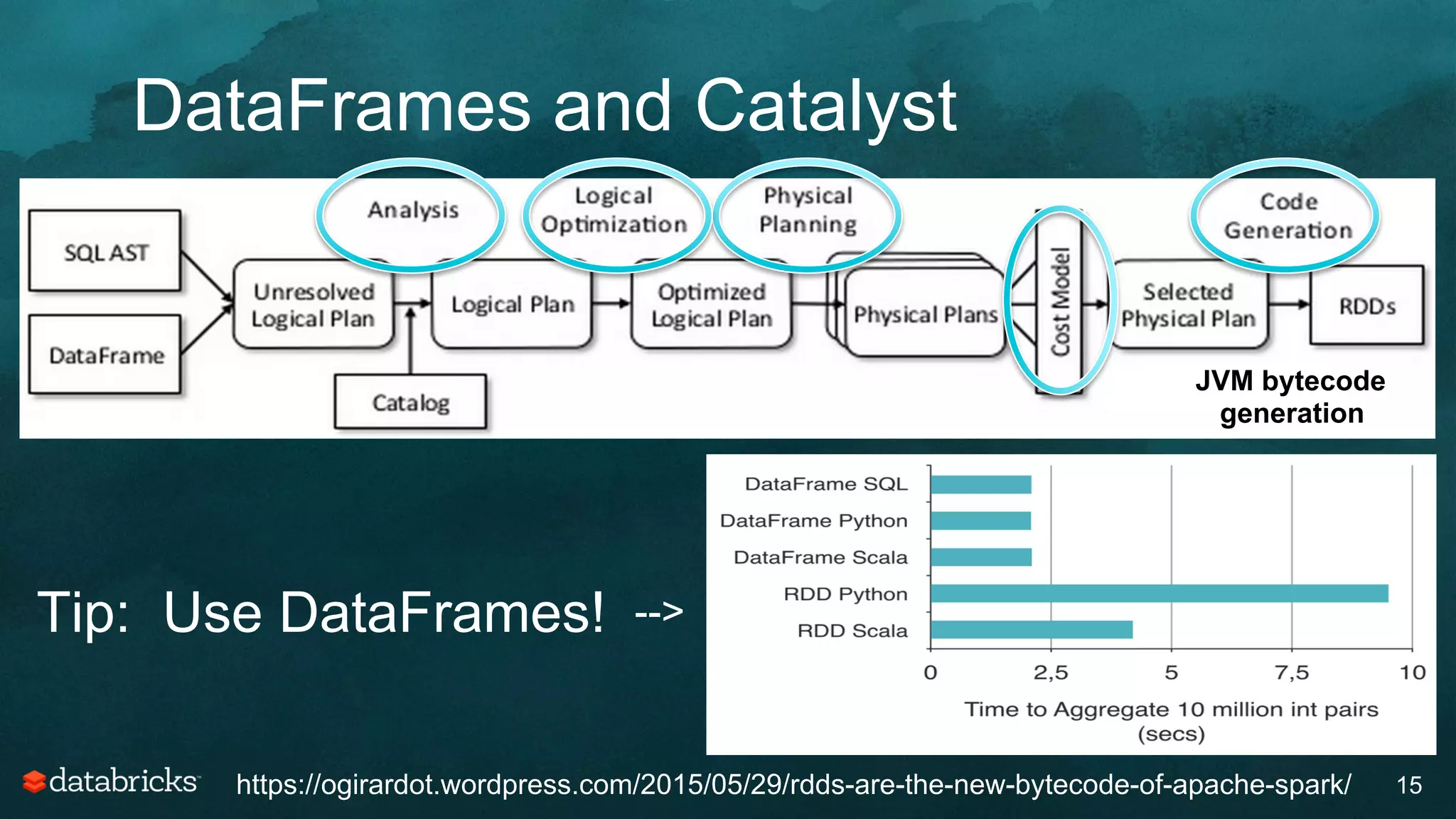
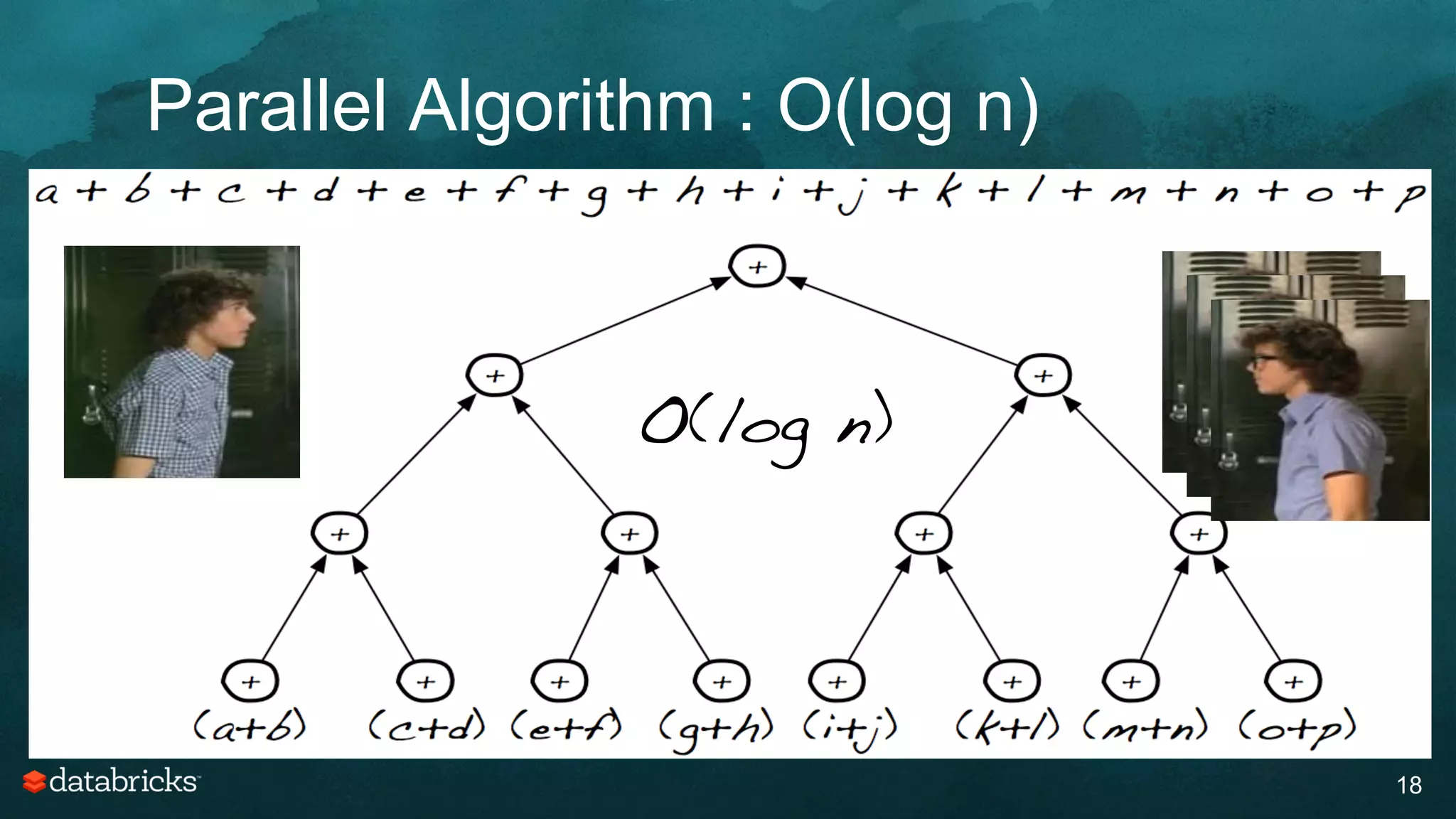
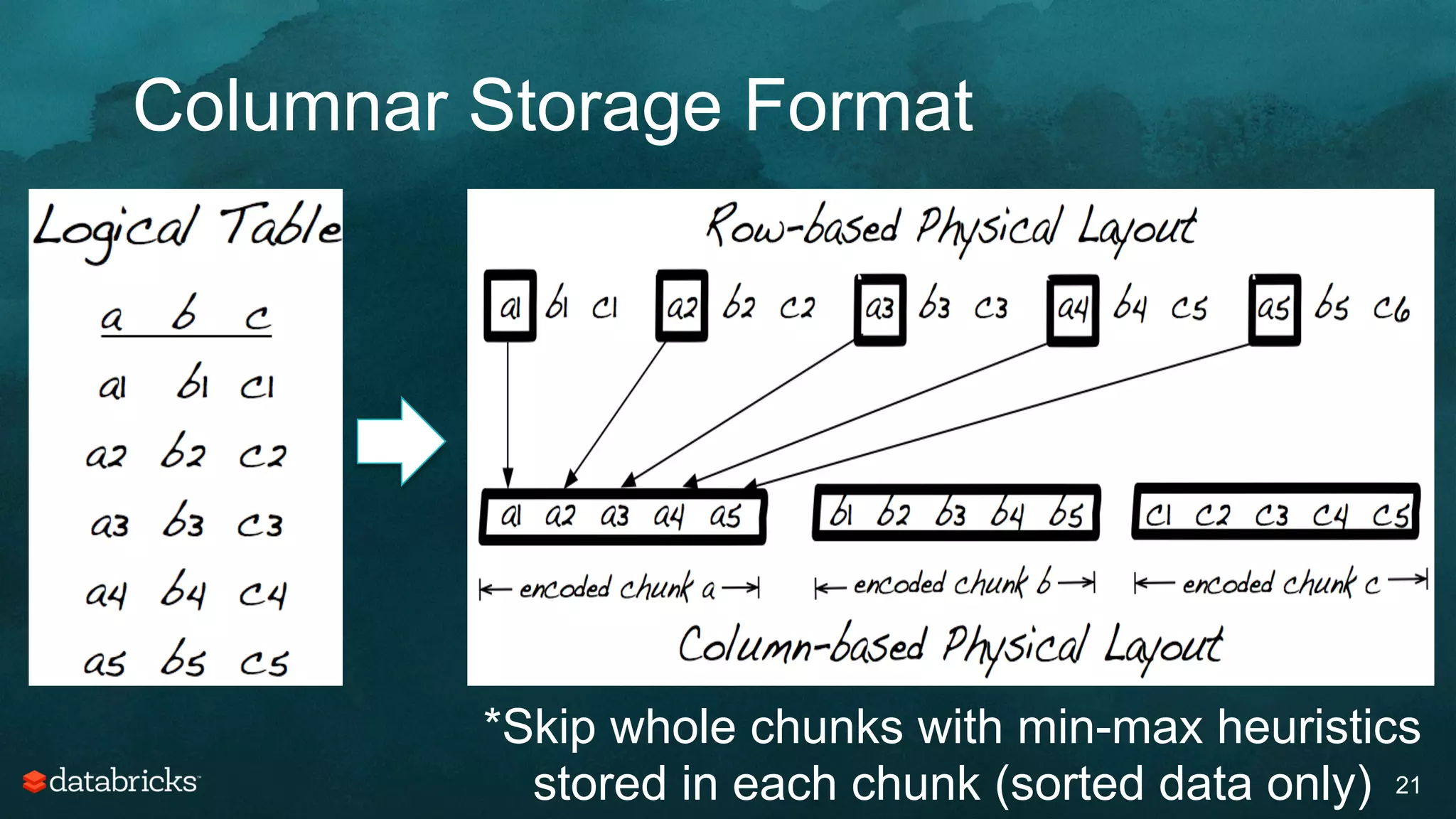
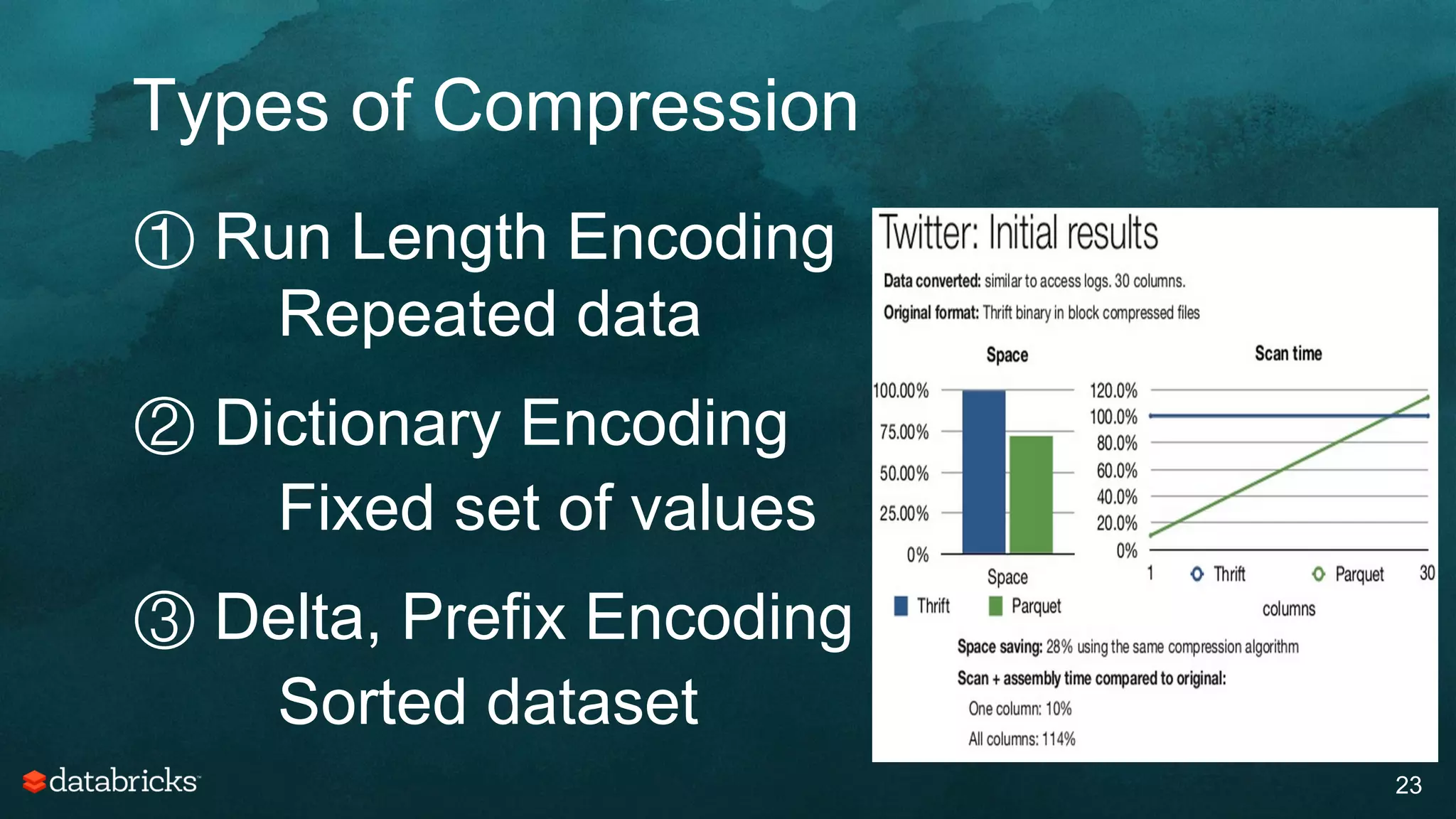
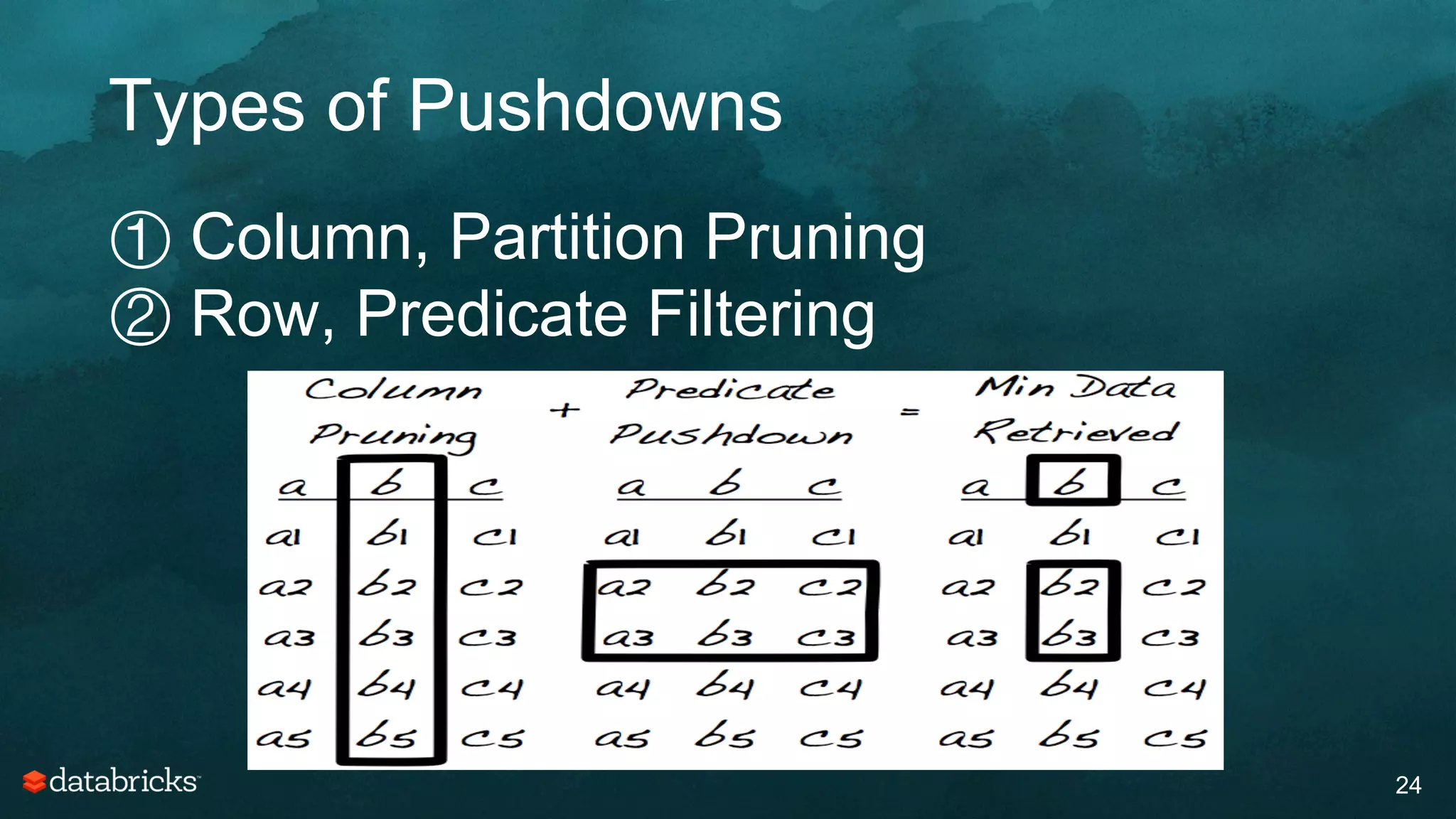
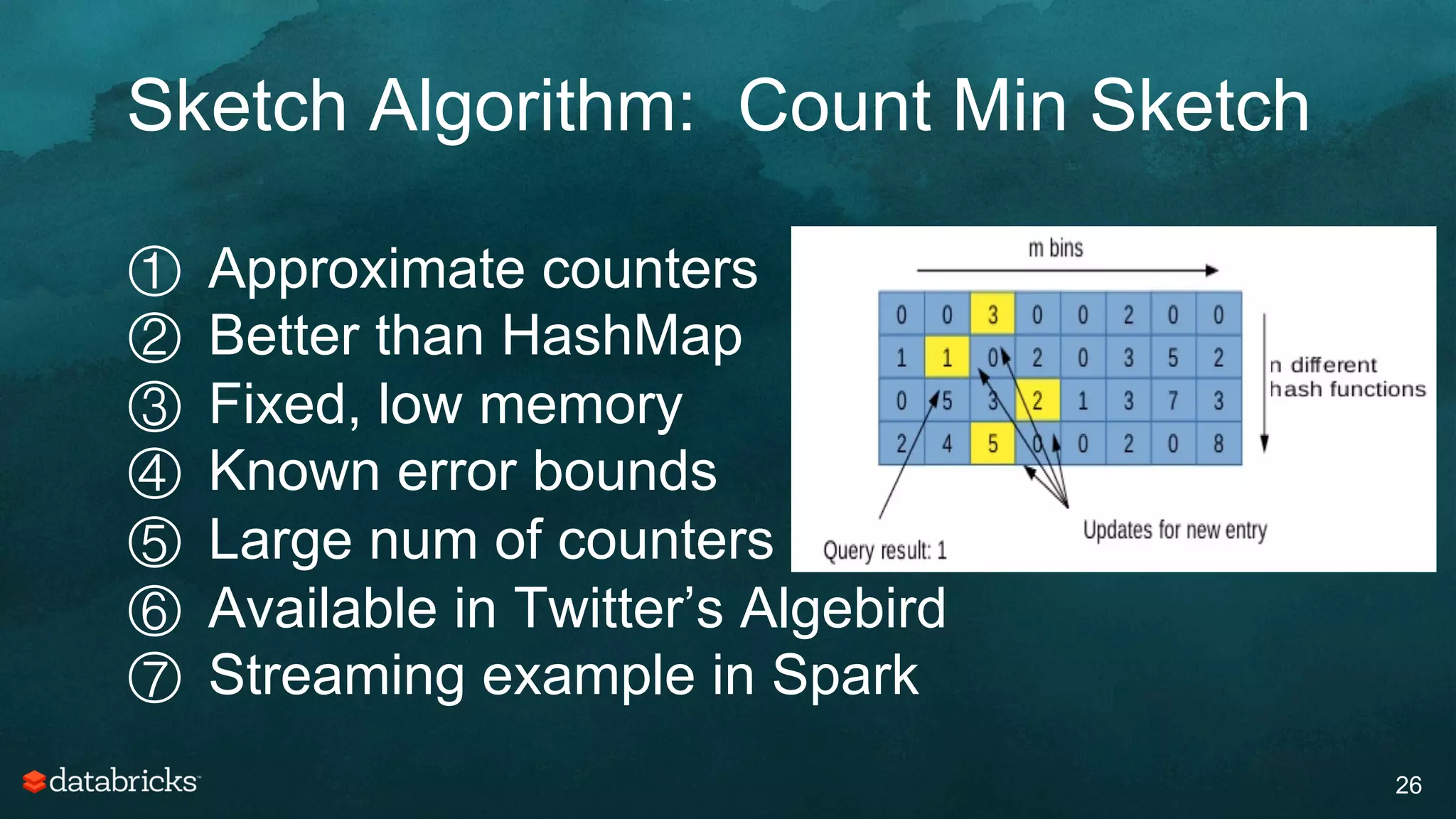
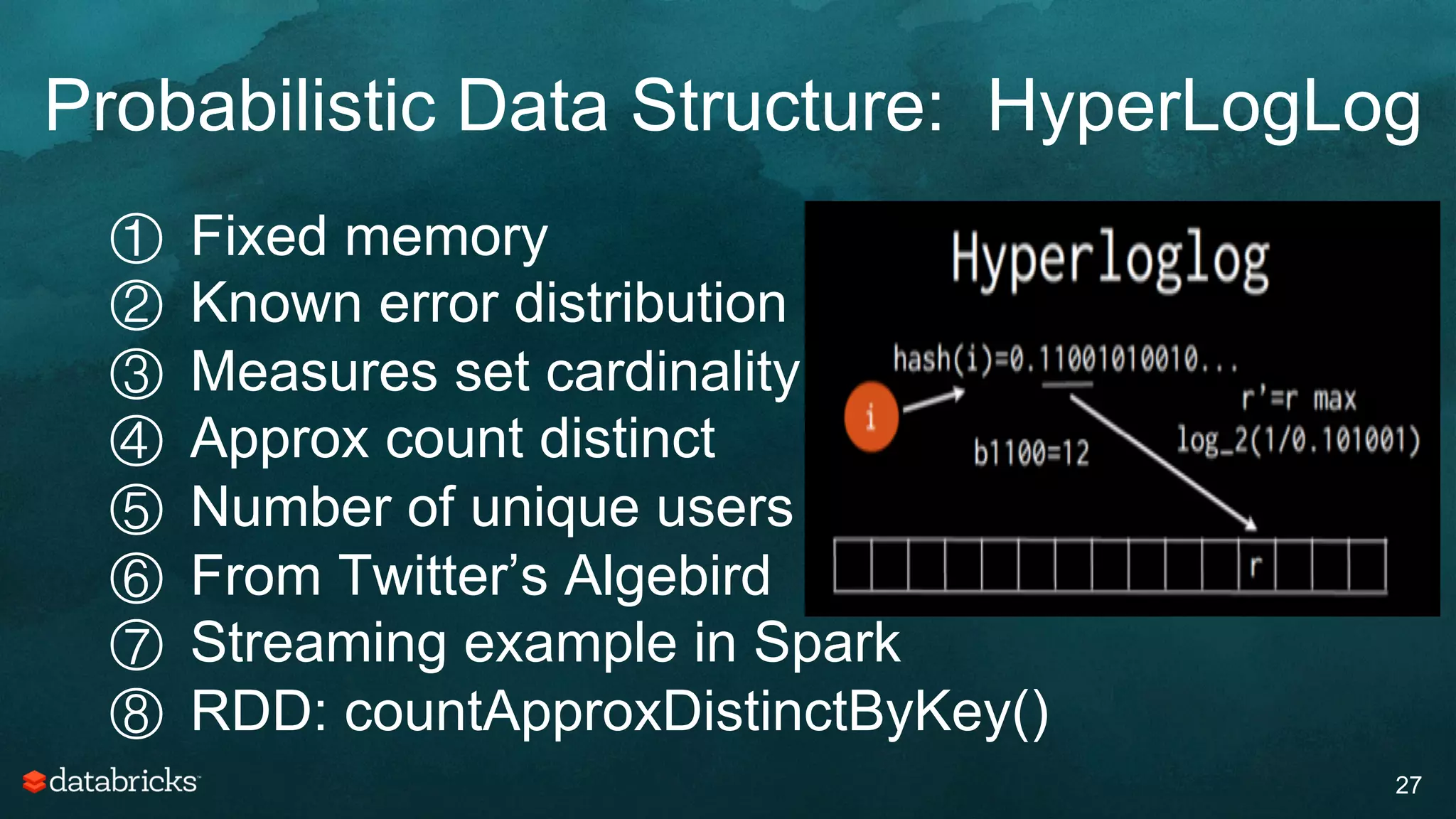
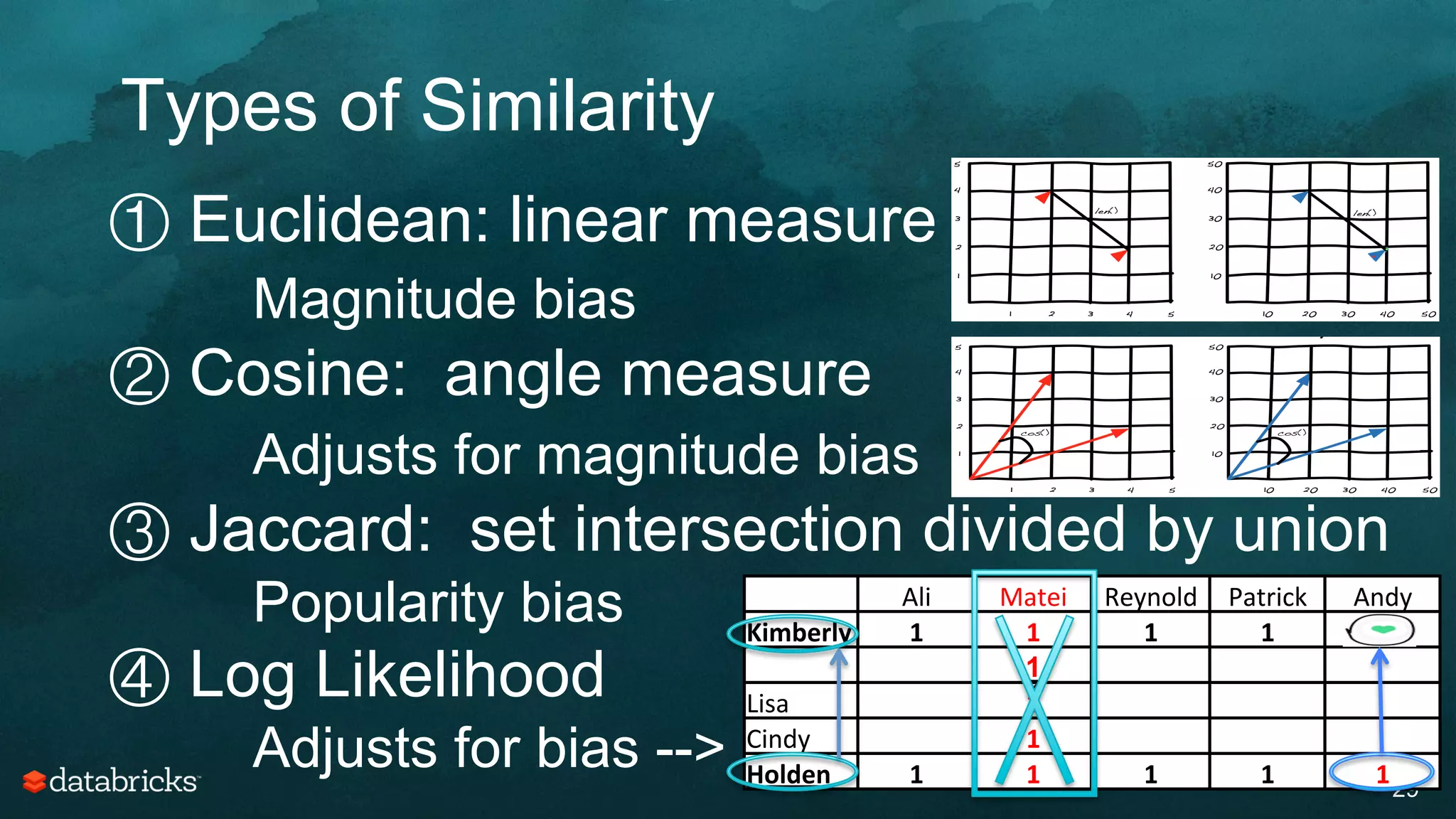
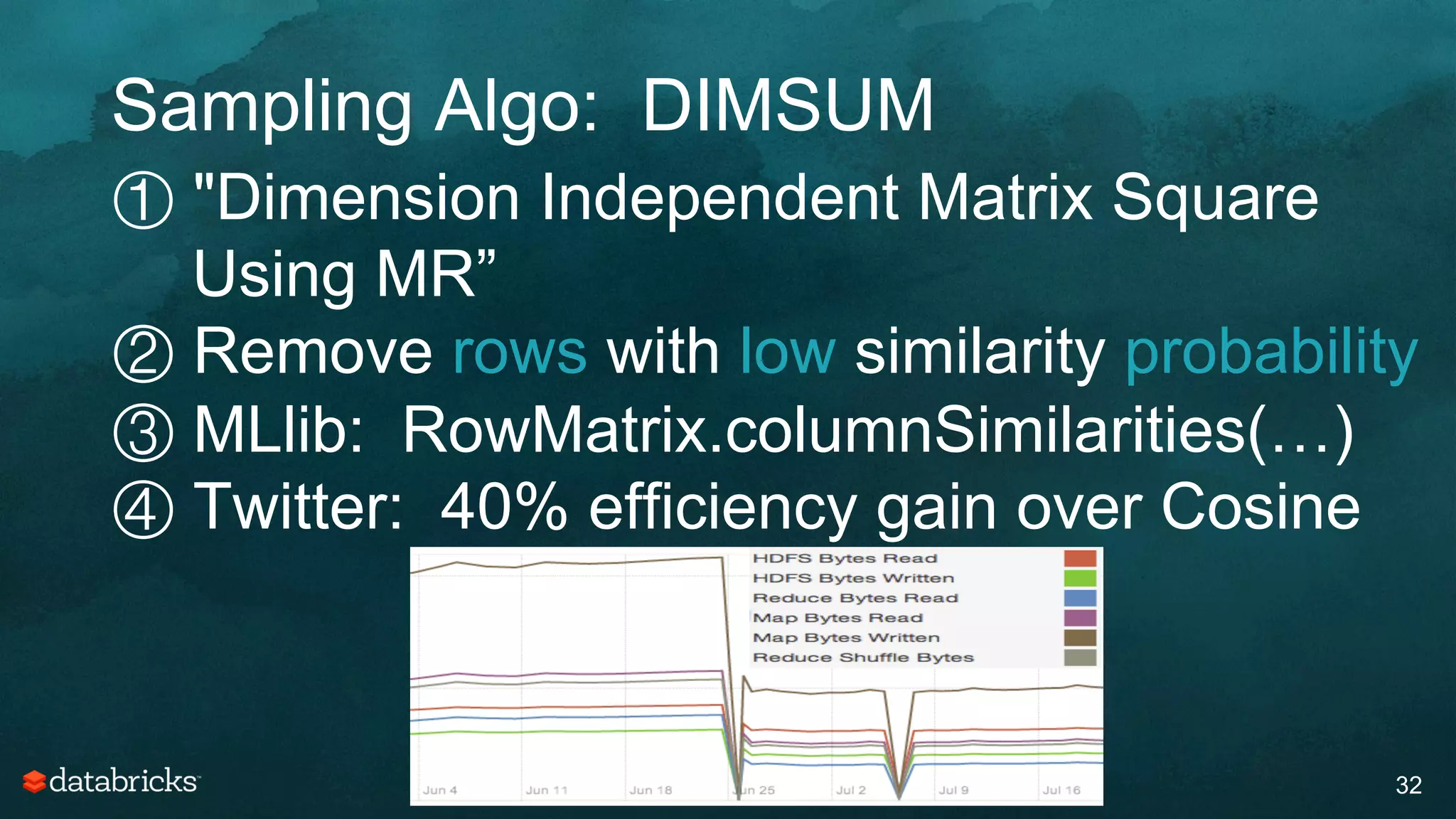
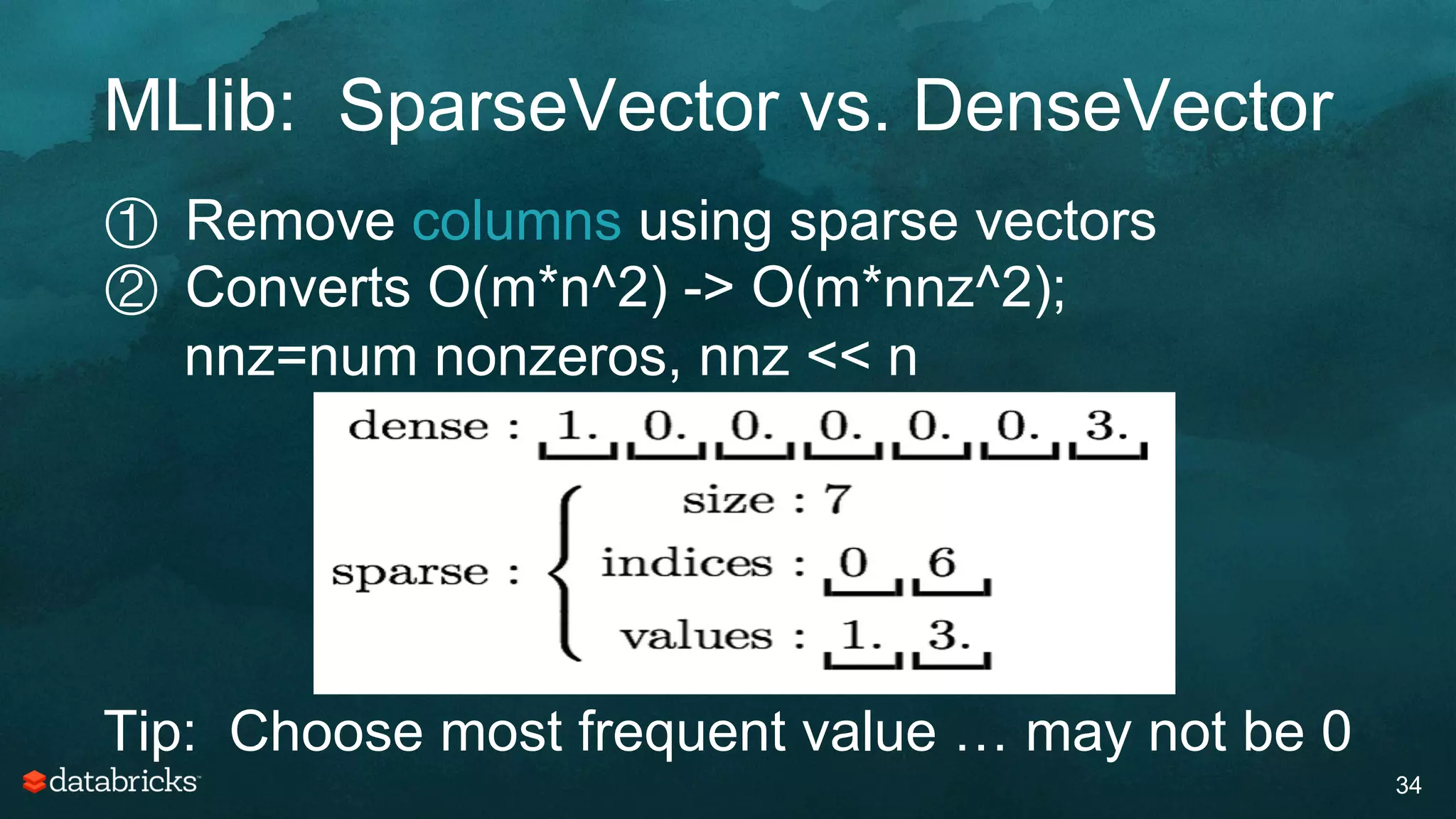
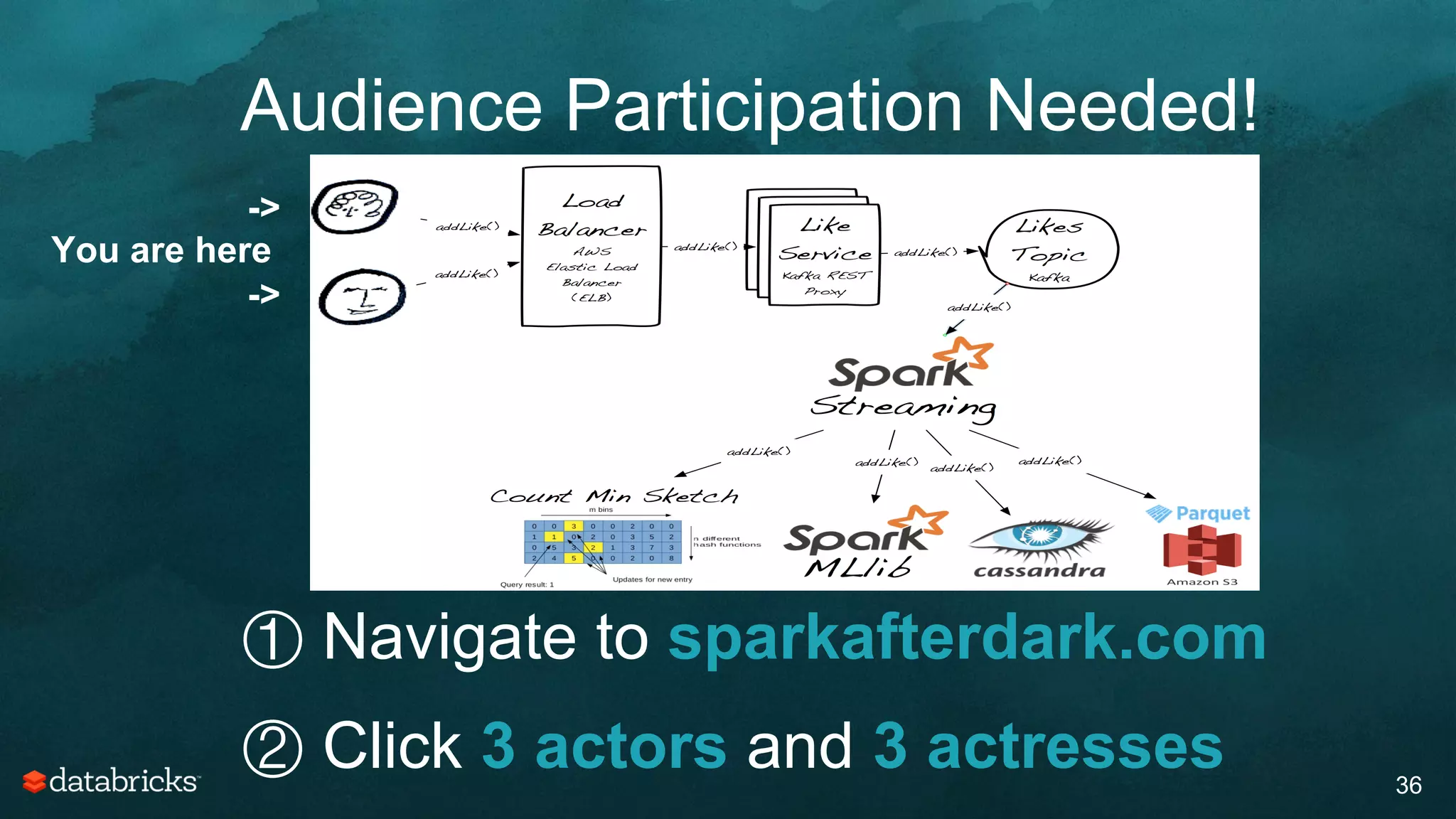
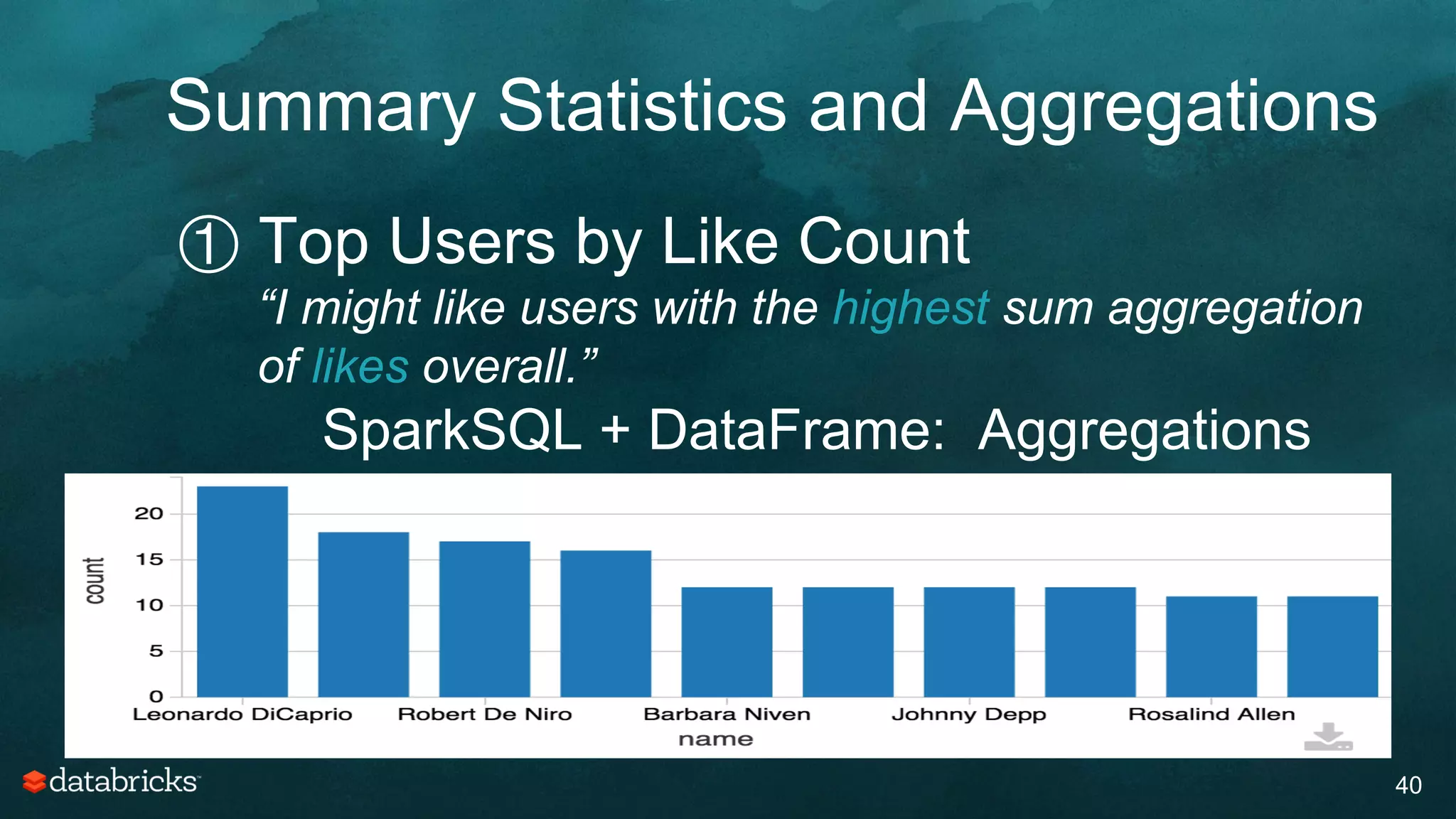
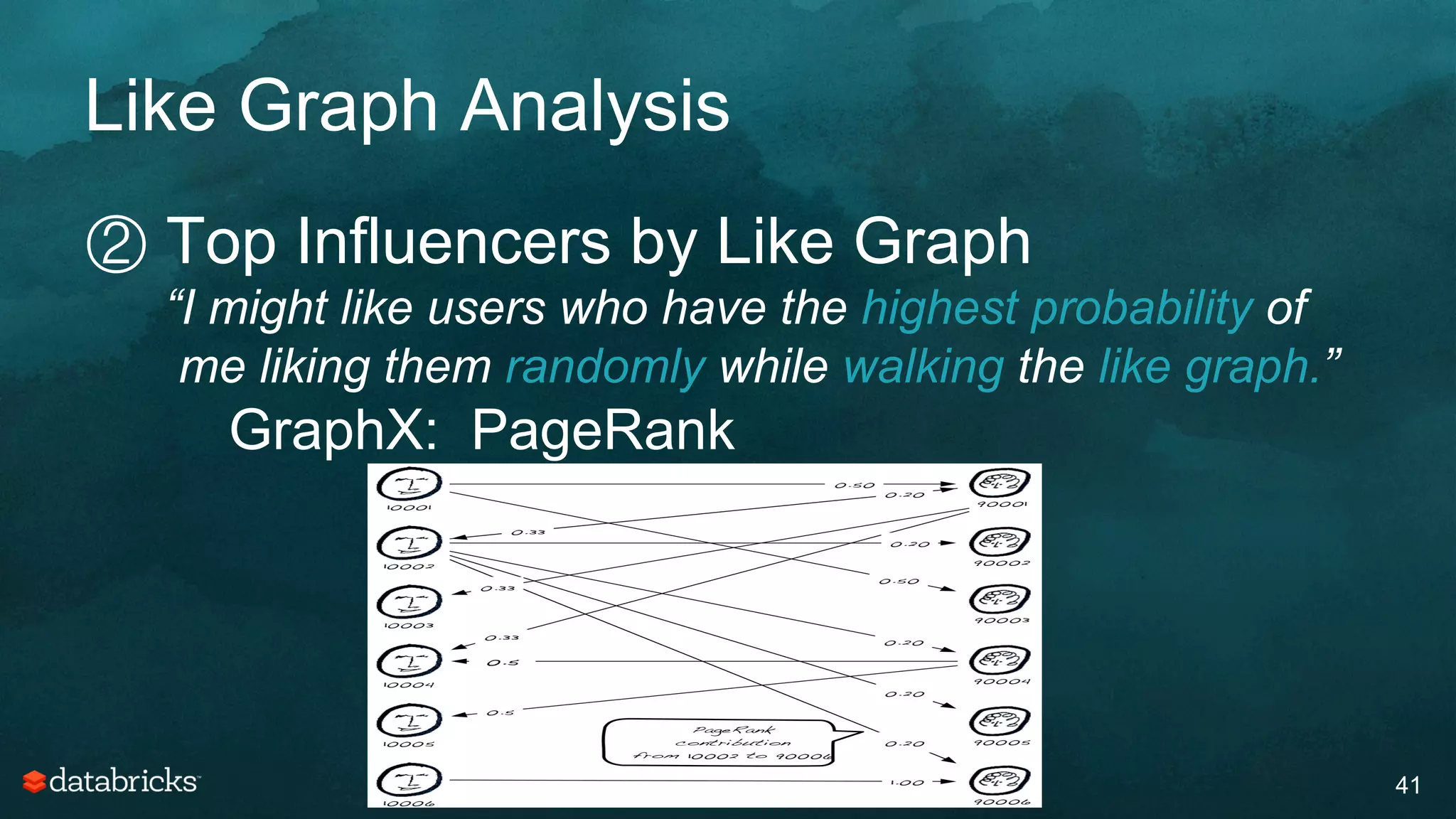
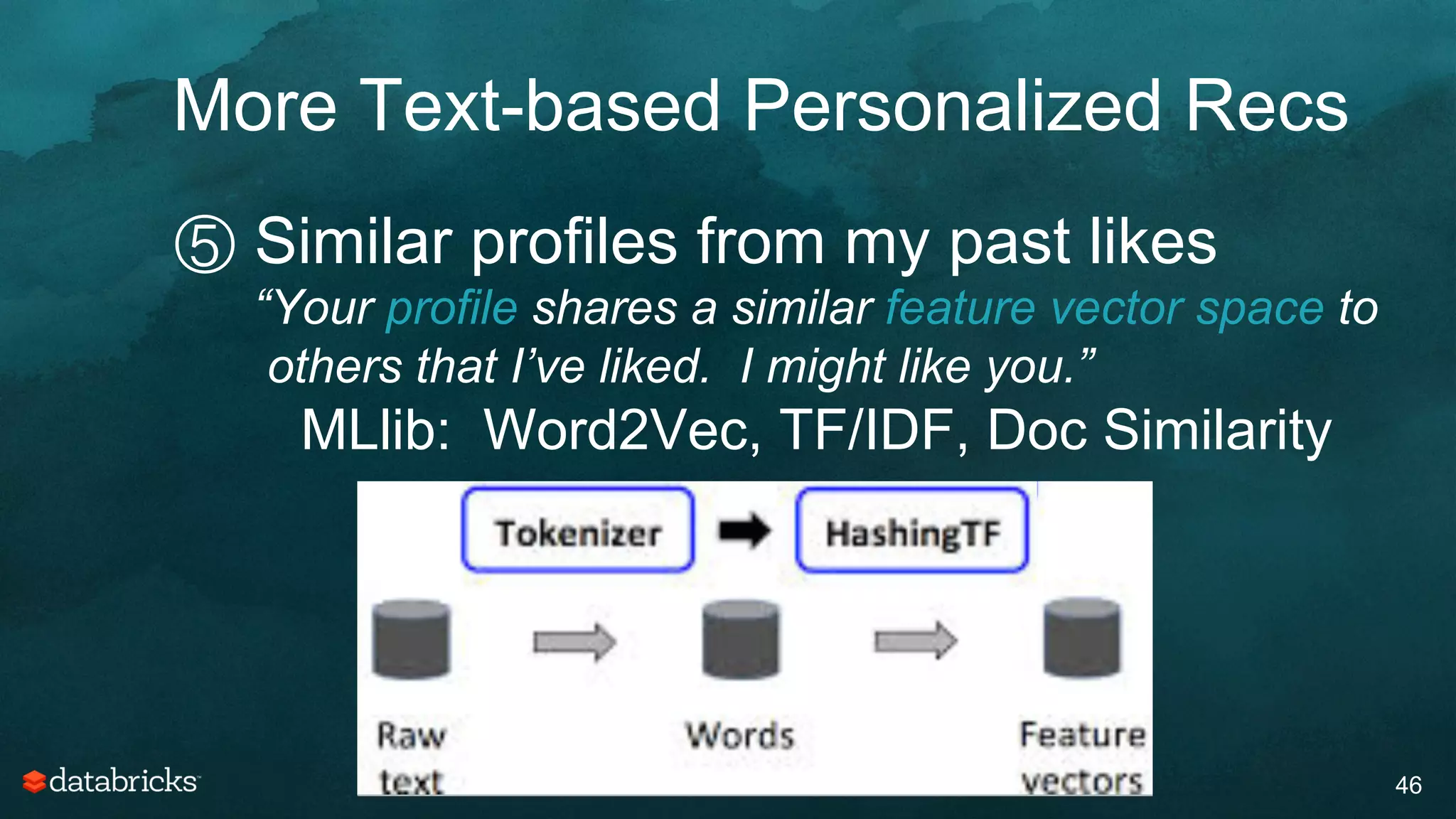
The document discusses generating high-quality recommendations using advanced analytics and machine learning techniques, specifically focusing on Apache Spark and its high-level libraries. It explores various themes like performance, parallelism, columnar storage, and similarity measures, while also outlining types of recommendations and advanced techniques for collaborative filtering. The presentation aims to demonstrate the transformative power of data-driven recommendations, including future possibilities like facial recognition and NLP.